A method for dynamic monitoring of urban traffic emission pollution based on taxi gps data
A GPS data and dynamic monitoring technology, which is applied in the traffic control system of road vehicles, traffic flow detection, traffic control system, etc., can solve the problem of low data accuracy, and achieve the effect of high accuracy and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
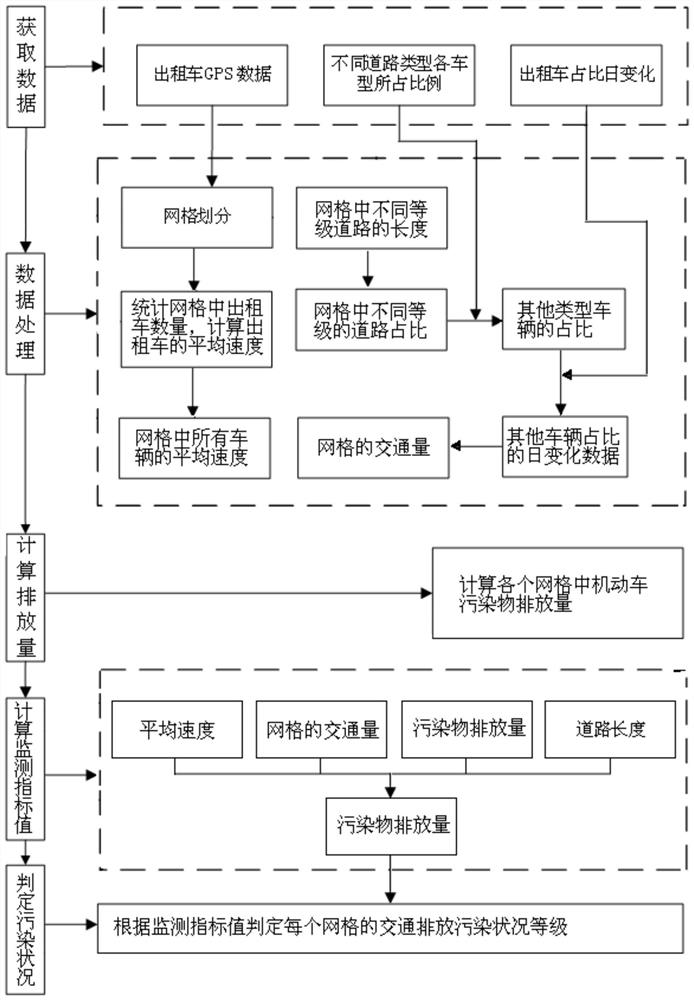
[0039] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 The present embodiment is described, the method that the present embodiment provides based on the taxi GPS data dynamic monitoring urban traffic emission pollution situation, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0040] 1), collect taxi GPS data, the proportion of each vehicle type of different road types and the daily change of taxi proportion; Proportion;
[0041] Data collection is mainly to provide data basis for the calculation of monitoring factors. Among them, taxi GPS data is mainly collected by relevant departments; GPS data includes: vehicle ID, latitude and longitude, sampling time, instantaneous speed, GPSID and driving direction; Rely on traffic survey data collection, but need to be updated from time to time to ensure the accuracy of the data. The data collected by the traffic survey needs to cover four types of roads: expressway, main road, secondary road and branch road, and the vehicle types ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0052] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the specific steps of motor vehicle pollutant emissions in the calculation grid described in step 4) are:
[0053] Step 41) Calculate the emissions of n types of pollutants in the grid j, the specific steps are as follows:
[0054]
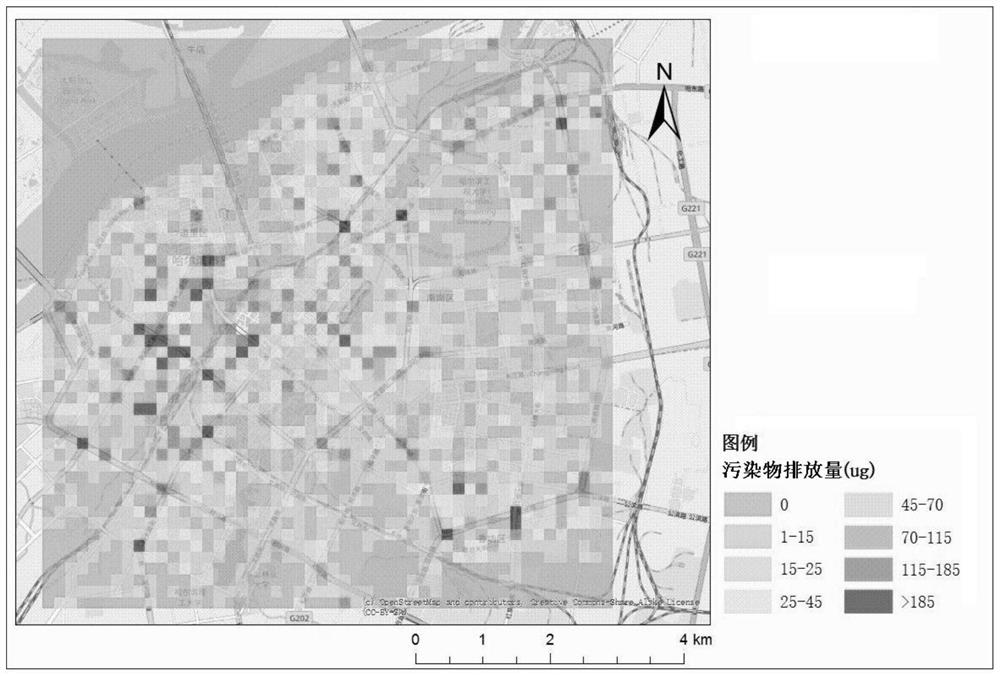
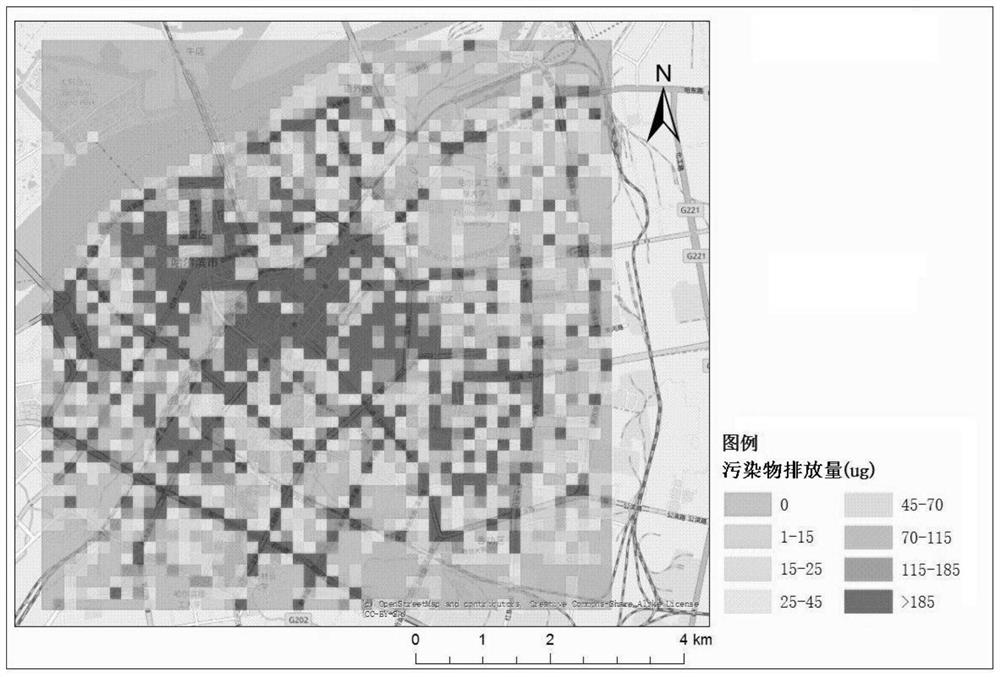
[0055] Among them, E j,n Indicates the emission of n types of pollutants in grid j in T time interval, the unit is grams; E j,i,n Indicates the emission of n types of pollutants emitted by i-type motor vehicles in grid j in the time interval T, the unit is grams; i∈{1,...,I}, I represents the total number of motor vehicle types counted, n ∈{1,…,N}, where N represents the total number of pollutant types calculated; EF i,n Indicates the amount of n-type pollutants emitted by i-type motor vehicles per unit distance, in grams / km; P j,i Indicates the number of motor vehicles of type i in grid j, unit is vehicle; VKT j,i Indicates the mileag...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0062] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that the discharge amount of n type pollutants discharged by i type motor vehicle traveling unit distance (that is, i type motor vehicle n type pollutant emission coefficient) EF i,n The specific calculation steps are as follows:
[0063]
[0064] Among them, BEF i,n Indicates the comprehensive benchmark emission coefficient of n-type pollutants of i-type motor vehicles, Indicates the environmental correction factor (where grid j is located), γ indicates the average speed correction factor, λ i Denotes the degradation correction factor of type i motor vehicle, θ i Indicates the correction factor for other service conditions (such as load factor, oil quality, etc.) of the type of motor vehicle.
[0065] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com