Marker for early diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection
A technology of syncytial virus and respiratory tract, applied in the field of molecular diagnosis, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, non-specific staining, difficulties, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing mortality, more accurate genetic diagnosis, and timely genetic diagnosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Screening of genes differentially expressed in patients with respiratory syncytial virus infection and normal people
[0045] 1. Case collection population
[0046] Children treated by the inpatient department of the pediatric department of the hospital (RSV infection group, 5 cases) and children with routine physical examination in the pediatric outpatient growth and development clinic (control group, 5 cases).
[0047] 2. Clinical case screening criteria
[0048] 2.1 Inclusion criteria of RSV infection group
[0049] (1) Age: 1 month to 1 year old;
[0050] (2) Past history: no RSV infection and / or wheezing attack;
[0051] (3) Clinical symptoms: cough and / or wheezing and / or shortness of breath;
[0052] (4) Physical examination: increased respiratory rate / three inspiratory depressions / wheeze or moist rales on lung auscultation;
[0053] (5) Auxiliary examination: the throat swab is positive for RSV antigen;
[0054] (6) Imaging examination: Chest X-ra...
Embodiment 2
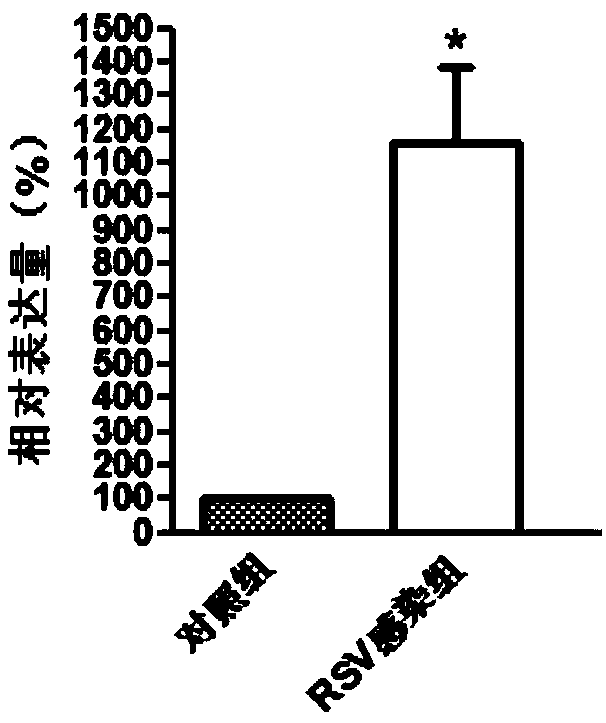
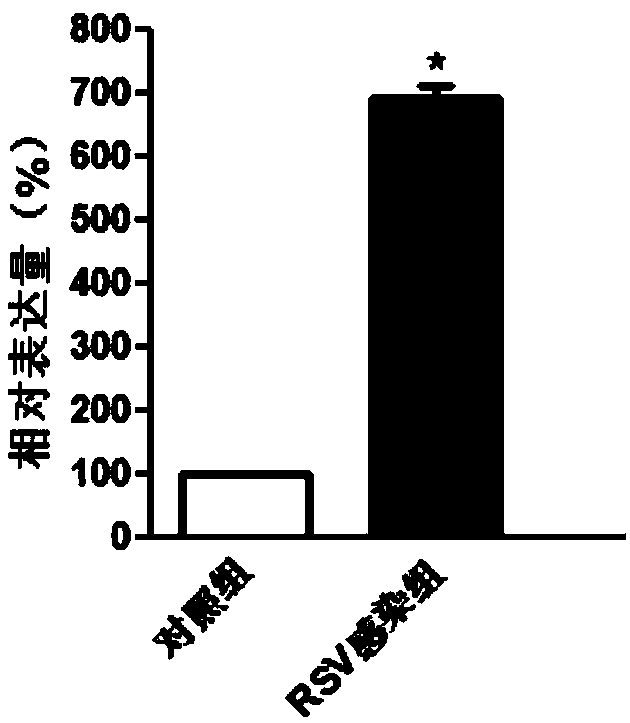
[0103] Embodiment 2QPCR experiment verifies the genes differentially expressed in patients with respiratory syncytial virus infection and normal people
[0104] 1. Research object:
[0105] The screening criteria were the same as in Example 1, with 30 cases in each of the RSV infection group and the control group.
[0106] 2. Extraction of total RNA in blood
[0107] Step is with embodiment 1.
[0108] 3. RT-PCR
[0109] (1)RT
[0110] RT reaction system (20μl):
[0111]
[0112] RT reaction procedure:
[0113] 42°C 15min
[0114] 85℃ 5s
[0115] 4℃ ---
[0116] (2) qPCR
[0117] PCR reaction system (20μl):
[0118]
[0119] PCR reaction program:
[0120] Amplification procedure:
[0121] Stage 1 95°C 10min
[0122] Stage 2 95°C 10s
[0123] 49.1°C 10s
[0124] Repeat for 45 cycles
[0125] Three replicate wells were set for each sample, and the internal reference was GAPDH.
[0126] (3) Primers
[0127] The primer sequences of CTSD gene and GAPDH gene ...
Embodiment 3
[0141] Example 3 Western blot experiment to verify the expression products of differentially expressed genes in patients with respiratory syncytial virus infection and normal people
[0142] 1. Research object: same as embodiment 2.
[0143] 2. Mononuclear cell isolation
[0144] Take 10ml of venous blood from patients in the RSV infection group and the control group, inject it into a sterile vial containing heparin, and shake it gently immediately after capping. Add an equal volume of HBSS (NaCl 8.0g, NaCl 2 HPO 4 0.132g, KH 2 PO 4 0.06g, KCl 0.4g, phenol red 1ml, NaHCO 3 0.35g, D-glucose 1.0g, dissolved in 1000ml double distilled water), to reduce the aggregation of red blood cells. Draw 8ml of lymphocyte stratification solution into a 50ml centrifuge tube, slowly add the diluted blood along the tube wall, keep the interface clear, do not mix the two, centrifuge at 20°C 2000r / min for 30min, carefully absorb the stratification solution and plasma transfer The turbid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com