In-mold foam vulcanization molding rubber tire with double density and its manufacturing process
A rubber tire, vulcanization molding technology, applied to tire parts, tires, non-pneumatic tires, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient elasticity, high cost, and energy consumption of rubber tires, and achieve the elimination of transportation costs, low energy consumption, and increased elasticity effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
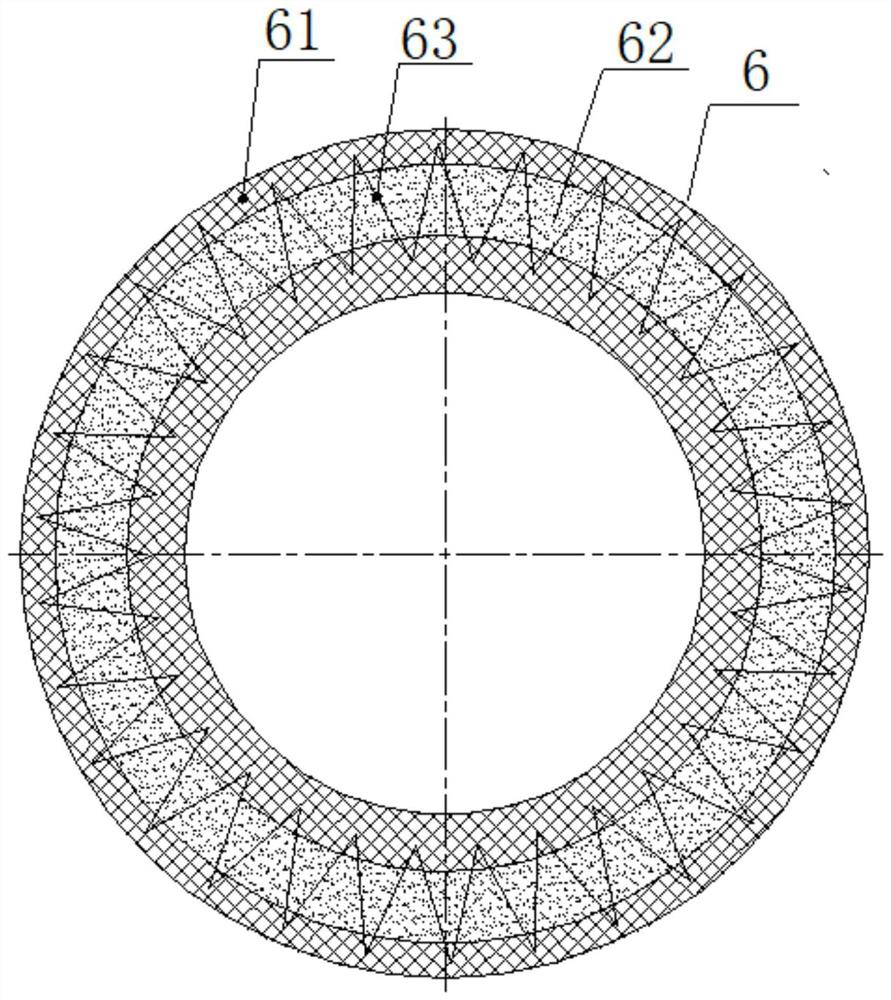
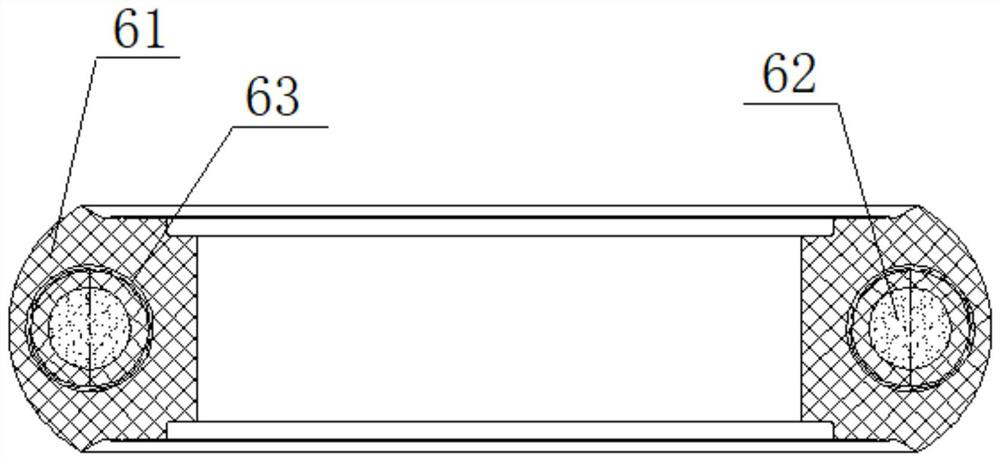
[0056] The foam vulcanization molded rubber tire in the double-density forming mold of the present embodiment, such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, it includes a high-density outer layer 61 and a low-density inner layer 62, which is an integrated structure that is released from the same mold; the materials of the high-density outer layer 61 and the low-density inner layer 62 are high-density rubber and low-density rubber respectively. The low-density rubber is made by adding a foaming agent to the high-density rubber after foaming, and the double-density injection in-mold foaming production system is used to complete the double-density rubber injection, foaming and vulcanization processes in one mold. Effectively avoid the circulation of products in each process, thereby reducing production costs. The density ratio of the high-density outer layer 61 and the low-density inner layer 62 can be 2:1, wherein the density of the high-density outer layer 61 is 1000kg / m 3 .
Embodiment 2
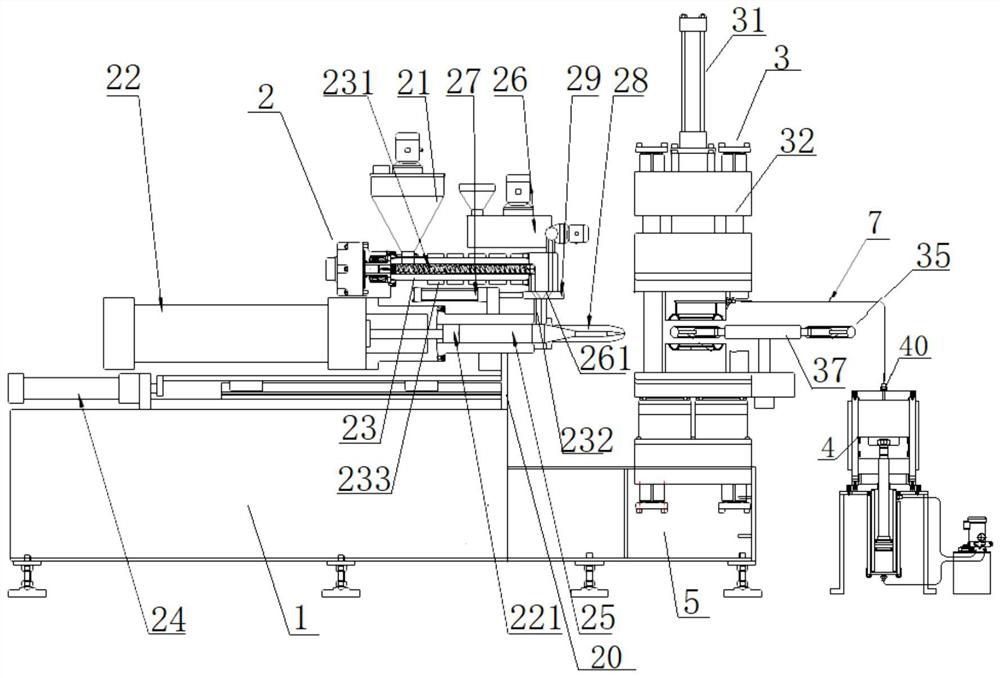
[0058] The basic structure of the double-density molding in-mold foam vulcanization rubber tire of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the improvements are as follows: figure 1 , 2As shown, the low-density inner layer 62 is also buried with an annular spring support 63, which acts as a skeleton support. The spring elasticity can be selected to be consistent with the elasticity of the low-density rubber, so as to strengthen the support strength of the low-density inner layer 62 and slow down the low-density Elastic attenuation caused by frequent deformation of the inner layer 62 . The double-density injection in-mold foam molding production system includes an injection machine base 1, a compression molding vulcanization base 5, an injection device 2 fixed on both, a compression molding and foaming vulcanization device 3, and a compression molding vulcanization base 5 The mold exhaust and inflation mechanism 4 on the side. The compression molding and foamin...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The basic structure of the dual-density molding production system of the double-density molding in-mold foaming vulcanization molding rubber tire used to produce rubber tires in this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 2, and the improvements are as follows: image 3 As shown, the injection device 2 in the double-density injection in-mold foam molding production system includes a hopper 21, an injection cylinder 22, a plasticizing injection screw barrel 23, an injection seat moving cylinder 24, a pre-injection chamber 25, a rubber plastic chemical machine 26, material switching oil cylinder 27, injection head 28 and material switching switching valve 29; the feeding hopper 21 communicates with the beginning of the plasticizing injection screw barrel 23, and the plasticizing injection screw barrel 23 is fixed on the end of the injection oil cylinder 22 side; the plasticizing injection screw barrel 23 and the discharge port of the rubber plasticizing machine 26 co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com