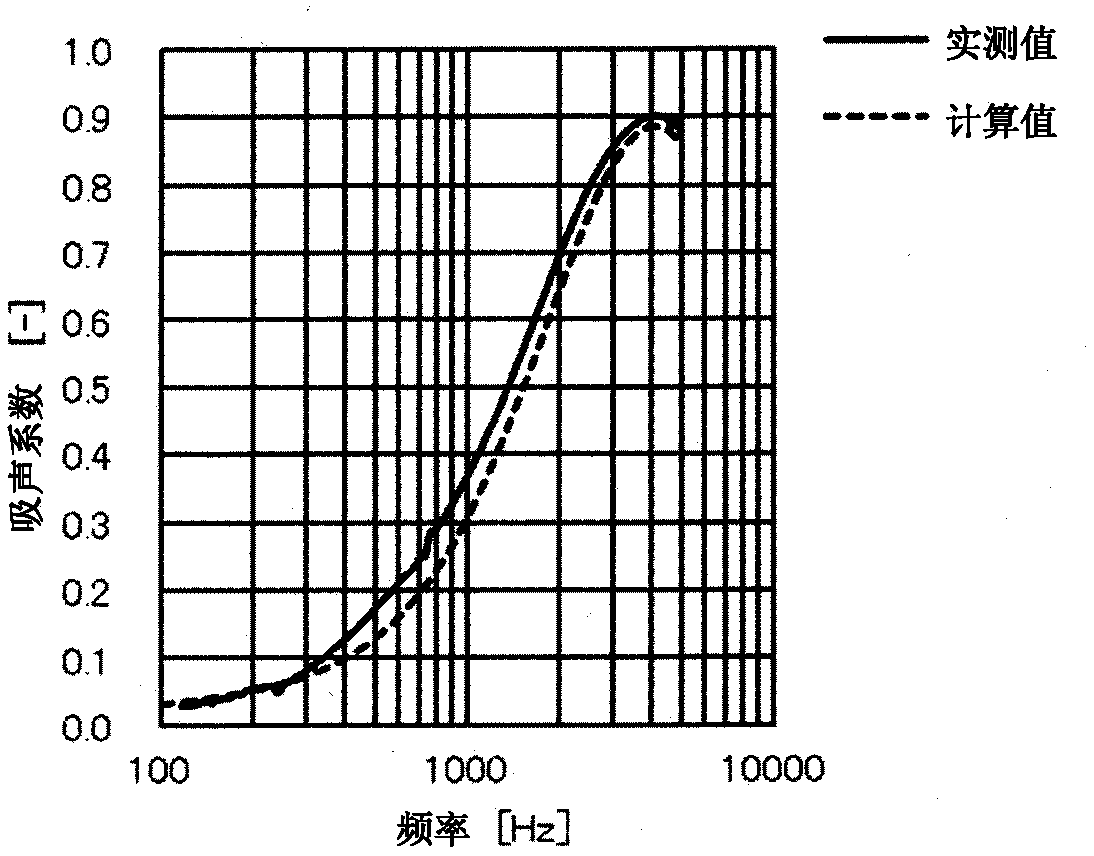
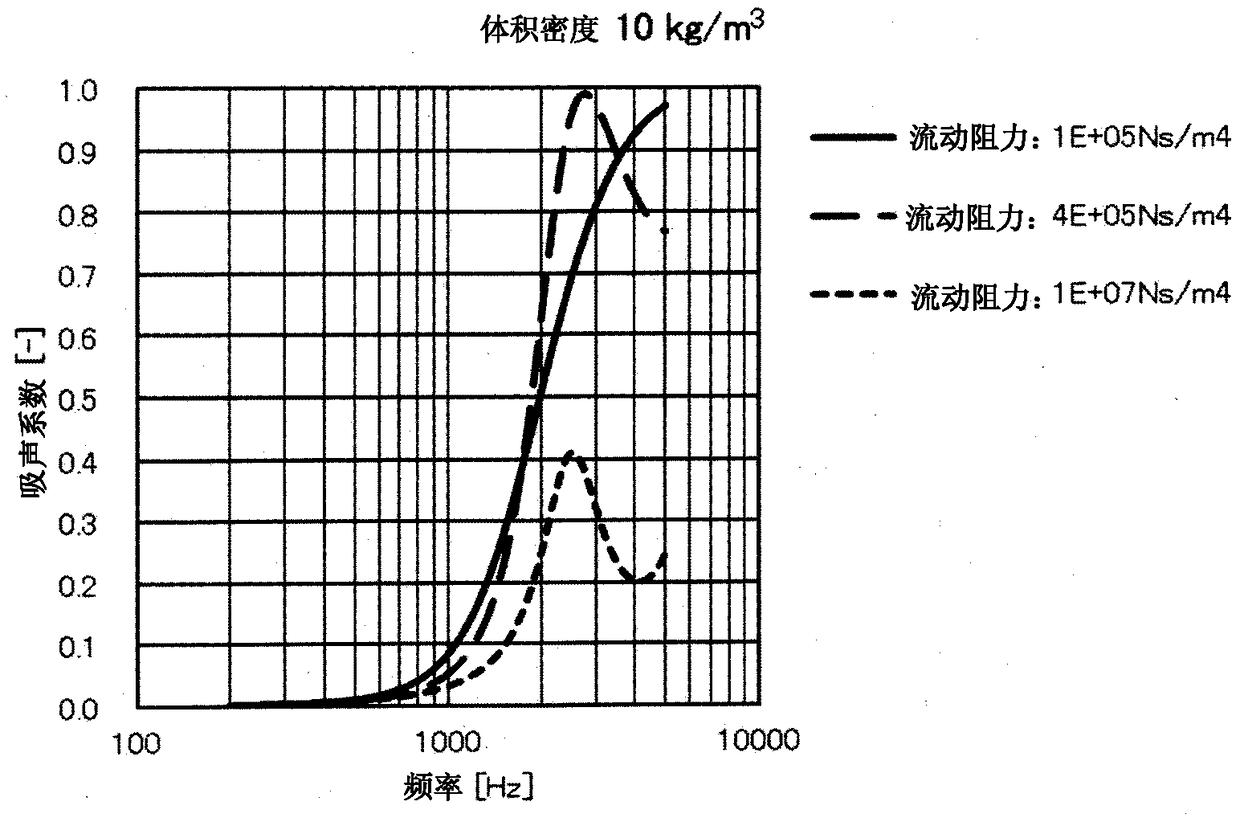
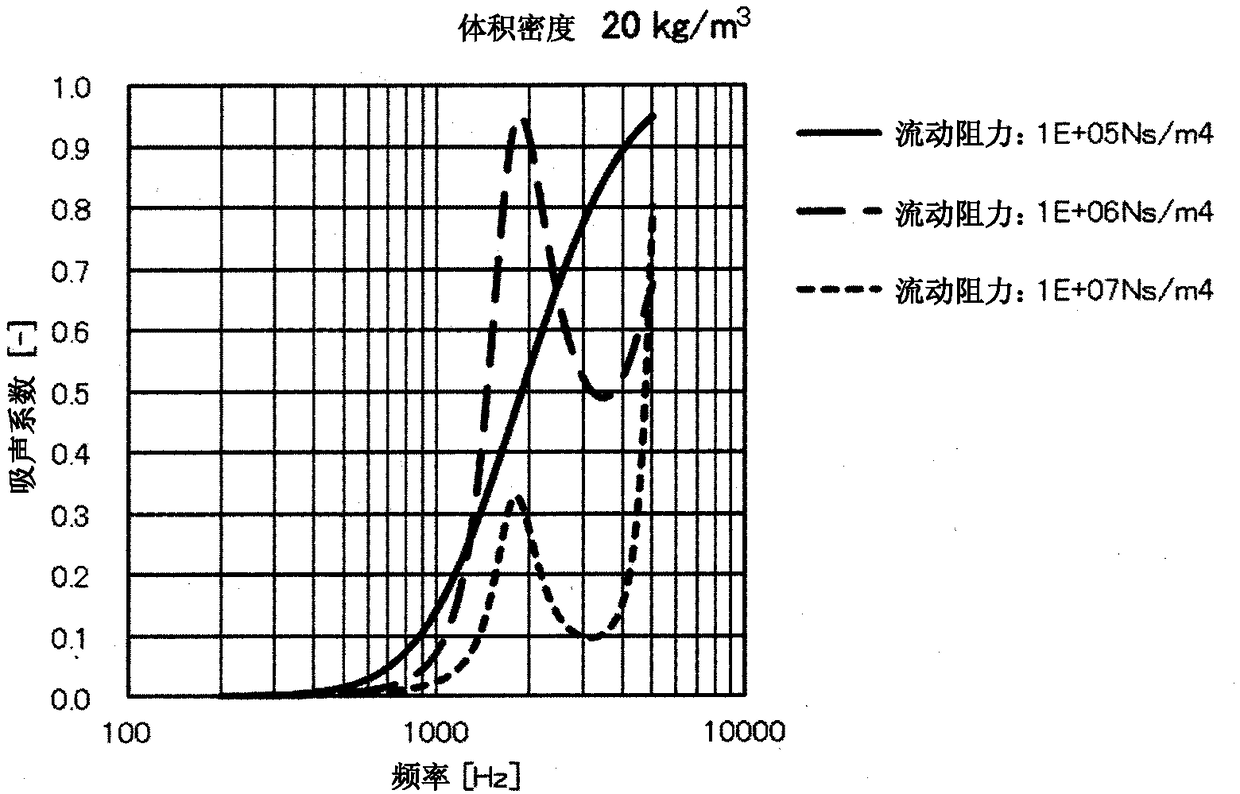
Soundproofing material
A technology of sound insulation materials and porous bodies, applied in the field of sound insulation materials, can solve the problems of poor processability, poor dispersibility, poor flocculation, hard resilience of foam, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] The microglass fibers (average fiber diameter: 0.4 μm) were dispersed in ammonia water of pH 10 so that the concentration became 0.5% by weight, and the electrokinetic potential of the fiber surface was adjusted to -55 mv for treatment. Next, add 0.5 parts by weight of cationic surfactant (lauryl trimethyl ammonium chloride (trade name: Kohtamin 24P, manufactured by Kao Co., Ltd.)) based on 100 parts by weight of fibers in terms of the solid content of the surfactant. , And stir and mix. At this time, air is introduced to make it foam. The obtained wet foam was dried and treated at 450°C for 1 hour using an electric furnace to remove the surfactant adhering to the foam. Next, the coupling agent is supplied. The coupling agent uses methyltriethoxysilane (trade name: KBE-13, manufactured by Shin-Etsu Chemical Industry). Add the silane coupling agent to a closed container and heat it to about 160°C to generate vapor of the silane coupling agent. The foam is treated for 4...
Embodiment 2
[0152] Disperse ceramic fibers (approximately 50% by weight of alumina and about 50% by weight of silica) (average fiber diameter of 2.0μm) in ammonia water at pH 10 so that the concentration becomes 2% by weight, so that the electrokinetic potential on the fiber surface becomes -32mv . Next, 0.5 parts by weight of a cationic surfactant (lauryl trimethyl ammonium chloride (trade name: Kohtamin 24P, Kao Co., Ltd.) is added to 100 parts by weight of the fiber in terms of the solid content of the surfactant. Manufacturing)), and stir and mix. At this time, air is introduced to make it foam. In the same manner as in Example 1, the obtained foam was subjected to drying, firing, and coupling agent supply treatments. The average equivalent circle diameter of the pore diameter of the foam when it is not compressed at normal temperature is about 0.53 mm. In the same manner as in Example 1, the obtained foam was evaluated. The results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0154] Except that an anionic surfactant (sodium laurylbenzene sulfonate (trade name: NEOPELEX G65, manufactured by Kao Co., Ltd.)) was used instead of the cationic surfactant in Example 1, the same procedure as in Example 1 was carried out to produce hair Foam and evaluate. The results are shown in Table 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com