Non-syndromic autosomal dominant hereditary deafness pathogenic gene KCNQ4 mutation detection kit
A kit and gene technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of different effects on protein functions, the difficulty of increasing the pathogenicity of mutation sites, etc., and reduce the birth rate , to avoid economic loss and reduce the burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
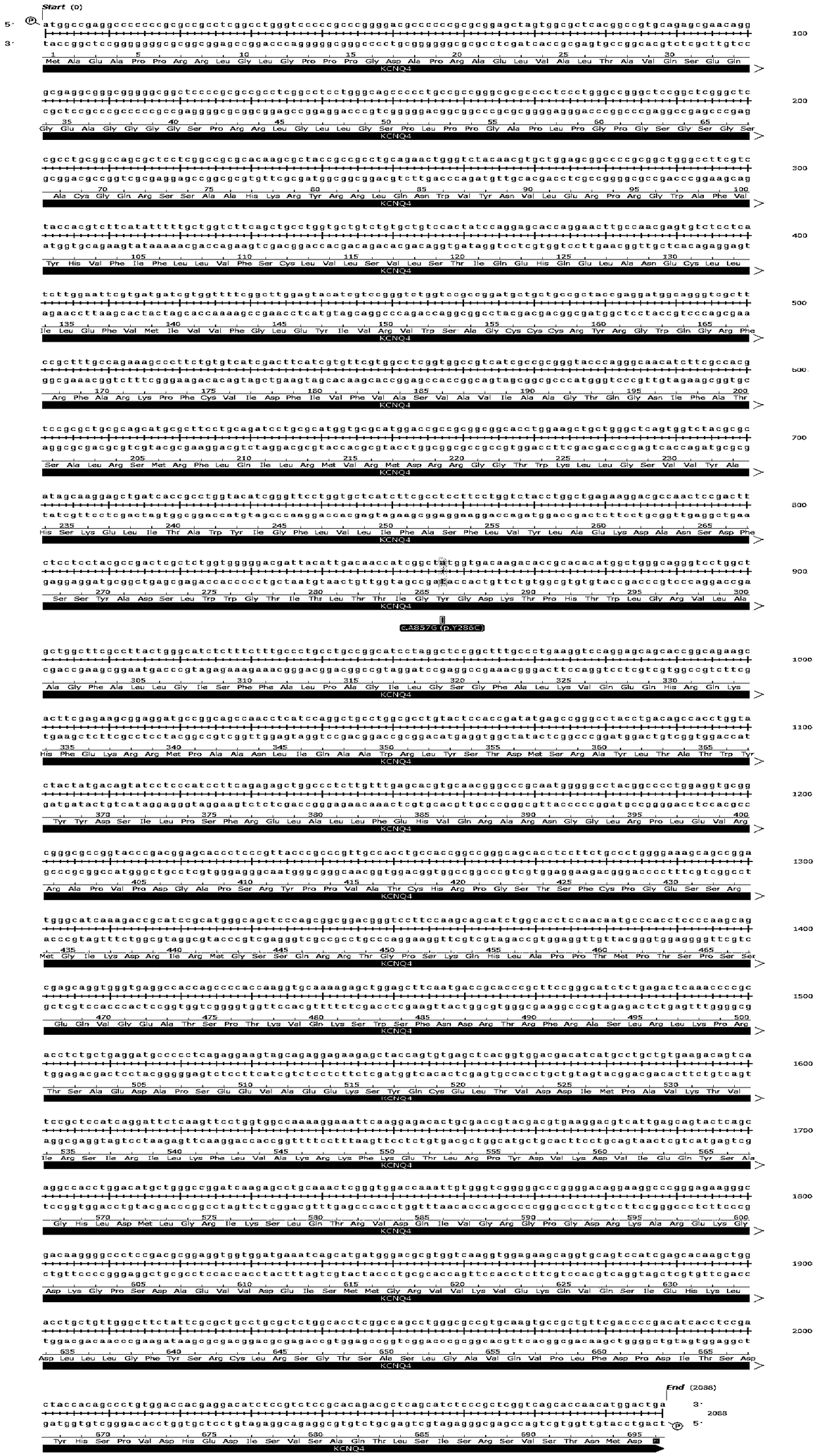
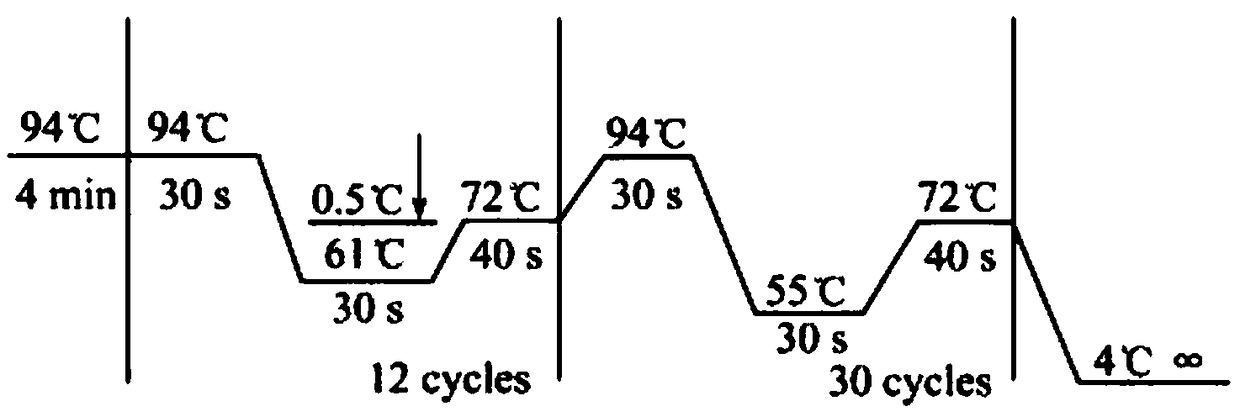
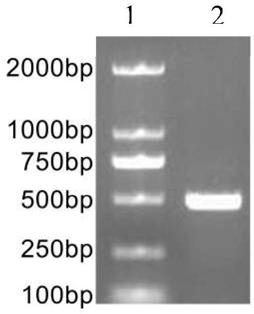
[0069] Collect all kinds of non-syndromic autosomal dominant deafness through the deaf clinic and resource collection network, and establish a resource bank. On the premise that the patient is voluntary, after signing the informed consent, 5-10mL blood samples will be collected, and an outpatient medical record database will be established to record the patient's condition, family history and contact information in detail. Then, the genomic DNA was extracted by phenol-chloroform extraction, quantified and stored at -20°C. Each DNA sample corresponds to the registered patient's clinical data in detail. Then, use the online primer design software Primer3 to design primers (including the entire exon6 region of KCNQ4), and use genomic DNA as a template for PCR amplification. Direct sequencing of PCR amplification products: the sequencing primers are the same as the PCR amplification primers, forward and reverse sequencing, using ABI 3700 DNA sequencer. The sequence obtained by se...
example 2
[0170] PCR amplification primers (design completed in March 2018) are any pair of the following primers, and others are the same as Example 1:
[0171] Upstream primer KCNQ4-F2: 5`-TATGACCCTAACCAGCCCC-3`;
[0172]Downstream primer KCNQ4-R2: 5`-TTGGCTGCCGGCATCCTCCGCTTCT-3`;
[0173] Upstream primer KCNQ4-F3: 5`-CAGGAGAGGGAGAATCCATC-3`;
[0174] Downstream primer KCNQ4-R3: 5`-CGAAGTGCTTCTGCCGGTGCT-3`;
[0175] Upstream primer KCNQ4-F4: 5`-TATACCCCTTTCCCCTGACCAGCC-3`;
[0176] Downstream primer KCNQ4-R4: 5`-GCTCCTGGACCTTCAGGGCAAA-3`;
[0177] Upstream primer KCNQ4-F5: 5`-CCTACCTGCCTGTACCCCCA-3`;
[0178] Downstream primer KCNQ4-R5: 5`-GCCGGAGCCTAGGATGCCCTAGAGGGATA-3`;
[0179] Upstream primer KCNQ4-F6: 5`-CGTGGGTGACCAGGGGCCCC-3`;
[0180] Downstream primer KCNQ4-R6: 5`-GGGCATGGTTGGGGGAATGTGCT-3`;
[0181] Upstream primer KCNQ4-F7: 5`-ACAAGCCGTAGGTGGCCCCC-3`;
[0182] Downstream primer KCNQ4-R7: 5`-GGCAGTGGTGGGGCAGTAAGAGGCT-3`;
[0183] Upstream primer KCNQ4-F8: 5`-GTGACC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com