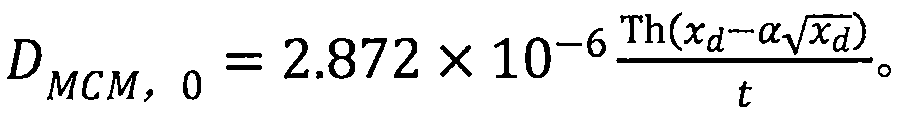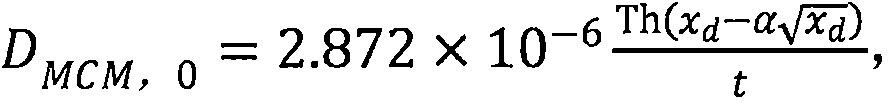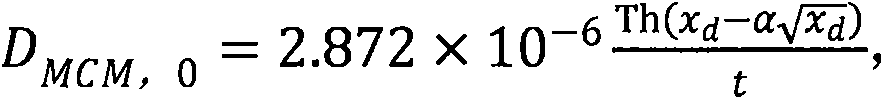Method for measuring chloride ion permeability resistance of concrete
A technology of chloride ion penetration and measurement method, which is applied in the field of concrete chloride ion permeability measurement, which can solve the problems of temperature rise, inaccurate and reliable detection results, and many defects, so as to achieve high detection accuracy and solve the problem of inaccurate detection results Reliable, Believable Results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] First, soak the specimen in the standard curing water pool for 4 days, then put the specimen into the rubber cylinder, and inject about 300mL of 0.2mol / L KOH solution into the rubber cylinder, so that both the anode plate and the surface of the specimen are immersed in the solution. Inject 0.2mol / L KOH solution containing 5% NaCl into the test tank until it is flush with the liquid level of the KOH solution in the rubber cylinder, turn on the power, record the time and immediately measure the parallel voltage, series current and initial temperature of the electrolyte (accurate to 0.2°C), take out the test piece after electrification, split it in half, use 0.1mol / L silver nitrate to titrate the diffusion depth of chloride ions, and finally calculate the chloride ion diffusion coefficient of concrete according to the formula, where the formula is
Embodiment 2
[0016] In Embodiment 1, add the following content:
[0017] The standard size of the test piece is (100±1)mm in diameter and (50±2)mm in height. The test piece is cored from the laboratory or the actual concrete structure and cut into standard sizes.
[0018] First soak the test piece in the standard curing water pool for 4 days, and then put the test piece into the rubber tube. The standard size of the test piece is (100±1) mm in diameter and (50±2) mm in height. Take the core from the concrete structure and cut it into a standard size. Inject about 300mL of 0.2mol / L KOH solution into the rubber cylinder, so that the anode plate and the surface of the test piece are immersed in the solution, and inject 5% NaCl into the test tank. 0.2mol / L KOH solution until it is flush with the liquid level of the KOH solution in the rubber cylinder, turn on the power, record the time and immediately measure the parallel voltage, series current and initial temperature of the electrolyte (accu...
Embodiment 3
[0021] In embodiment two, add the following content:
[0022] D. RCM,0 Indicates the chloride ion diffusion coefficient of concrete determined by the RCM method, in m 2 / s; T is the average value of the initial and final temperature of the anolyte in K.
[0023] First soak the test piece in the standard curing water pool for 4 days, and then put the test piece into the rubber tube. The standard size of the test piece is (100±1) mm in diameter and (50±2) mm in height. Take the core from the concrete structure and cut it into a standard size. Inject about 300mL of 0.2mol / L KOH solution into the rubber cylinder, so that the anode plate and the surface of the test piece are immersed in the solution, and inject 5% NaCl into the test tank. 0.2mol / L KOH solution until it is flush with the liquid level of the KOH solution in the rubber cylinder, turn on the power, record the time and immediately measure the parallel voltage, series current and initial temperature of the electrolyte ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com