Novel fabric and novel leather product in which collagen fiber bundle forms network structure
A technology of collagen fiber bundles and network structure, which is applied in the chemical post-treatment of fibers, fabrics, fiber treatment, etc., can solve the problems of animal leather not adapting to water washing, rawhide hardening, and limited fiber length.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
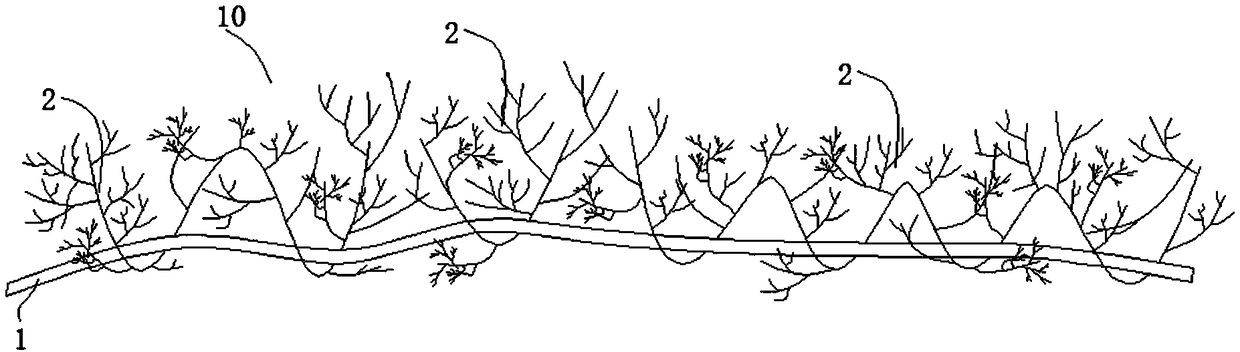
[0055] Such as figure 1 As shown, the new type of fabric in which the collagen fiber bundles form a network structure includes a bottom yarn weaving layer 1 and collagen fiber bundles 2 .
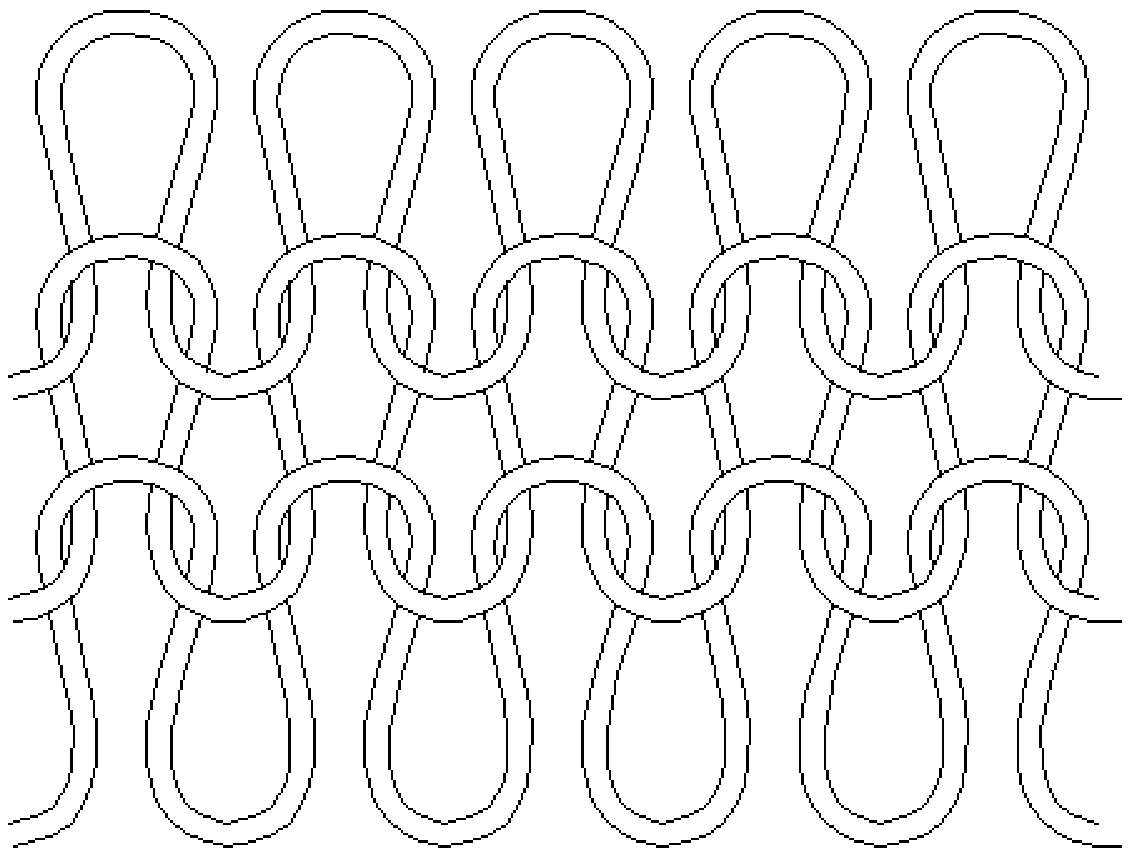
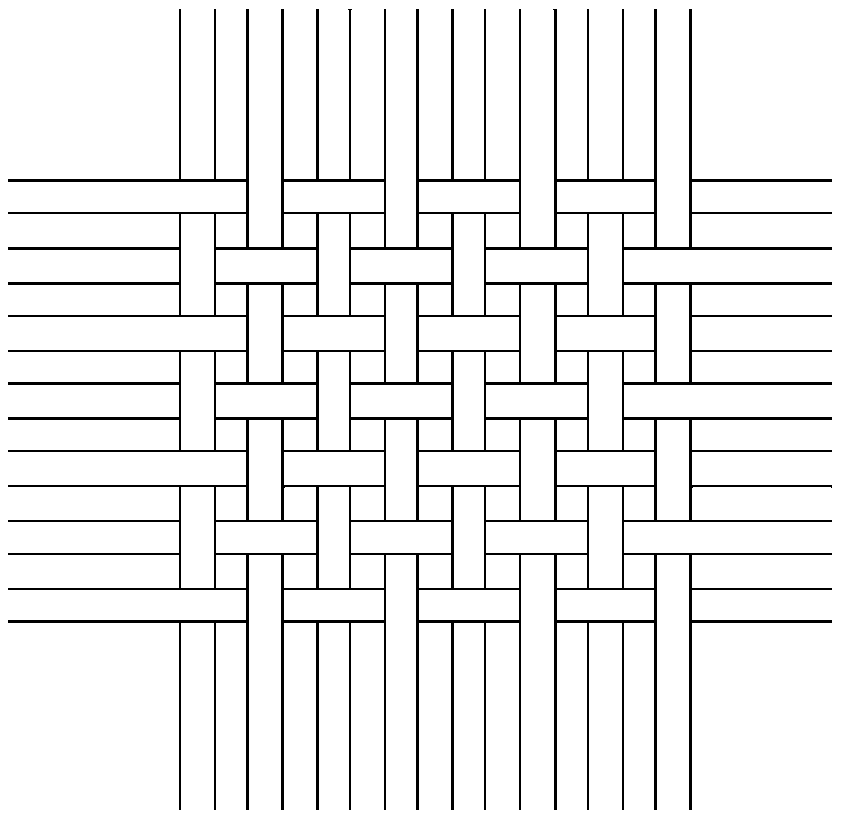
[0056] Such as figure 2 As shown, the base yarn braided layer 1 can be a knitted braided layer, or can be as image 3 Woven braid shown. The base yarn weaving layer can be woven by filaments, or by short fiber yarns, or mixed by long filaments and short fiber yarns.
[0057] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the collagen fiber bundle 2 is composed of a collagen fiber bundle main body 21 and branches 22 . The branch 22 is a step-by-step branch formed on the main body of the collagen fiber bundle. The step-by-step branch means that there are secondary branches from the main branch, and sub-branches are formed on the secondary branch, and so on.
[0058] Such as figure 1 and Figure 5 As shown, the collagen fiber bundles 2 are inserted into the bottom yarn braided layer 1, and the bottom yar...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the novel fabric formed by the collagen fiber bundle yarn includes a ground yarn braided layer 1 .
[0069] Such as figure 2 As shown, the base yarn braided layer 1 can be a knitted braided layer, or can be as image 3 Woven braid shown. The base yarn weaving layer can be woven by filaments, or by short fiber yarns, or mixed by long filaments and short fiber yarns.
[0070] Collagen fiber bundle yarns 20 are sheathed on the bottom yarns in the bottom yarn braiding layer 1 , and the collagen fiber bundle yarns protruding from the surface of the bottom yarn braiding layer 1 form a loose wool network structure 10 .
[0071] The collagen fiber bundle yarn is made by twisting the collagen fiber bundle or other processes. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the collagen fiber bundle 2 is composed of a collagen fiber bundle main body 21 and branches 22 . The branch 22 is a step-by-step branch formed on the main body of the collagen fiber bundle. The ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the novel fabric formed by the collagen fiber bundle yarn includes a ground yarn braided layer 1 .
[0081] Such as figure 2 As shown, the base yarn braided layer 1 can be a knitted braided layer, or can be as image 3 Woven braid shown. The base yarn weaving layer can be woven by filaments, or by short fiber yarns, or mixed by long filaments and short fiber yarns.
[0082] Collagen fiber bundle yarns 20 are inserted on the bottom yarn in the bottom yarn braided layer 1, and the collagen fiber bundle yarns protruding from the surface of the bottom yarn braided layer 1 form a network structure 200 of collagen fiber bundles and their branches intertwined with each other. .
[0083] The collagen fiber bundle yarn is made by twisting the collagen fiber bundle or other processes. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the collagen fiber bundle 2 is composed of a collagen fiber bundle main body 21 and branches 22 . The branch 22 is a step-by-step bran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com