Tunnel bottom structure of high water head water enriched tunnel and water draining method
A water-rich tunnel and high water head technology, applied in drainage, earthwork drilling, safety devices, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to ensure the effective operation of the drainage system, potential safety hazards in long-term stability, uplift and cracking of the inverted arch structure, etc., to achieve Simple construction, little impact on the construction period, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
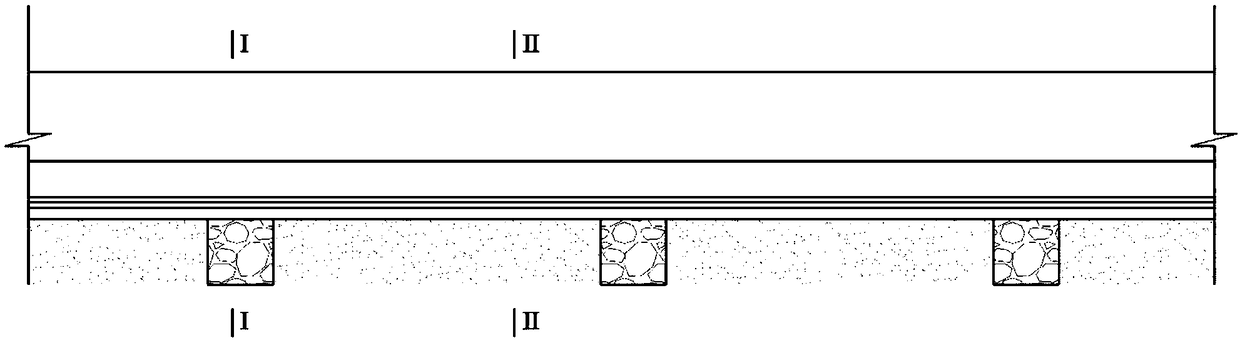
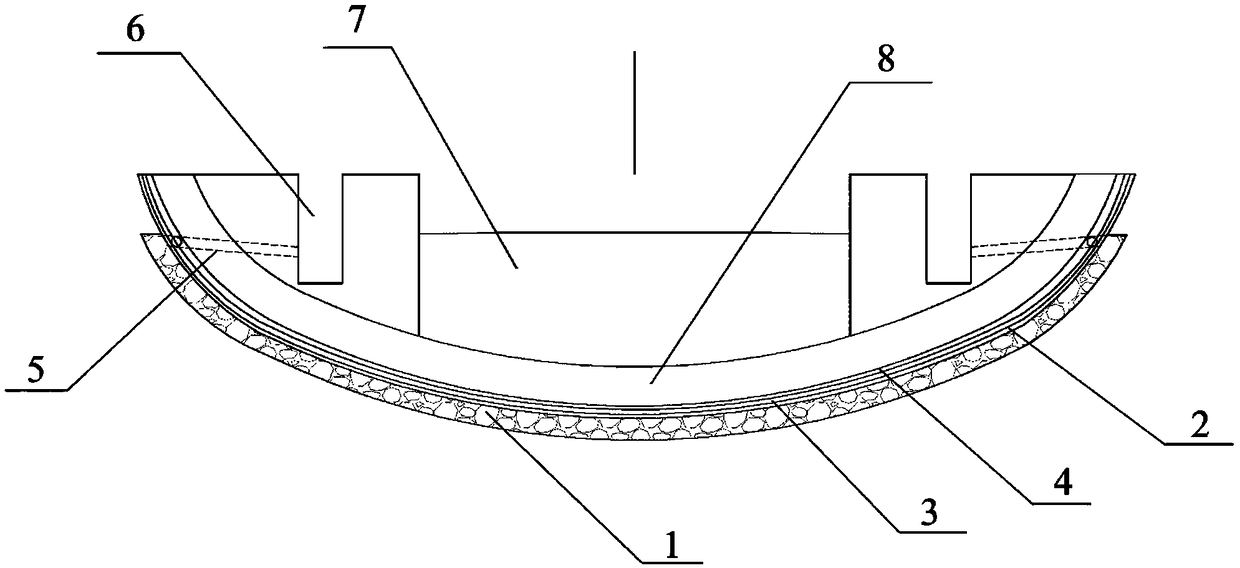
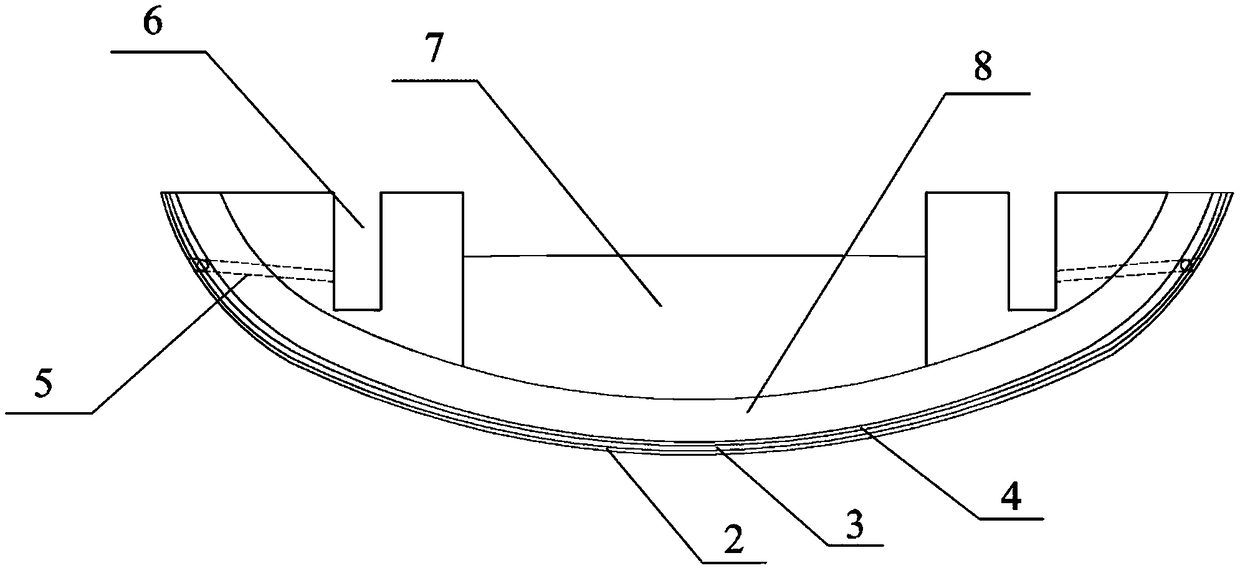
[0028] A tunnel bottom structure of a high-head water-rich tunnel, comprising a drainage groove 1 arranged along the tunnel ring in the surrounding rock of the tunnel bottom, the drainage groove 1 is connected to the drainage ditch 6; the drainage groove 1 is filled with permeable materials; the inverted arch surface of the tunnel bottom The inner side of the drainage tank 1 is the primary support 2 made of concrete; the non-woven fabric 3 and the waterproof layer 4 are sequentially arranged from the surface of the primary support 2 to the inverted arch 8 .
[0029] The drainage groove 1 extends to the foot of the wall, and communicates with the drainage ditch 6 through the drain hole 5 arranged at the foot of the wall of the drainage groove 1 .
[0030] The cross-section of the drainage groove 1 is a square structure; multiple drainage grooves...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com