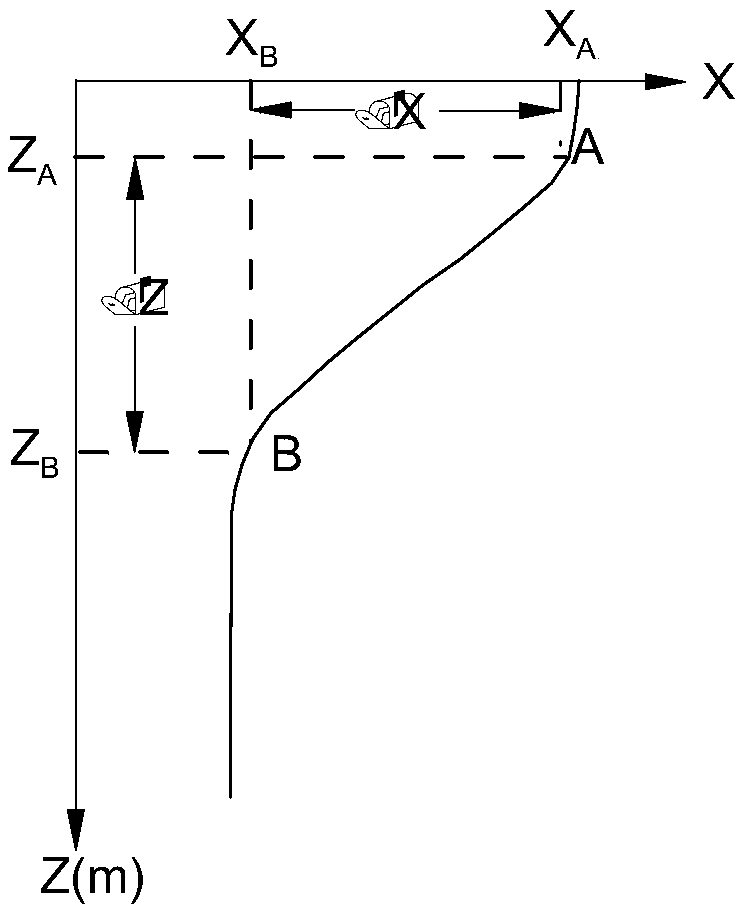
Multi-segment least-square fitting method for calculating the eigenvalues of oceanic meteoroid
A least-squares, multi-line segment technology, applied in the field of marine scientific research and application, can solve the problems of discontinuity, not necessarily continuous, and poor automatic recognition ability of the layer, so as to achieve a wide range of applicable sea areas and a high automatic recognition rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
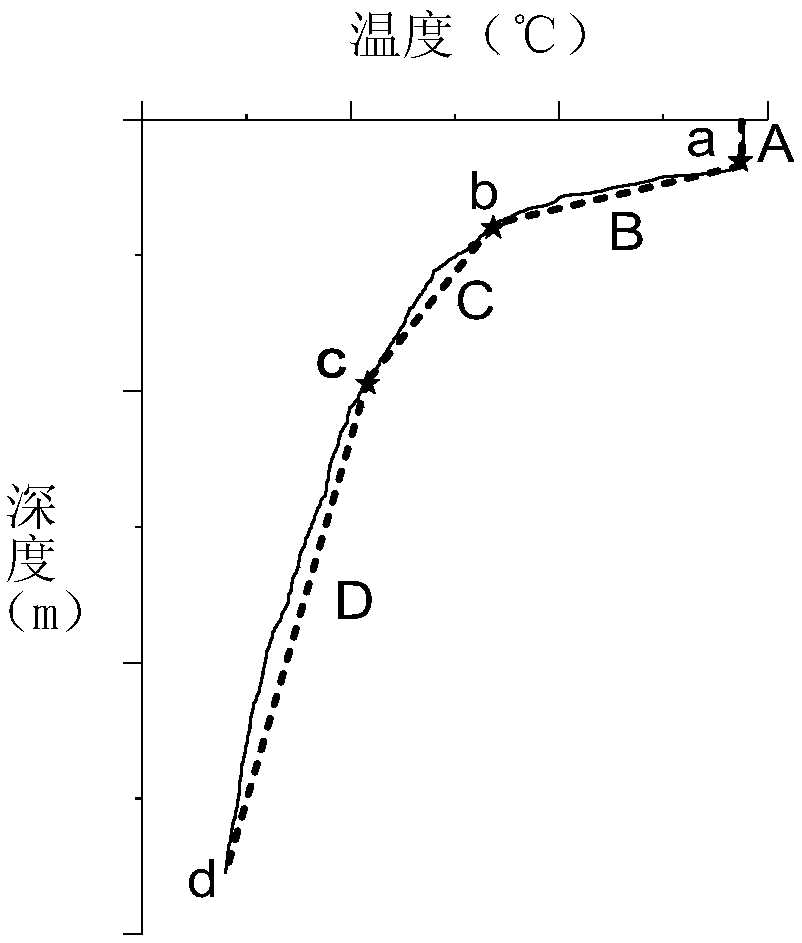
[0049] Figure 4 It is a typical deep-sea temperature profile using three methods (Ⅰ)(Ⅱ)(Ⅲ) to determine the upper and lower boundary points of the cline. Figure 4 (I) is a schematic diagram of the calculation results using the vertical gradient method; Figure 4 (II) is a schematic diagram of calculation results by the pseudo-step function approximation method; Figure 4 (Ⅲ) is a schematic diagram of the calculation results by the multi-line segment least squares fitting method.
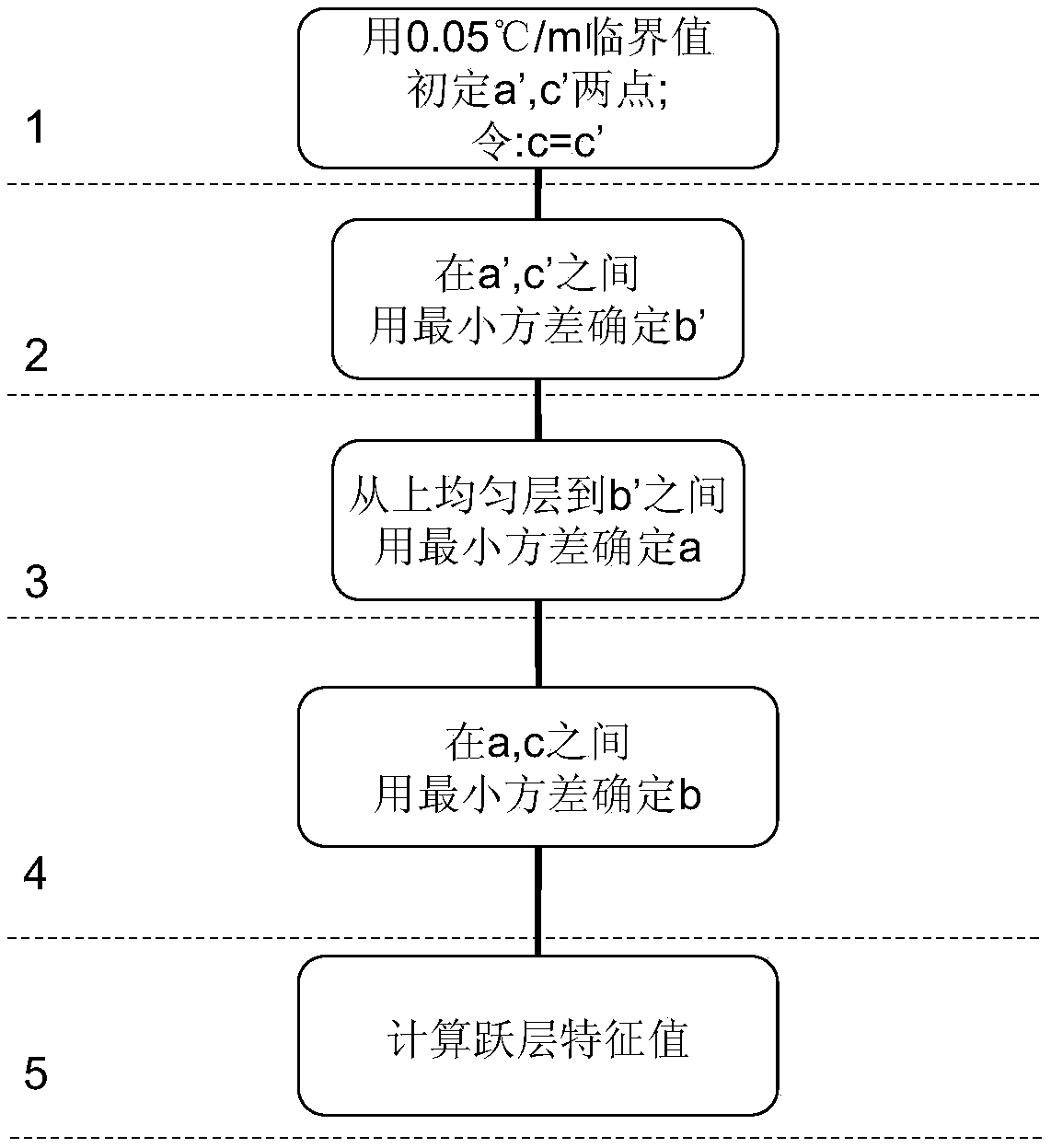
[0050] The specific steps of calculating the eigenvalues of the deep-sea temperature profile cline with the multi-line segment least squares fitting method of the present invention are as follows (flow process is shown in image 3 ):
[0051] 1. In this embodiment, the temperature profile data starts from 1m, the maximum observation depth is 1110m, the depth interval from the sea surface to the seabed is 1m, and the total number of data layers N=1110. Let the depth and temperature of each lay...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of calculating the upper and lower boundary points of the cline by three methods (I), (II) and (III) in a typical temperature profile in the slope break area of the continental shelf. Figure 5 (I) is a schematic diagram of the calculation results using the vertical gradient method; Figure 5(II) is a schematic diagram of calculation results by the pseudo-step function approximation method; Figure 5 (Ⅲ) is a schematic diagram of calculation results using the multi-line segment least squares fitting method of the present invention.
[0077] The steps to calculate the eigenvalues of the thermocline in the temperature profile of the continental shelf slope break sea area using the multi-line segment least squares fitting method are as follows (for the process, see image 3 ):
[0078] 1. The temperature profile of this embodiment starts from 1m, the maximum observation depth is 178m, the depth interval from the sea surface to the...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of calculating the upper and lower boundary points of the cline by the three methods (I), (II) and (III) of the temperature profile in a typical shallow sea area. Figure 6 (I) is a schematic diagram of the calculation results using the vertical gradient method; Figure 6 (II) is a schematic diagram of calculation results by the pseudo-step function approximation method; Figure 6 (Ⅲ) is a schematic diagram of calculation results by multi-line segment least squares fitting method;
[0103] The steps to calculate the eigenvalues of the shallow sea temperature profile using the multi-line segment least squares fitting method are as follows (for the flow chart, see image 3 ):
[0104] 1. The temperature profile of this embodiment starts from 1m, the maximum observation depth is 48m, the depth interval from the sea surface to the seabed is 1m, and the number of data layers in total is N=48. The depth and temperature of each layer a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com