Method for determining available limit of crack-type hard object damage of leading and trailing edges of blade by taking high and low cycle fatigue into account
A low-cycle fatigue and determination method technology, applied in the direction of applying repeated force/pulsation force to test the strength of materials, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of tearing/crack type hard object damage, lack of reasonable norms, available limit formulation process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
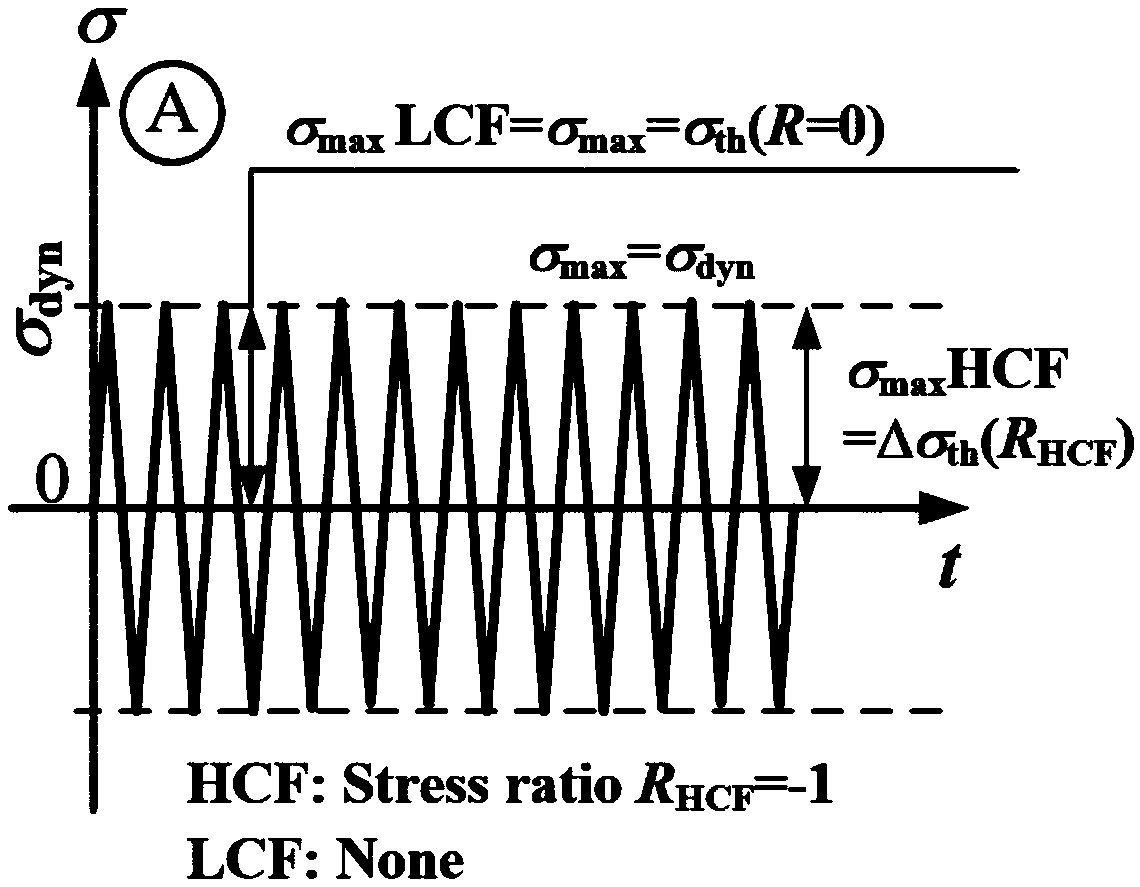
[0051] A method for determining the usable limit of crack-type hard object damage at the leading and trailing edges of a blade considering high and low cycle fatigue, comprising the following steps:
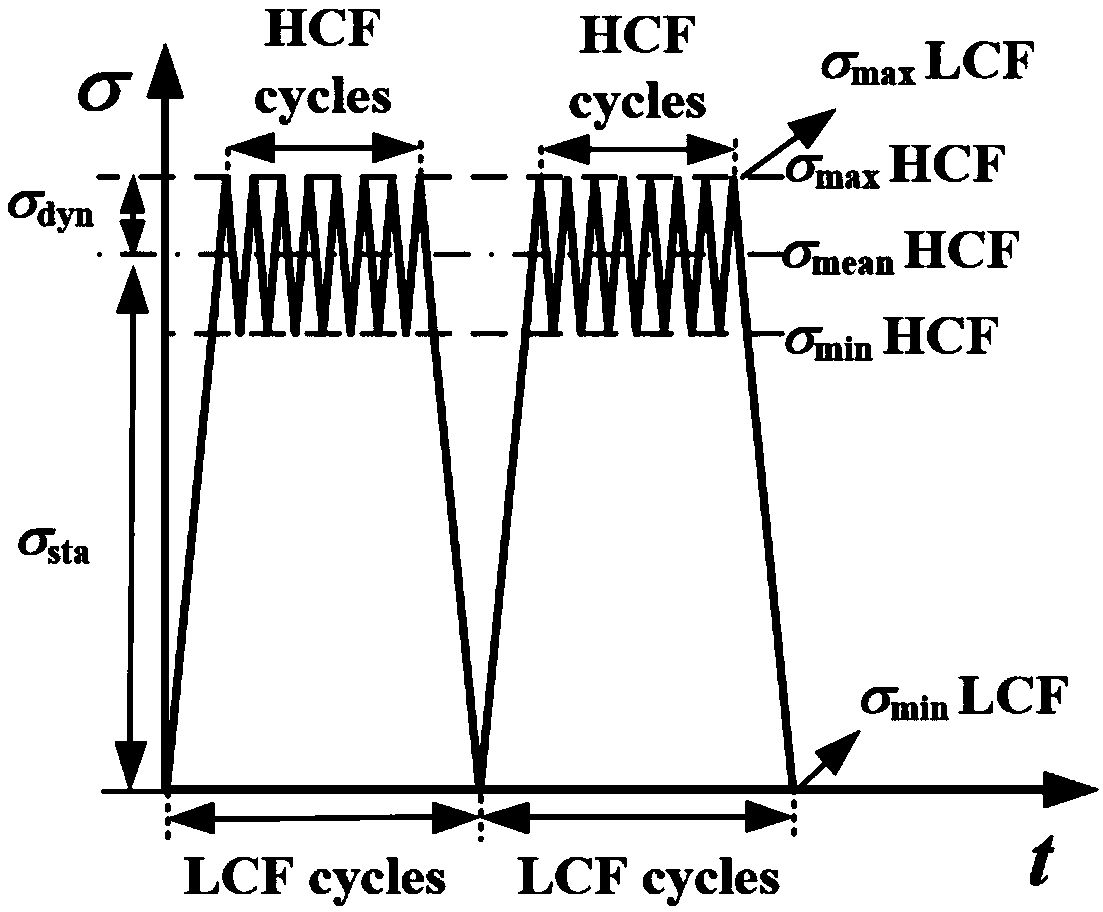
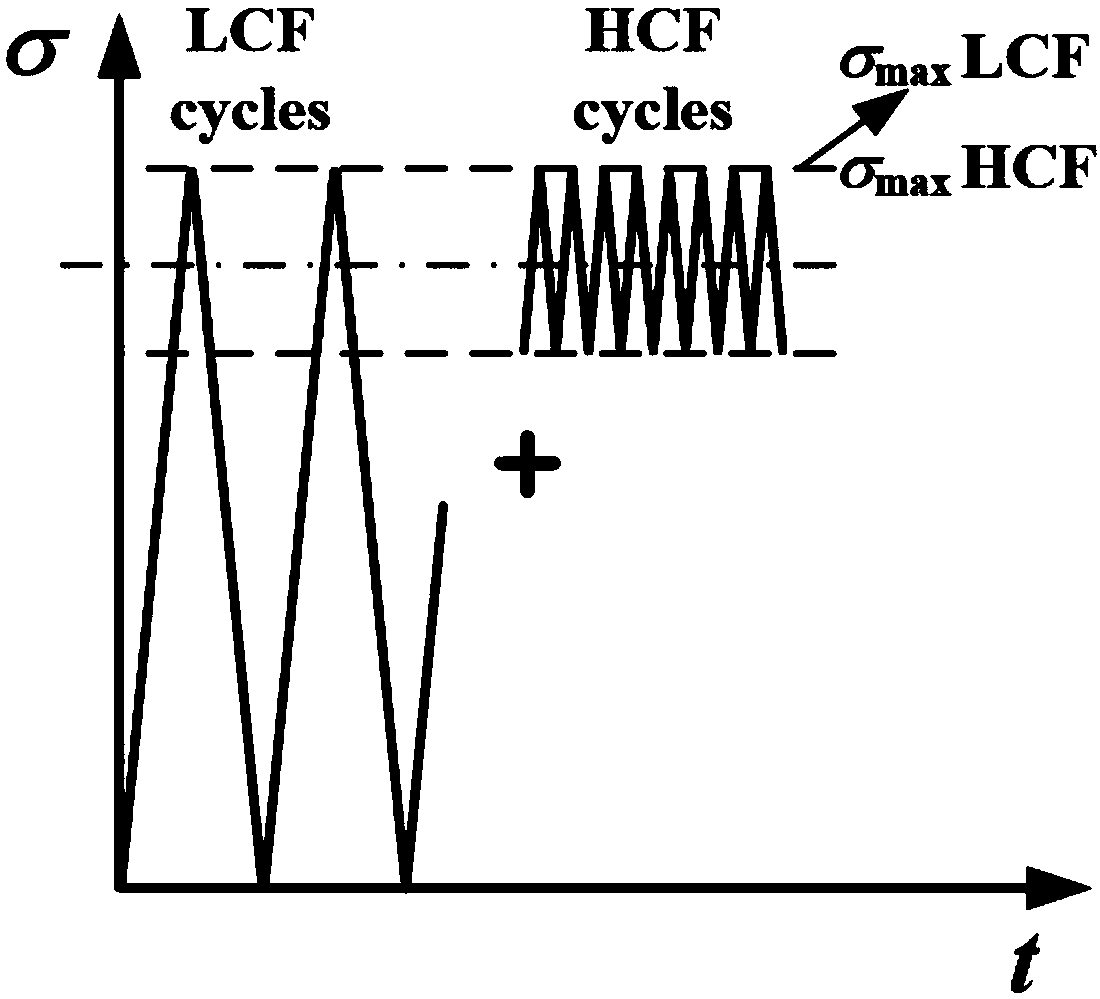
[0052] (1) The possible high-cycle fatigue load and low-cycle fatigue load are extracted from the high / low-cycle composite fatigue loads borne by each point on the leading and trailing edges of the blade. Among them, high cycle fatigue load is high cycle fatigue load, referred to as HCF, and low cycle fatigue load is low cycle fatigue load, referred to as LCF.
[0053] The high / low cycle composite load of the blade refers to the interaction between the low frequency centrifugal force cycle load and the high frequency vibration load of the blade when the engine is working normally, such as figure 1 shown. In the present invention, the centrifugal force cyclic load in the blade is recorded as low cycle fatigue load, i.e. low cycle fatigue load, and the high frequency vibration loa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com