Preparation method of MOFs polymer compound electrode and compound electrode and use method thereof
A composite electrode and polymer technology, applied in the field of electrodes, can solve problems such as poor compatibility and electrode surface shedding, and achieve the effects of simple production, increased adsorption rate, and improved catalytic oxidation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
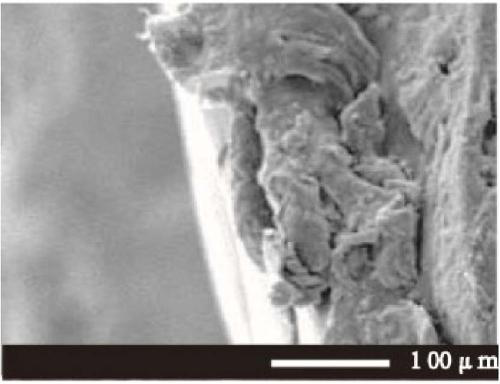
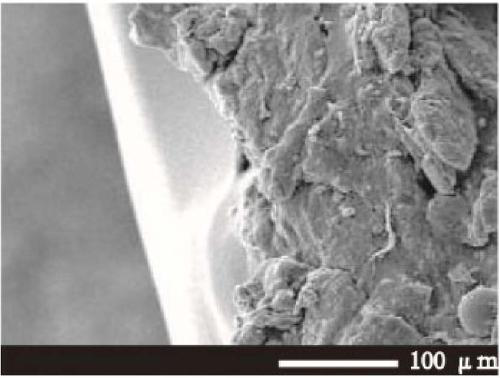
[0044] Take 0.1g of MIL-53(Al), 1g of PTFE, and 2g of carbon black in a 10mL volumetric flask, and pour it into a beaker after constant volume with DMF, stir at 140rpm for 15 minutes, take 0.3mL of the mixed solution and use a metal die to uniformly Cover it on a 4cm×1cm titanium electrode and dry it at 38°C. The section of the finished composite electrode material ( figure 2 ) and surface ( Figure 7 ) for scanning electron microscope test, and with the section of pure titanium electrode ( figure 1 ) and surface ( Figure 6 )comparing. Compared with the pure titanium electrode, the surface of the composite electrode material in Example 1 has an obvious MOFs crystal structure, and it can be seen that there is an additional modification layer in the cross section, which can confirm that the composite electrode material was successfully prepared.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Take 0.3g of MIL-100(Fe), 1.5g of PVDF, and 1.5g of graphite in a 10mL volumetric flask, and pour it into a beaker after constant volume with acetonitrile, stir at 200rpm for 26 minutes, take 1.6mL of the mixed solution and use a metal die Cover evenly on a 4cm×4cm titanium electrode, and dry at 55°C. The section of the finished composite electrode material ( image 3 ) and surface ( Figure 8 ) for scanning electron microscope test, and with the section of pure titanium electrode ( figure 1 ) and surface ( Figure 6 )comparing. Compared with the pure titanium electrode, the surface of the composite electrode material in Example 2 has an obvious MOFs crystal structure, and it can be seen that there is an increased modification layer in the cross section, which can confirm that the composite electrode material was successfully prepared.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Take 0.4g of MIL-101(Cr), 0.5g of PE, and 0.5g of graphene in a 10mL volumetric flask, pour it into a beaker after constant volume with chloroform, stir at 240rpm for 48 minutes, and take 2.5mL of the mixed solution with metal The stamper is evenly covered on the 4cm×10cm titanium electrode, and dried at 66°C. The section of the finished composite electrode material ( Figure 4 ) and surface ( Figure 9 ) for scanning electron microscope test, and with the section of pure titanium electrode ( figure 1 ) and surface ( Figure 6 )comparing. Compared with the pure titanium electrode, the surface of the composite electrode material in Example 3 has obvious MOFs crystal structure, and it can be seen from the cross-section that there is an increased modification layer, which can confirm that the composite electrode material was successfully prepared.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com