Cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum with low-temperature resistance as well as preparation method and application of cellulose degradation composite microbial inoculum
A technology for degrading cellulose and compound bacterial agents, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, preparation of organic fertilizers, and methods based on microorganisms, etc. The implementation process is complicated and other problems, to achieve the effect of easy implementation, efficient degradation, and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] This embodiment is an exemplary preparation method of a low-temperature-resistant cellulose-degrading bacteria composite bacterial agent. The method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0035] 1) Take Flavobacterium johnsoniae and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia with inoculation loops respectively, numbered X24 and X26 respectively, and insert each loop strain into NA medium for activation and expansion culture in turn ;
[0036] 2) Pick the activated colonies and inoculate them in the corresponding liquid fermentation medium respectively, and culture them with shaking at 25°C and 200r / min for 48 hours to the logarithmic growth phase to obtain liquid bacterial agent seed liquid;
[0037] 3) After amplifying the above-mentioned seed solution to obtain a bacterial solution with a suitable concentration, collect the bacterial cells after high-speed centrifugation to prepare a dry powder bacterial agent, and mix it at a weight ratio of 1:1.
Embodiment 2
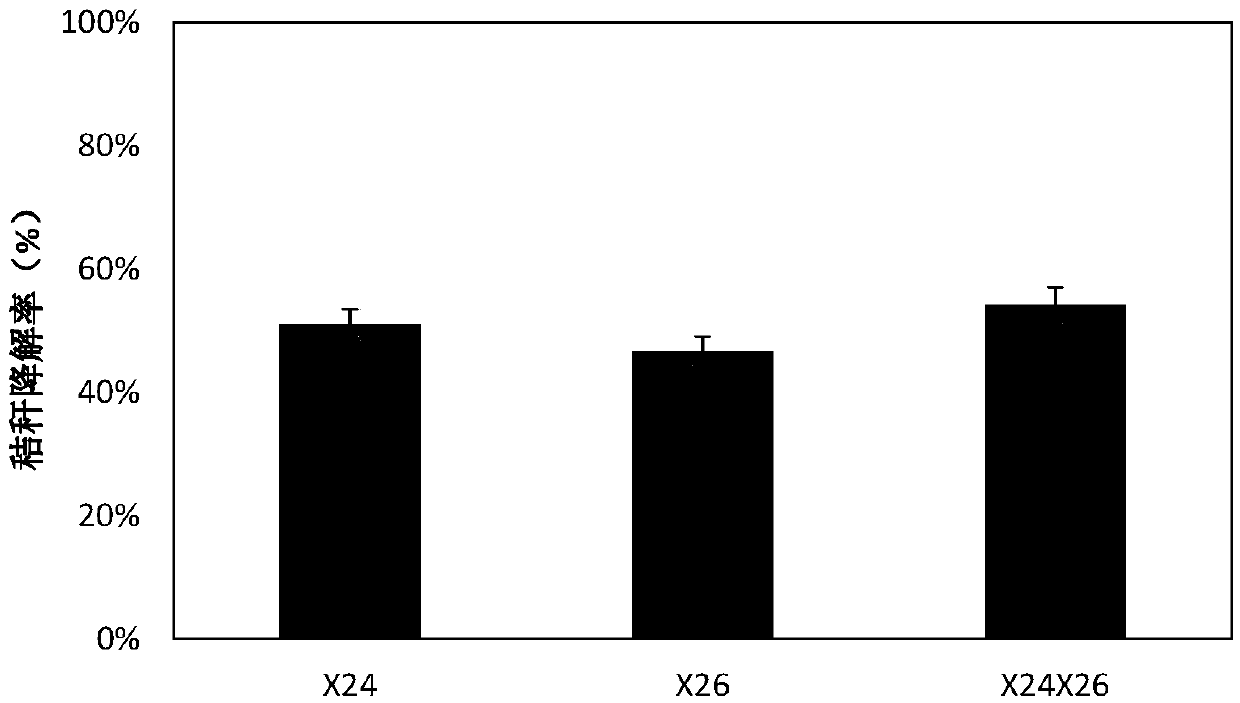
[0039] This example is the determination of the cellulase activity and degradation rate of the low temperature resistant cellulose degrading bacteria alone and the composite bacterial agent.
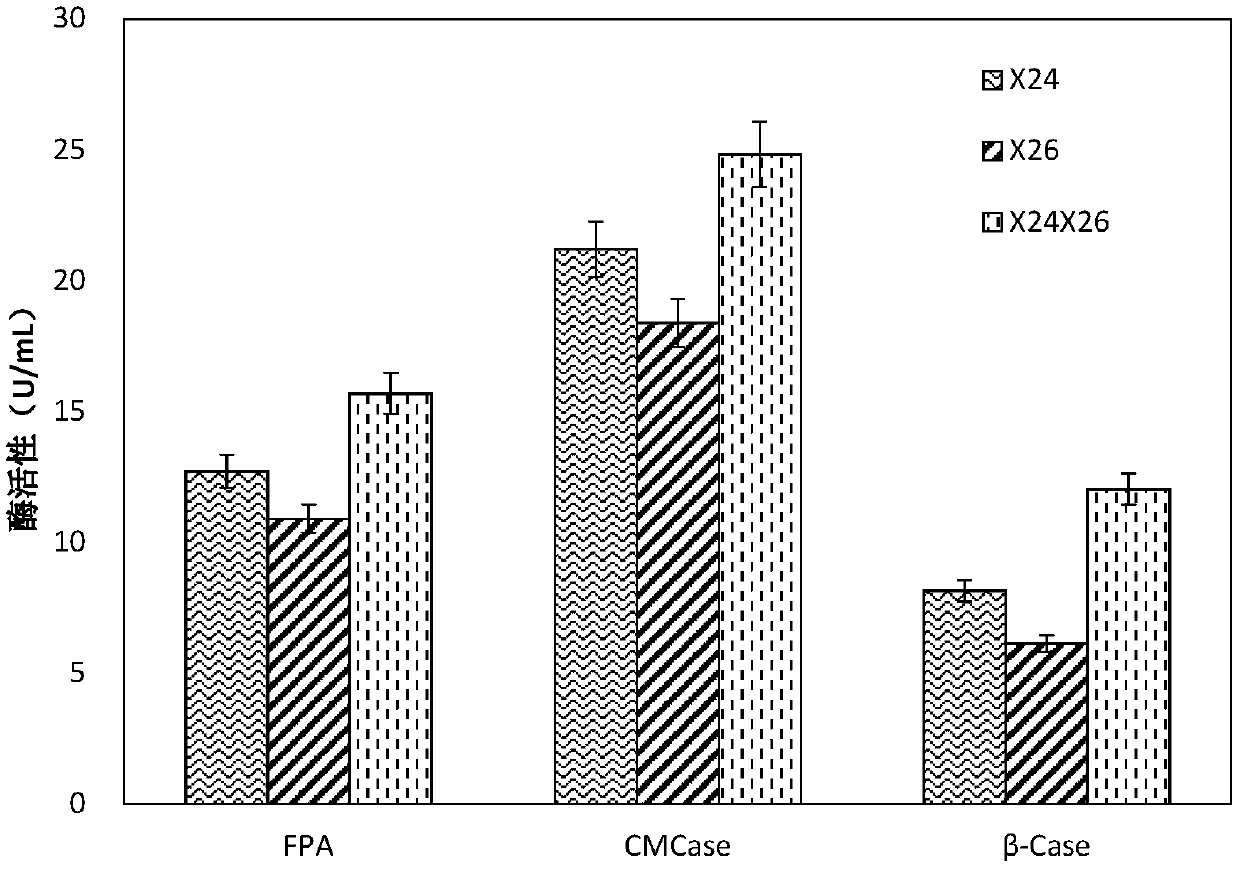
[0040] (1) Determination of enzyme activity
[0041] The two strains of single bacteria and the composite bacterial agent in Example 1 were respectively inserted into the enzyme-producing fermentation medium, and cultured at 12 ° C. Using straw powder as a carbon source, the two strains were continuously fermented for 5 days to produce enzymes. And measure FPA enzyme activity, CMC enzyme activity and β-glucosidase activity with DNS method every 24h, do 3 groups of parallels for each bacterial strain, measure the highest activity of each cellulase of 2 single strains and compound bacterial agents, such as figure 1 shown. Enzyme production medium composition: KH 2 PO 4 2g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.4g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.3g, CaCl 2 0.3g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.005g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.0016g, Z...
Embodiment 3
[0048] This embodiment is a method for in-situ degradation of straw and returning it to the field. The composite bacterial agent adopted in the method of the present embodiment adopts the microbial agent of Example 1. Method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0049] 1) According to the dosage of 4.5kg of bacterial agent per mu of land, mix the bacterial agent with the soil and spread it on the straw;
[0050] 2) According to the dosage of 7kg urea per mu of land, mix urea with an appropriate amount of water and sprinkle it on the straw;
[0051] 3) Rotary tillage to bury the straw into the soil, keep the water content of the straw and soil at 50%-65%, and degrade the straw in a low temperature environment for ≥ 45 days, so that the straw is fully decomposed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com