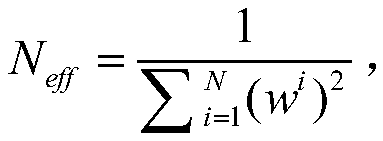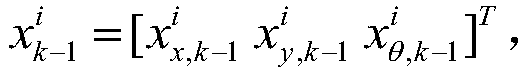Robot non-trace quick simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) method based on multiple fading factors
A fading factor and synchronous positioning technology, applied in navigation computing tools and other directions, can solve problems affecting the real-time performance of SLAM algorithms, increasing algorithm complexity, and decreasing filtering accuracy of SLAM algorithms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] The present invention is an improved mobile robot synchronous positioning and mapping method, the flow chart is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific implementation steps are:
[0075] Step 1. The system is initialized to determine the global coordinate system and the initial pose of the mobile robot at time k under the coordinate system, the estimated mean value and covariance matrix of the initial state;
[0076] In the step 1, the robot pose X r =[x r the y r θ r ] T , the landmark position m i =[x i the y i ] T Both use a two-dimensional plane Cartesian coordinate system, the global coordinate system takes the initial position of the robot as the origin, and the initial heading is the positive direction of the X-axis;
[0077] Step 2. Perform time update according to the process model and observation model, and calculate the predicted pose and covariance of the particle at k+1 time;
[0078] In the step 2, the mobile robot system can be expressed a...
Embodiment 2
[0141] The invention provides an improved method for synchronous positioning and mapping of mobile robots. In view of the inaccurate modeling of the system or the sudden change of the state, the filtering accuracy of the FastSLAM algorithm will be reduced or even divergent. The multiple fading factor matrix and The unscented Kalman filter is introduced into the FastSLAM algorithm to generate a suggestion distribution function whose parameters can be adaptively adjusted. Compared with the traditional method, the multi-fading unscented Kalman filter is applied to the simultaneous positioning and mapping of the mobile robot, which reduces the error originally introduced by the linearization process, not only improves the filtering accuracy of the system, but also improves the accuracy of the filter. The ability to adjust the strain when there is a sudden change in the system state, thereby enhancing the robustness of the robot navigation and positioning system.
[0142] The techn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com