Method for constructing low-initial-quantity PCR-free high-throughput sequencing library
A technology for constructing a method and a sequencing library, which is applied in chemical libraries, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, and can solve the problems of low-input PCR-free high-throughput sequencing libraries, small initial sample sizes, Unable to accurately build the library and other problems, to avoid the occurrence of adapter dimer phenomenon, improve efficiency, and omit the effect of purification steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1 The construction method of low-input PCR-free high-throughput sequencing library of the present invention (1)
[0044] 1. cfDNA extraction
[0045] The peripheral blood of pregnant women was collected using Streck tubes and transported at room temperature for 24 hours.
[0046] For the first plasma separation, 1600g of peripheral blood from pregnant women was centrifuged at 4°C for 10 minutes; the shape of the upper layer of plasma was checked, and it was qualified if it appeared transparent and yellowish, and had no abnormal phenomena such as hemolysis. Draw the upper layer of plasma into a new centrifuge tube, then centrifuge at 16,000g at 4°C for 10 min; take the upper layer of plasma for subsequent cfDNA extraction, and discard the residual precipitate at the bottom of the tube. The plasma cfDNA was extracted by the magnetic bead method, and the extracted cfDNA was stored in a -80°C refrigerator.
[0047] 2. End repair and phosphorylation reaction
...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2 The construction method of low-input PCR-free high-throughput sequencing library of the present invention (2)
[0077] Similarly, 2ng of starting cfDNA from 3 different pregnant women’s blood samples in Example 1 were used to build a library. The method of building a library was the same as that in Example 1, except that:
[0078] Step 2.3 Reaction conditions: place at 20°C and react for 30 minutes.
[0079] In step 2.4, use 2.5 times the volume of the reaction product to purify and recover the reaction system with Ampure Xp magnetic beads.
[0080] In the reaction of adding "A" at the 3' end, the reaction condition is 30°C for 30 minutes;
[0081] In the linker ligation reaction, the reaction condition is 20°C, and the reaction is 15 minutes;
[0082] 70°C, react for 10 minutes.
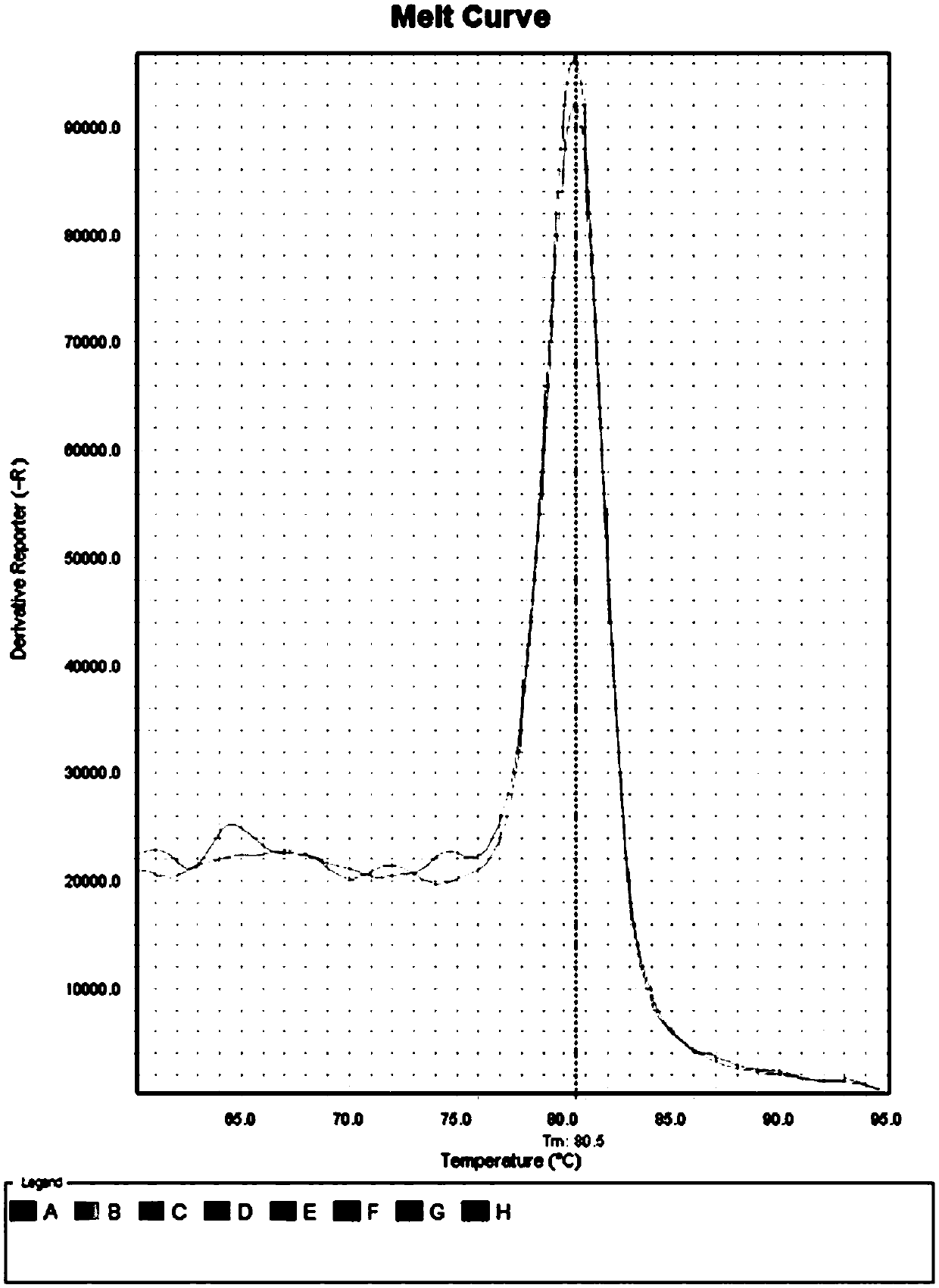
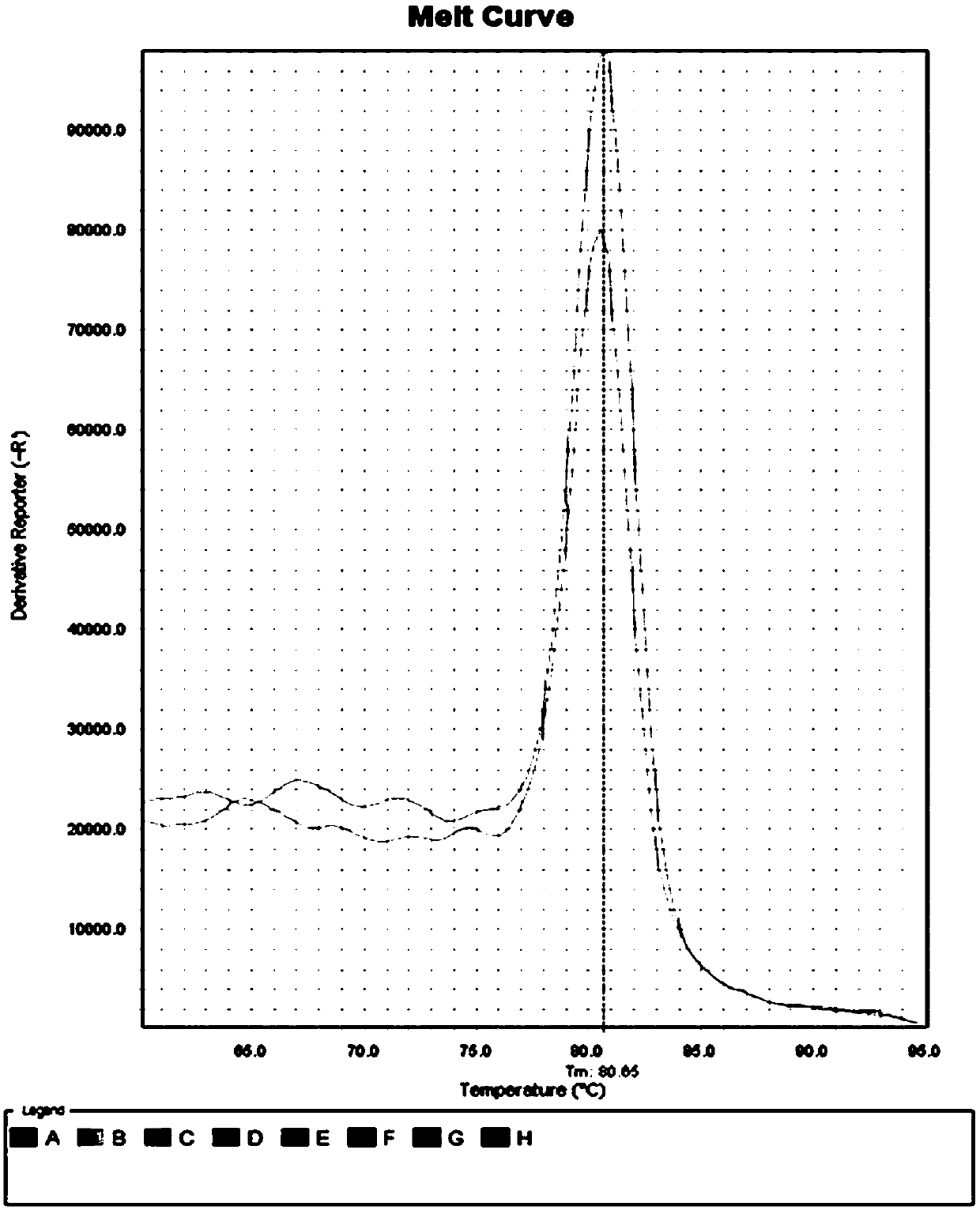
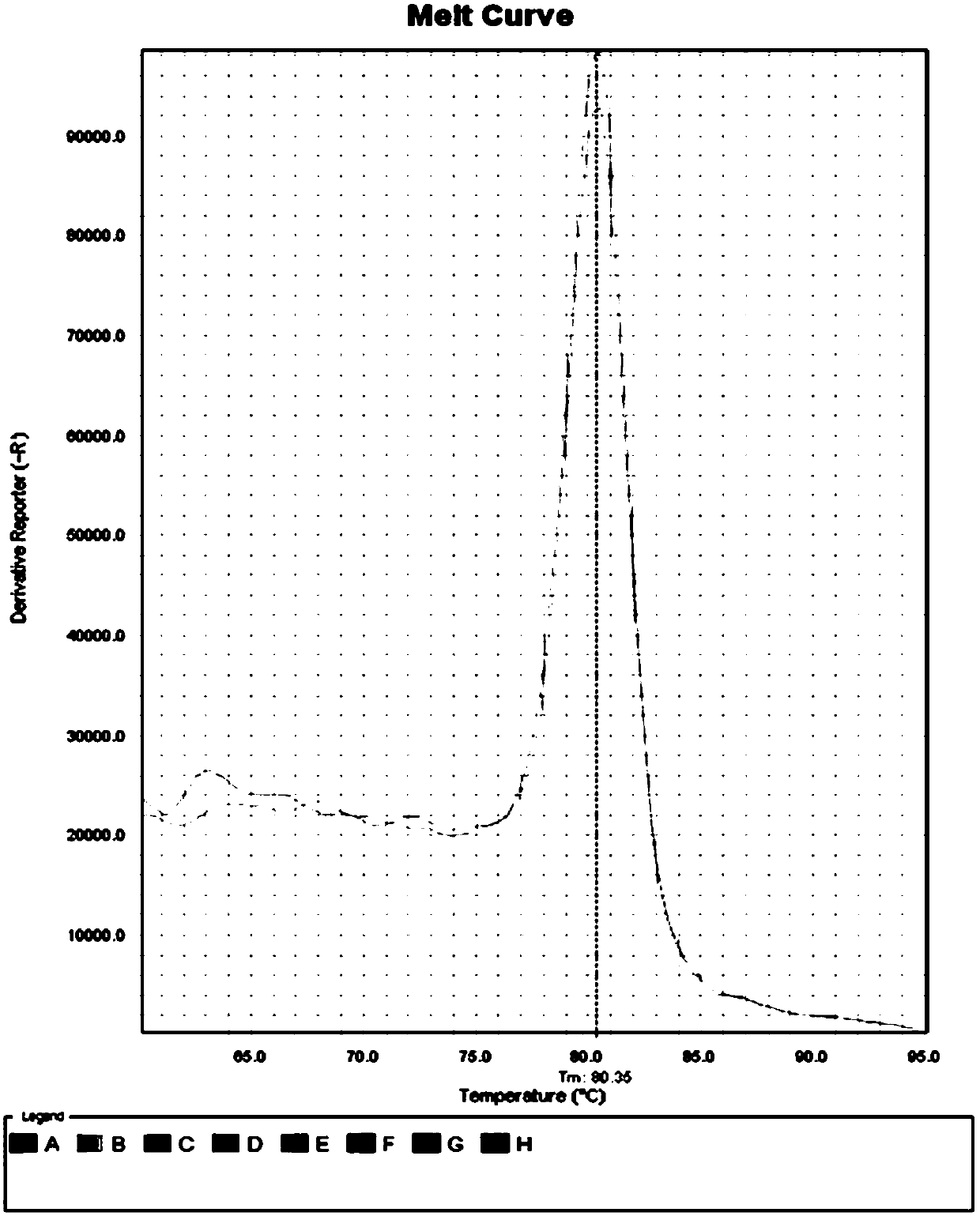
[0083] After the library was built, the quality inspection showed that the results were similar to those in Example 1, indicating that the data obtained from the 3 test sample...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com