A table-level bidirectional synchronization realization method and system based on trigger
A two-way synchronization and realization method technology, applied in the direction of structured data retrieval, database distribution/replication, etc., can solve data modification conflicts, cycle synchronization conflicts, synchronization failures and other problems, and achieve the effect of solving data conflicts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
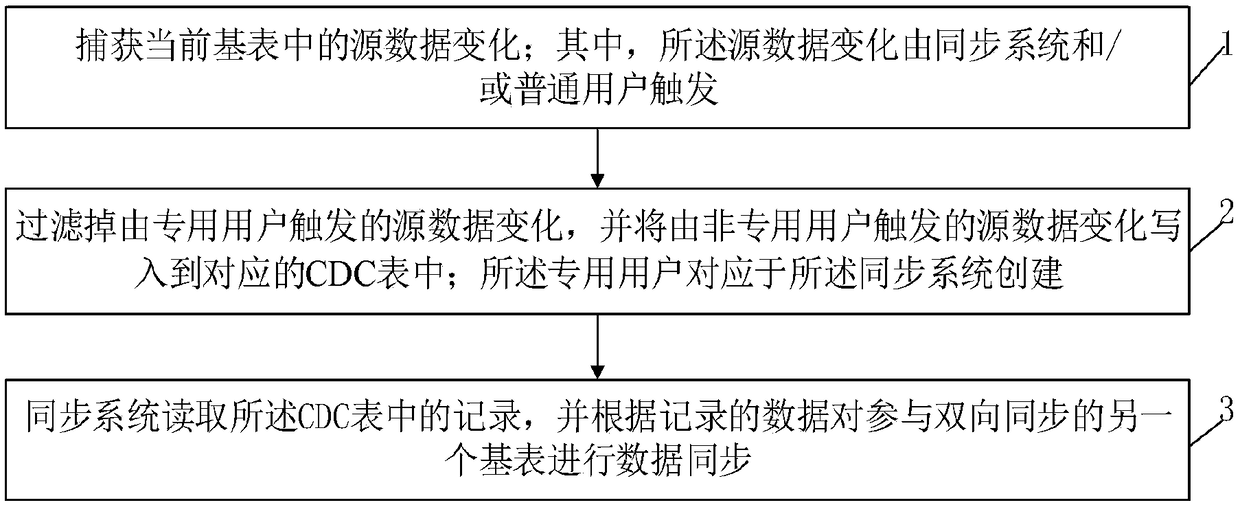
[0056] The present invention provides a trigger-based table-level two-way synchronization implementation method. Here, the base table A and the base table B are still used to represent the two base tables participating in the two-way synchronization, which are used to store source data A and source data B respectively. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0057] Step 1, capturing source data changes in the current base table; wherein, the source data changes are triggered by a synchronization system and / or a common user. In the embodiment of the present invention, triggers are still used to capture source data changes: trigger A is used to capture source data changes in base table A, and trigger B is used to capture source data changes in base table B. For the source data A in the base table A, the data change may be from the operation of ordinary users, such as the data modification of the source data A by the above-mentioned use...
Embodiment 2
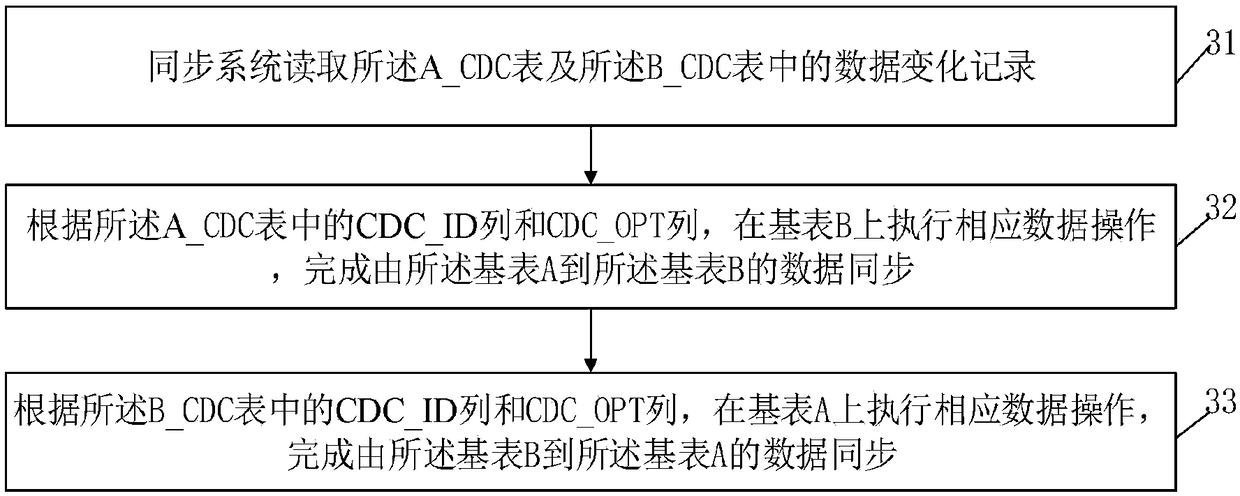
[0067] In one synchronization operation, two one-way synchronization processes need to be performed sequentially to complete two-way data synchronization. The execution processes of the two one-way synchronizations are the same. Based on the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the embodiment of the present invention uses the The one-way data synchronization from the base table A to the base table B is taken as an example, and the execution of the step 32 is introduced in detail.
[0068]At the same time, when source data changes occur in both the base table A and the base table B, there may be conflicts of changed data in the two base tables, and the conflicts of changed data include data modification conflicts and data insertion conflicts. Wherein, the data modification conflict is specifically: the same field of the record with the same primary key is modified in the base table A and the base table B at the same time, if the base table A to the base table B and the base table B to ...
Embodiment 3
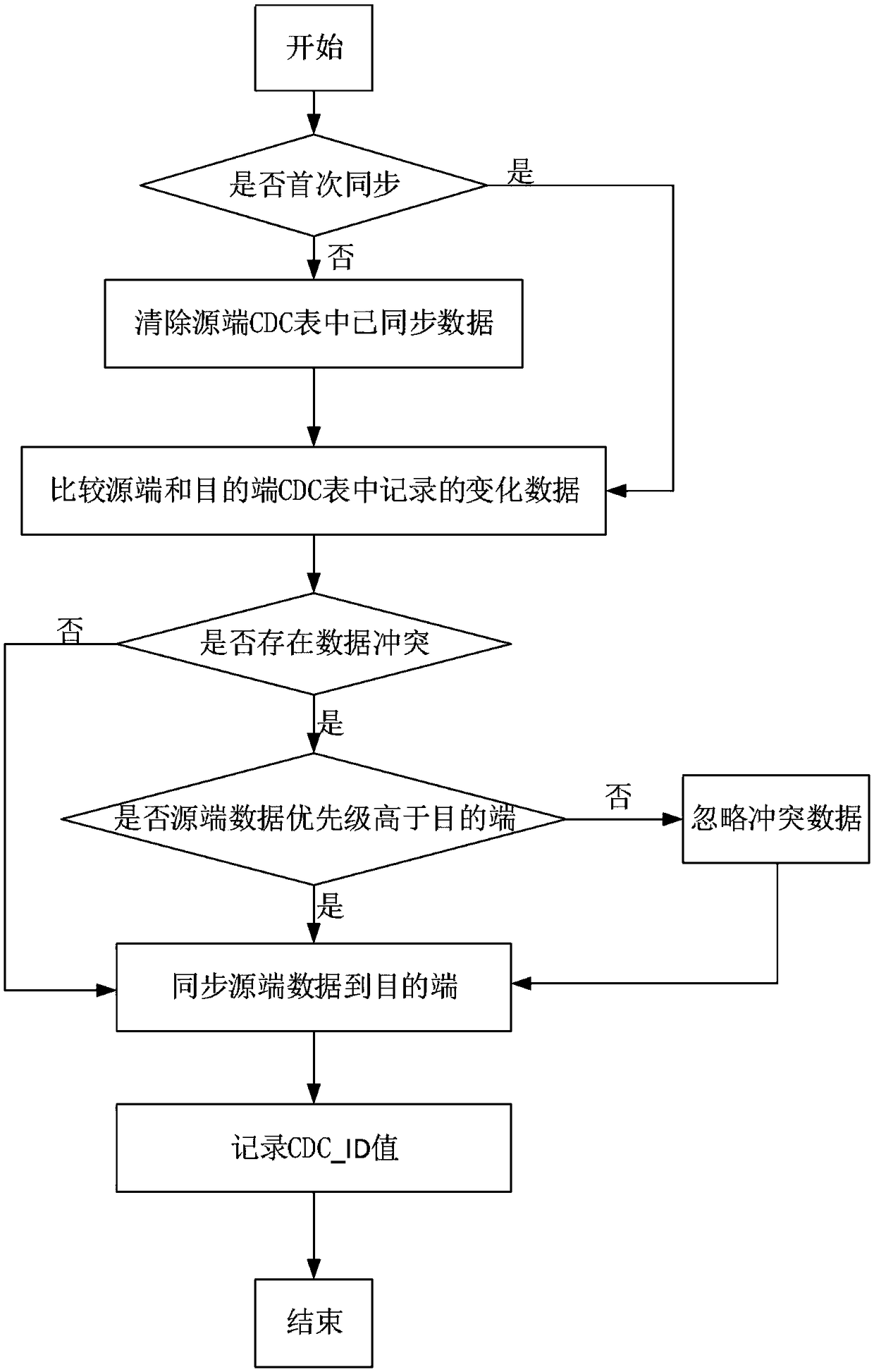
[0077] The two-way synchronization of table-level data is mainly divided into an initialization process and a data synchronization process. The initialization process only needs to be performed once, while the data synchronization is performed periodically. The foregoing embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 have introduced the data synchronization process, on this basis, the embodiment of the present invention specifically introduces the initialization process before the data synchronization.
[0078] During two-way synchronization, both databases participating in two-way synchronization need to be initialized, and the steps and methods are the same. For each database, refer to Figure 4 , the initialization process specifically includes the following steps:
[0079] Step 01, create a dedicated user for the synchronization system on the database, and grant corresponding permissions; wherein, the dedicated user corresponds to a dedicated user ID.
[0080] For ordinary users, such as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com