Crop slow-release fertilizer prepared by using edible fungus residue
A slow-release fertilizer and edible fungus technology, applied in fertilizers, applications, nitrogen fertilizers, etc. made of biological waste, can solve problems such as affecting the normal use of land, reducing land quality, and being difficult to degrade, and achieving extended retention time and strong integrity. , The effect of not easy to loosen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
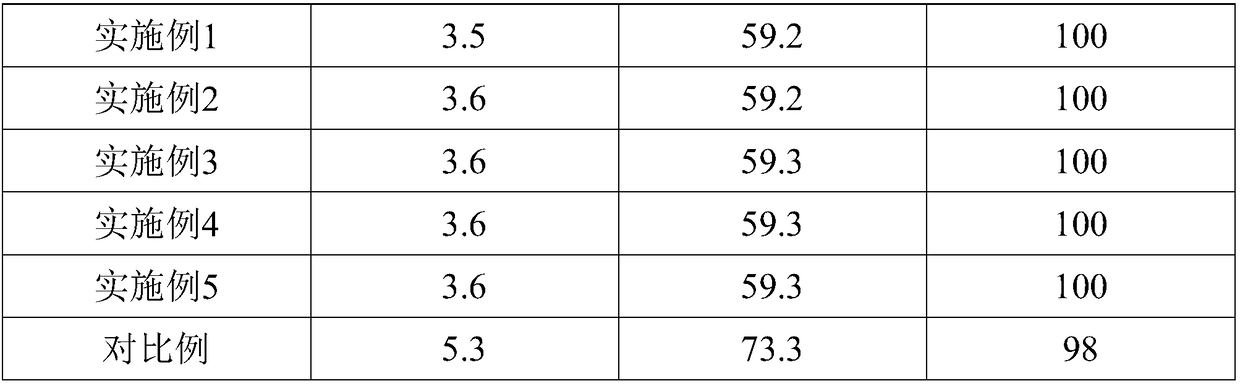
Embodiment 1
[0025] A slow-release fertilizer for crops prepared from edible fungus slag, comprising a slow-release fertilizer matrix, a slow-release fertilizer coating and an adhesive, the slow-release fertilizer matrix is composed of the following raw materials by weight: bauxite modified edible fungi 200 parts of bacteria residue, 120 parts of urea, 70 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 35 parts of ammonium chloride, 15 parts of ammonium sulfate, 8 parts of magnesium aluminosilicate, 40 parts of amino acid compound, 20 parts of potassium sulfate, 5 parts of ferric chloride 30 parts of soybean meal, 3 parts of fulvic acid;
[0026] The slow-release fertilizer coating is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50 parts of polylactic acid, 30 parts of starch, 30 parts of bamboo fiber composite polyhydroxybutyrate, 25 parts of polypropylene, and 6 parts of propylene glycol methyl ether acetate;
[0027] The binder is clay.
Embodiment 2
[0029] A slow-release fertilizer for crops prepared from edible fungus slag, comprising a slow-release fertilizer matrix, a slow-release fertilizer coating and an adhesive, the slow-release fertilizer matrix is composed of the following raw materials by weight: bauxite modified edible fungi 300 parts of bacteria residue, 180 parts of urea, 100 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 55 parts of ammonium chloride, 35 parts of ammonium sulfate, 16 parts of magnesium aluminosilicate, 80 parts of amino acid compound, 45 parts of potassium sulfate, 9 parts of ferric chloride 50 parts of soybean meal, 7 parts of fulvic acid;
[0030] The slow-release fertilizer coating is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 80 parts of polylactic acid, 40 parts of starch, 50 parts of bamboo fiber composite polyhydroxybutyrate, 30 parts of polypropylene, and 8 parts of propylene glycol methyl ether acetate;
[0031] The binder is clay.
[0032] The preparation method of th...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A slow-release fertilizer for crops prepared from edible fungus slag, comprising a slow-release fertilizer matrix, a slow-release fertilizer coating and an adhesive, the slow-release fertilizer matrix is composed of the following raw materials by weight: bauxite modified edible fungi 220 parts of bacteria residue, 140 parts of urea, 80 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 40 parts of ammonium chloride, 20 parts of ammonium sulfate, 10 parts of magnesium aluminosilicate, 50 parts of amino acid compound, 25 parts of potassium sulfate, 6 parts of ferric chloride 35 parts of soybean meal, 4 parts of fulvic acid;
[0038] The slow-release fertilizer coating is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 60 parts of polylactic acid, 35 parts of starch, 40 parts of bamboo fiber composite polyhydroxybutyrate, 28 parts of polypropylene, and 7 parts of propylene glycol methyl ether acetate;
[0039] The binder is clay.
[0040] The amino acid compounding ag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com