Method for preparing bean pulp through bacterium enzyme cooperative fermentation
A technology for co-fermenting and fermenting soybean meal, applied in the direction of bacteria, Lactobacillus, food science, etc. used in food preparation, can solve problems such as the general effect of degrading antigenic proteins, affecting animal feed intake, affecting product palatability, etc. palatability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
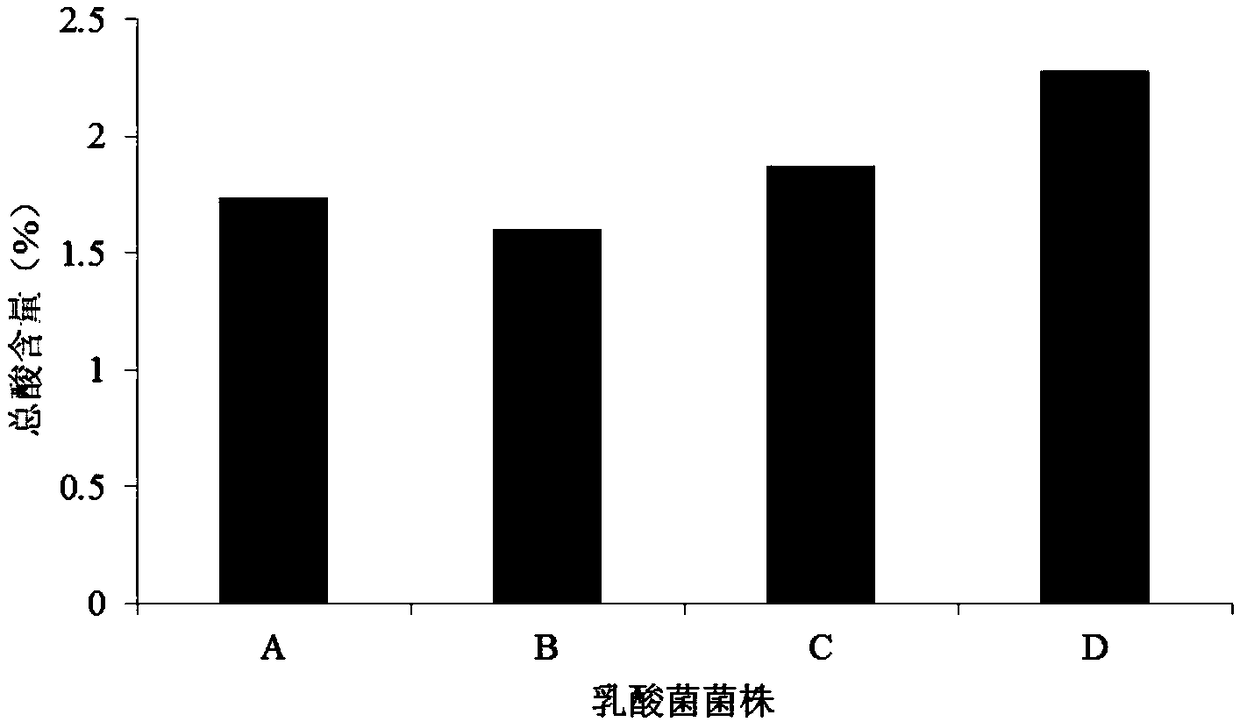
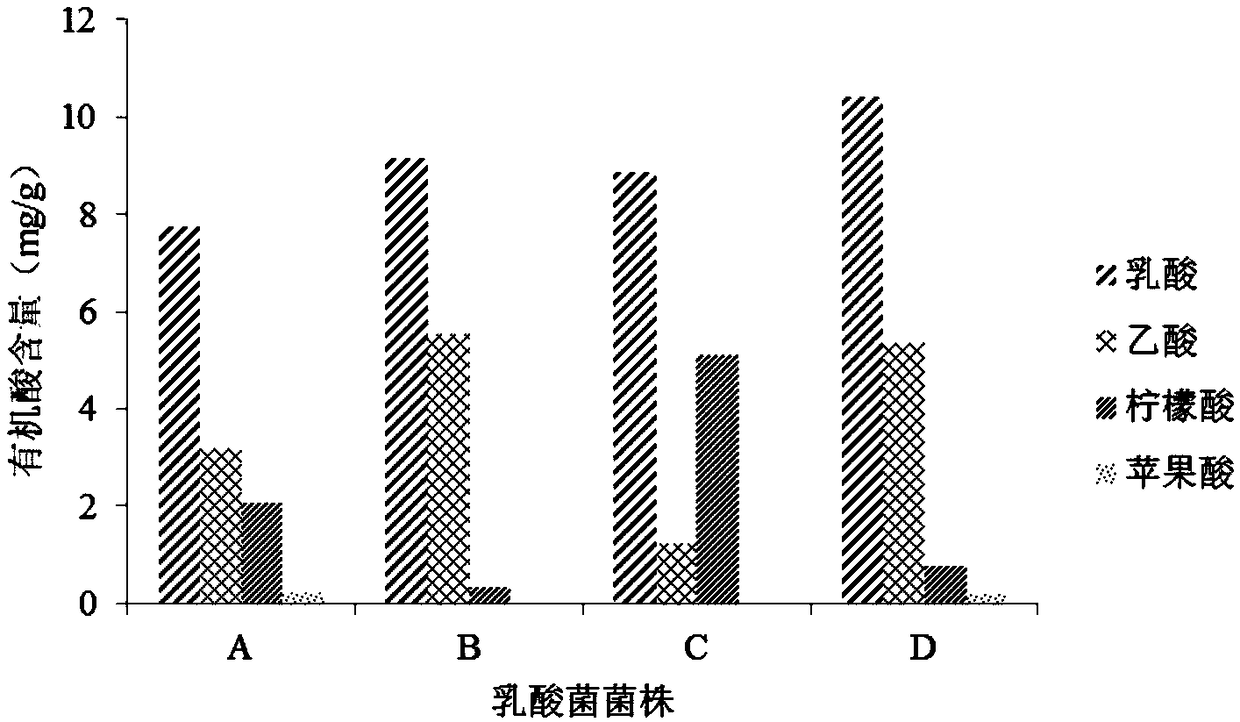
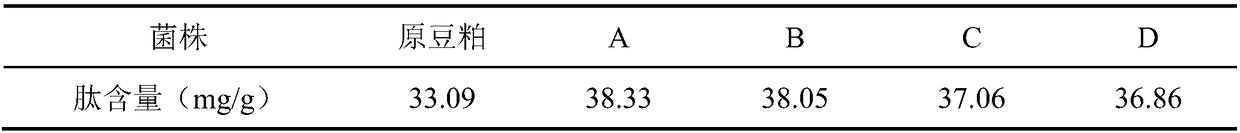
[0025] Embodiment 1: the selection of bacterial enzyme synergistic fermentation bacterial strain
[0026] Lactobacillus paracasei DY2, Lactobacillus rhamnosus DY4, Pediococcus lactis DY5 and Lactobacillus plantarum JUN-DY-6 were used as candidate strains for soybean meal fermentation. Among them, Lactobacillus paracasei DY2 has been disclosed in the patent application whose publication number is CN107227280A; Lactobacillus rhamnosus DY4 has been disclosed in the patent application whose publication number is CN107217022A; Pediococcus lactis DY5 has been disclosed in the patent application whose publication number is CN107227279A in public.
[0027] 1. Activation of the sample: inoculate different lactic acid bacteria into the MRS medium according to the inoculum amount of 1%, activate at 37°C for 24 hours, activate 2-3 generations in the same way, and continue to culture in the MRS medium to obtain the bacterial liquid of the lactic acid bacteria.
[0028] 2. Screening of fer...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: the selection of bacterial enzyme synergistic fermentation protease
[0034] Air-dried soybean meal, water, molasses, and different proteases are mixed according to: the amount of water added accounts for 50% of the total mass of soybean meal, the amount of molasses stock solution accounts for 3% of the total mass of soybean meal, and the amount of protease added is 1000U / g. Put it in a sterile ziplock bag, seal it and put it in a 37°C incubator to ferment for 48 hours. After the end, the sample is dried at 55°C, pulverized, and then the small peptide content is determined.
[0035] The results are shown in Table 2. After comparing the small peptides after enzymatic hydrolysis with different proteases, it was found that the content of small peptides was the highest after enzymatic hydrolysis by neutral protease, showing its excellent enzymatic hydrolysis ability, so neutral protease was selected.
[0036] Table 2 Peptide content of soybean meal hydrolyzed ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: bacterial enzyme synergistic fermentation process under different inoculum sizes
[0039] The addition of control water, molasses, and protease is the same as embodiment 2 (the addition of water accounts for 50% of the total mass of soybean meal, and molasses accounts for 3% of the total mass of soybean meal, and the addition of protease is 1500U / g), respectively inoculate 1 %, 2%, 3%, 4%, 5% of the bacterial solution by mass, the concentration of the bacterial solution is 1×10 9 CFU / mL, fermented at 37°C for 48h, after the end, the samples were dried and pulverized at 55°C to determine the content of small peptides. The results are shown in Table 3. When the inoculum amount exceeds 2%, the peptide content is higher than 100.07mg / g.
[0040] Table 3 Effect of different inoculation amounts on the peptide content of fermented soybean meal
[0041]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com