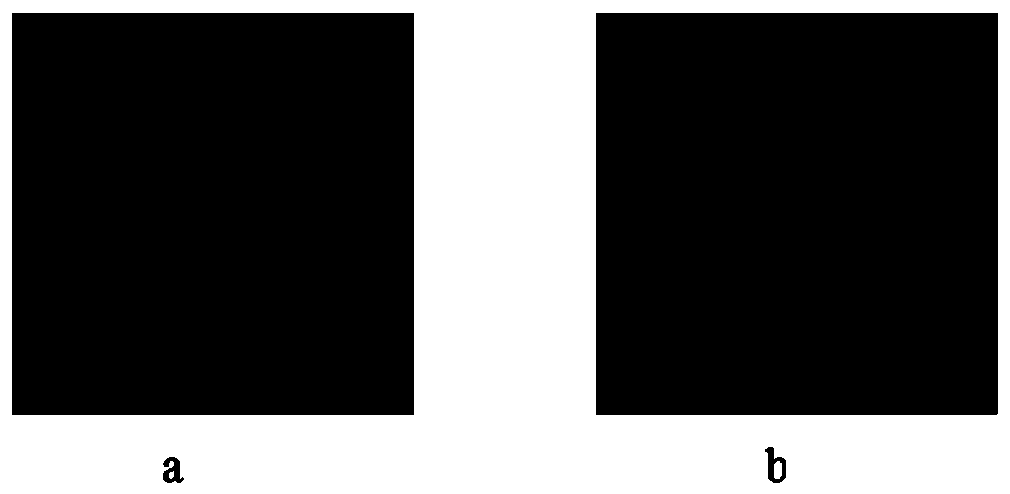A general image noise estimation method based on self-similarity measure
A technology of image noise and noise estimation, applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of complex algorithm theory, reduced accuracy of image noise estimation, unfavorable application in practice, etc., and achieve the effect of simple theory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
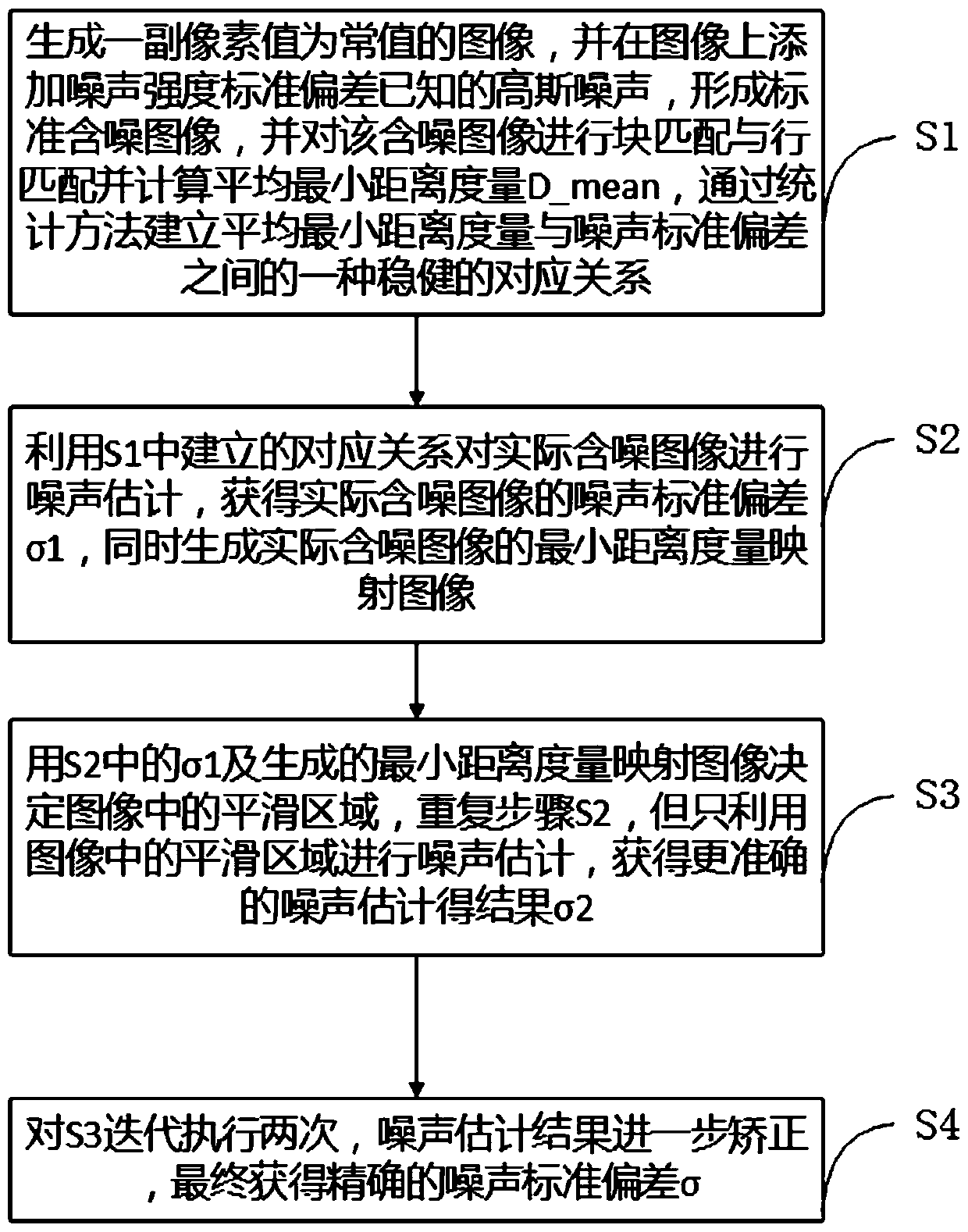
[0031] refer to figure 1 As shown, a general image noise estimation method based on self-similarity metric, including the following steps:
[0032] S1. Generate an image with a constant pixel value, and add Gaussian noise with known noise intensity standard deviation to the image to form a standard noisy image, and perform block matching and row matching on the noisy image and calculate the average minimum distance metric D mean , to establish a robust correspondence between the average minimum distance metric and the noise standard deviation through statistical methods;
[0033] S2. Using the corresponding relationship established in S1 to perform noise estimation on the actual noisy image, obtain the noise standard deviation σ1 of the actual noisy image, and simultaneously generate the minimum distance metric mapping image of the actual noisy image;
[0034] S3. Use σ1 in S2 and the generated minimum distance metric mapping image to determine the smooth area in the image, ...
Embodiment 2
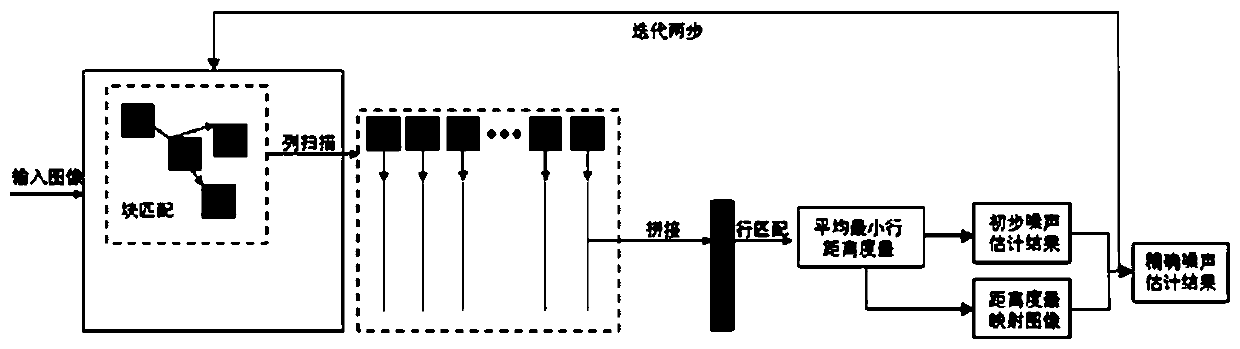
[0038] refer to figure 2 as shown, figure 2 Be the method flowchart of the general image noise estimation method based on self-similarity measure of the present invention;'
[0039] The first step: image block matching and row matching calculate the average minimum distance metric;
[0040] refer to image 3As shown, first generate a 256×256 grayscale image with a pixel value of 0.5, the pixel value can also be set as other parameters according to the needs of the image, add Gaussian noise with a noise intensity of standard deviation of 1.0 to the image, and execute the generated For block matching of noisy images, an image block of size N_step is used to extract an image block of size N_step as a reference block, and then block matching is performed in a neighborhood of size NS×NS centered on the reference block to obtain a number of N2 Similar to the image blocks, all the matching image blocks are column-scanned and spliced into a matrix M with a size of (N1×N1)×N2, a...
Embodiment 3
[0052] refer to image 3 As shown, the constant value image and the noisy image in the noise estimation experiment of this embodiment; Figure 4 is an actual noisy image and the distance metric mapping image obtained from it;
[0053] In the research of image denoising in this embodiment, Figure 5 The 10 standard images shown are used MATLAB software to carry out noise addition and noise estimation experiments to the image, adding noise of different intensities to the image each time, and then using the method in Example 2 to noise the image with noise. estimate. Figure 6 is the image noise estimation result of this embodiment. It can be seen from the data in the table that the noise estimation result of this embodiment is very accurate, and can be completely applied to image denoising practice to realize blind image denoising. The estimated results are basically a bit high, because there are more or less noises in the original image.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com