Synthetic method of methyl hypophosphorous acid monoalkyl ester
A technology of monoalkyl methyl hypophosphite and methyl hypophosphorous acid is applied in the field of synthesis of monoalkyl methyl hypophosphite to achieve the effect of less control points
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
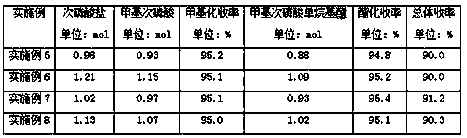
[0033] First, 100 g of ammonium hypophosphite (1.20 mol) and 253 mL of hexamethyldisilazane (1.20 mol) were mixed, stirred at 110 °C for 2 h under nitrogen protection, then cooled to 0 °C, and 1200 mL of new Distill dichloromethane, then add 60.6 g of methyl chloride (1.20 mol), stir at room temperature for 12 hours, filter to remove the yellow precipitate, first distill the filtrate under normal pressure to recover the solvent dichloromethane, then distill under reduced pressure to recover hexamethyldisilazide Alkanes, the distillation bottom liquid is 91.2 g methyl hypophosphorous acid (1.14 mol).
[0034] Add 91.2 g (1.14 mol) of methyl hypophosphorous acid and 313 mL (3.42 mol) of n-butanol into a 1 L three-neck flask, and then add 6.0 g of anhydrous CuSO 4 , stirred and reacted at 110-120°C, during the reaction process, the water produced by the reaction was continuously separated out, and after 8 hours, the reaction solution was rectified under reduced pressure to obtain...
Embodiment 2
[0036] First, mix 100 g of sodium hypophosphite (1.14 mol) and 105 mL of piperidine (1.14 mol), under nitrogen protection, stir at 110 °C for 2 h, then cool down to 0 °C, add 1200 mL of freshly distilled toluene to the reaction solution, and then add 57.6 g of methyl chloride (1.14 mol), stirred at room temperature for 12 h, filtered to remove the white precipitate, and the filtrate was distilled at normal pressure to recover the solvent dichloromethane, then distilled under reduced pressure to recover piperidine, and the distillation bottom liquid was 86.4 g of methyl methine Phosphoric acid (1.08 mol).
[0037]Add 86.4 g (1.08 mol) of methyl hypophosphorous acid and 297 mL (3.24 mol) of n-butanol into a 1 L three-necked flask, then add 3.0 g of strong acidic ion exchange resin, stir and react at 110-120 °C, and keep stirring during the reaction process. The water produced by the reaction was separated, and after 8 h, the reaction liquid was rectified under reduced pressure t...
Embodiment 3
[0039] First, mix 100 g of potassium hypophosphite (0.96 mol) and 78 mL of pyridine (0.96 mol), under nitrogen protection, stir at 110 °C for 2 h, then cool down to 0 °C, add 1200 mL of freshly distilled cyclohexane to the reaction solution, and then Add 48.5 g of methyl chloride (0.96 mol), stir at room temperature for 12 h, and filter to remove the white precipitate. The filtrate is distilled at normal pressure to recover the solvent methylene chloride, and then distilled under reduced pressure to recover pyridine. The bottom liquid of the distillation is 72.8 g of methyl chloride. Phosphoric acid (0.91 mol).
[0040] Add 72.8 g (0.91 mol) of methyl hypophosphorous acid and 251 mL (2.73 mol) of n-butanol into a 1 L three-necked flask, then add 6.0 g of ZnO, and stir the reaction at 110-120 °C. After 8 hours, the reaction solution was rectified under reduced pressure to obtain 117.3 g of mono-n-butyl methylphosphinate (0.86 mol), and recovered n-butanol (163 mL, 1.78 mol).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com