A symmetrical power converter circuit topology and control method thereof
A technology of circuit topology and power converter, which is applied in the directions of high-efficiency power electronic conversion, regulation of electric variables, control/regulation system, etc. Oxygen magnetic permeability changes and other issues, to achieve the effect of reducing reactive power loss, reducing design and manufacturing difficulty and cost, and reducing conduction loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
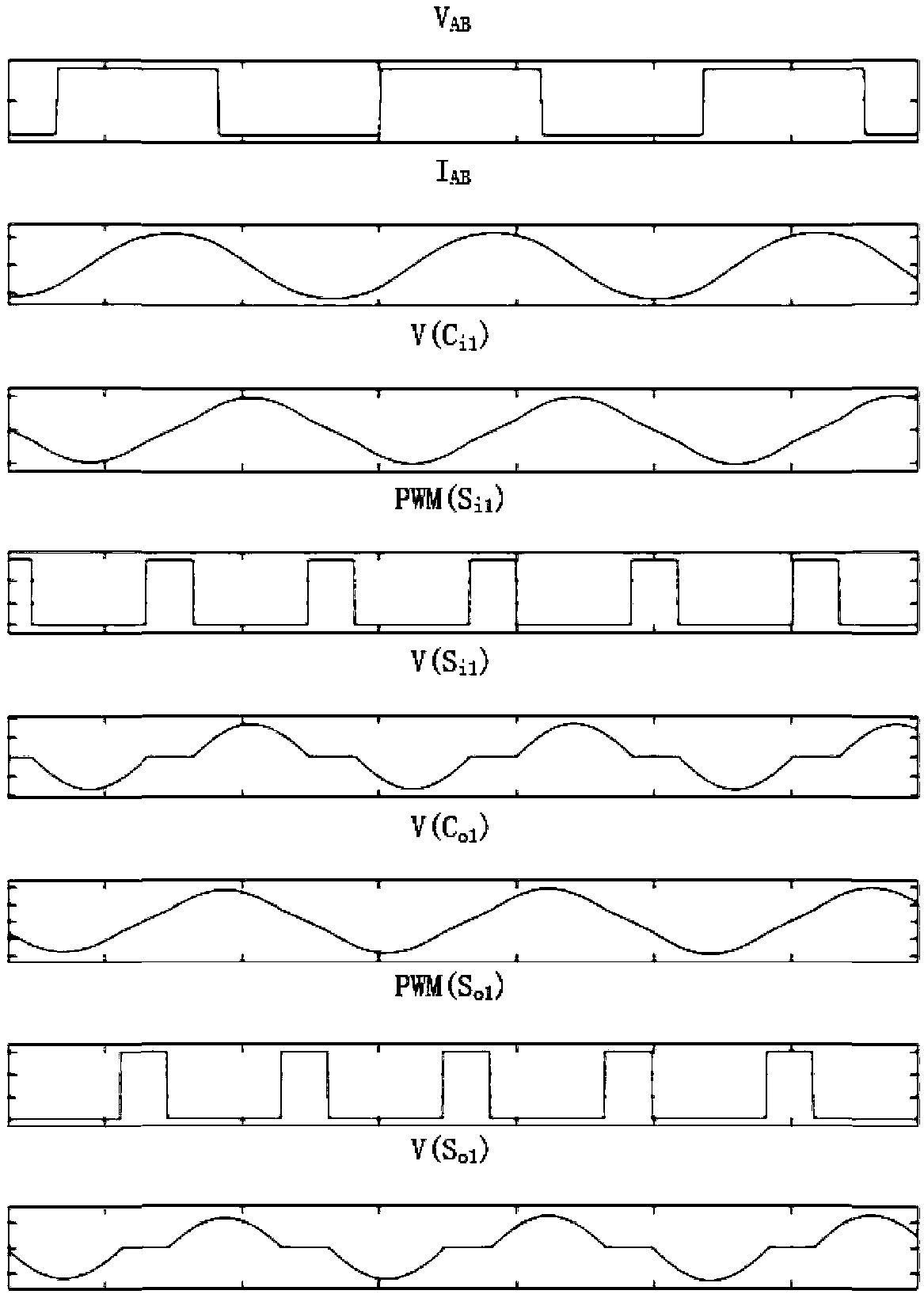
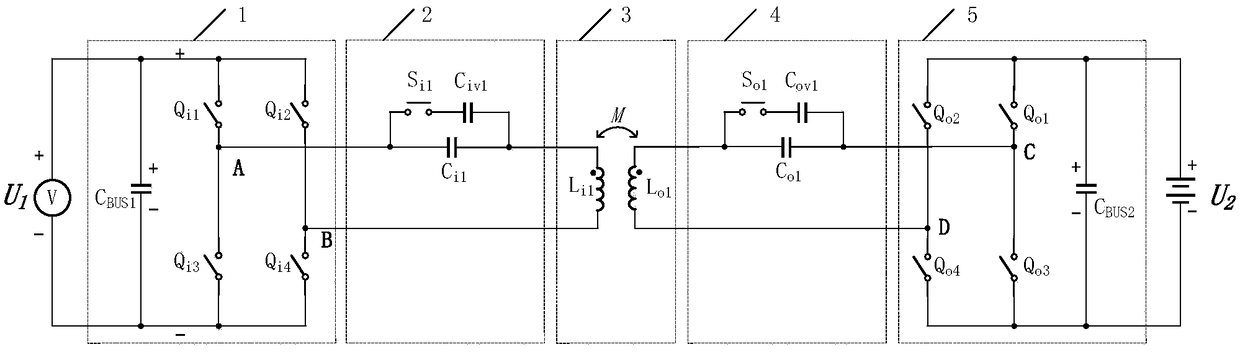
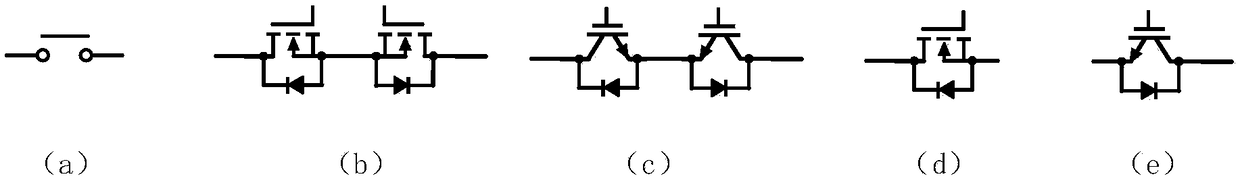
[0063] A circuit topology suitable for a two-way near-field power transmission system, in this embodiment, the first compensation switch S i1 and the second compensation switch S o1 The specific implementation mode is a single MOSFET, and the circuit topology of this embodiment is as follows Figure 9 shown.
[0064] The first compensation switch S i1 and the second control switch S o1 The rising edge of the control PWM is related to the output voltage of the full-bridge inverter V AB rising edge aligned, the first compensation switch S i1 and the second control switch S o1 The control PWM signal is the same, the frequency of the control PWM is the same as the system operating frequency, and the simulation waveform when the high output voltage (400V) is obtained by adjusting the duty cycle of the control PWM is as follows Figure 10 As shown, the simulation waveform obtained by adjusting the duty cycle of the control PWM to obtain a low output voltage (260V) is as follow...
Embodiment 2
[0067] A circuit topology suitable for a two-way near-field power transmission system, in this embodiment, the first compensation switch S i1 and the second compensation switch S o1 The specific implementation mode is two MOSFETs connected in series, and the circuit topology of this embodiment is as follows Figure 12 shown.
[0068] The first compensation switch S i1 The positive pulse center of the control PWM and the capacitor C in the resonant network i1 The zero-crossing points of the voltages at both ends are aligned, the frequency of the control PWM is twice the operating frequency of the system, and the second compensation switch S o1 The positive pulse center of the control PWM and the capacitor C in the resonant network o1 The zero-crossing points of the voltage at both ends are aligned, and the frequency of the control PWM is twice the system operating frequency. By adjusting the duty cycle of the control PWM, the simulation waveform obtained when the high outpu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com