Method for fixed-point labeled immunological reagent, labeled immunological reagent and application
An immune reagent and labeling technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of antigen/antibody inactivation, impaired stability, impaired affinity, etc., to achieve protective activity, small batch differences, and reduce The effect of wasting human, material and financial resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] This embodiment provides a method for acridinium ester-specific labeling of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antigens to obtain acridinium ester-labeled HIV antigens. The specific steps are:
[0028] Cloning the expression plasmid with Leu-Pro-Ala-Thr-Gly (Ala is alanine) at the end of the HIV antigen, transfecting the expression plasmid into Escherichia coli and expressing it, the polypeptide fragment Leu-Pro can be connected to the end of the HIV antigen -Ala-Thr-Gly, to transform HIV antigen;
[0029] Dissolve the acridinium ester activated by N-hydroxysuccinimide in DMF to obtain an acridinium ester solution; add ethylenediamine solution to the acridinium ester solution to adjust the pH to 8-9, and react at room temperature for 3 hours; add acetic acid solution Adjust the pH to 6.5-7.5, then add sulfo-SMCC, and react at room temperature for 2 hours; add ethylenediamine solution to adjust the pH to 8-9, add the polypeptide sequence Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Cys, and reac...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment provides a method for site-specific labeling of HIV antigens with acridine sulfonamide to obtain HIV antigens labeled with acridine sulfonamide. The specific steps are:
[0034] Cloning into the expression plasmid with Leu-Pro-Cys-Thr-Gly at the end of the HIV antigen, transfecting the expression plasmid into Escherichia coli and expressing it, then connecting the polypeptide fragment Leu-Pro-Cys-Thr-Gly to the end of the HIV antigen, Obtain modified HIV antigen;
[0035] Dissolve the acridine sulfonamide activated by N-hydroxysuccinimide in DMF to obtain an acridine sulfonamide solution; add triethylenediamine solution to the acridine sulfonamide solution to adjust the pH to 8-9, and react at room temperature for 2.5 hours Add adipic acid solution to adjust the pH to 6.5-7.5, then add sulfo-SMCC, and react at room temperature for 1.5 hours; add triethylenediamine solution to adjust the pH to 8-9, add the polypeptide sequence Gly-Gly-Gly-Cys, React at r...
Embodiment 3
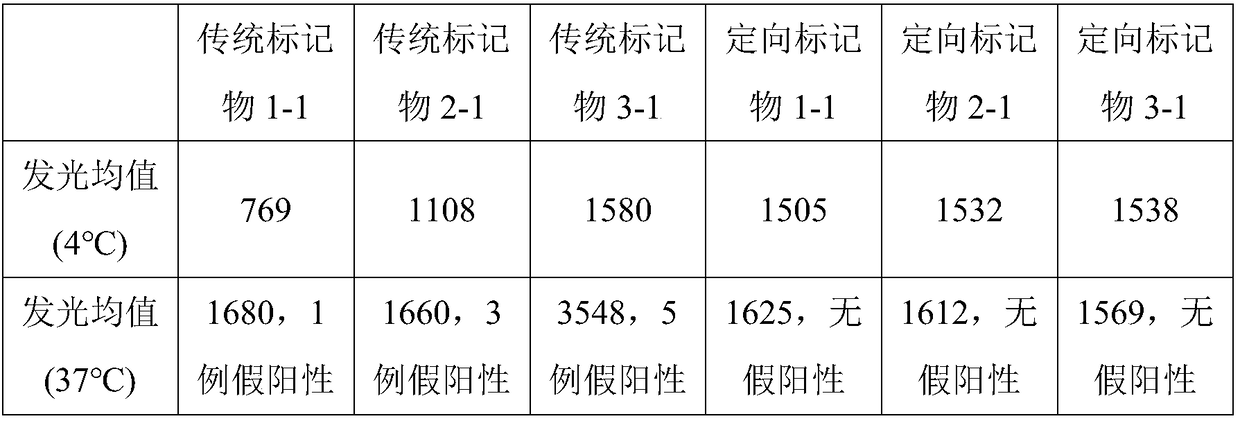
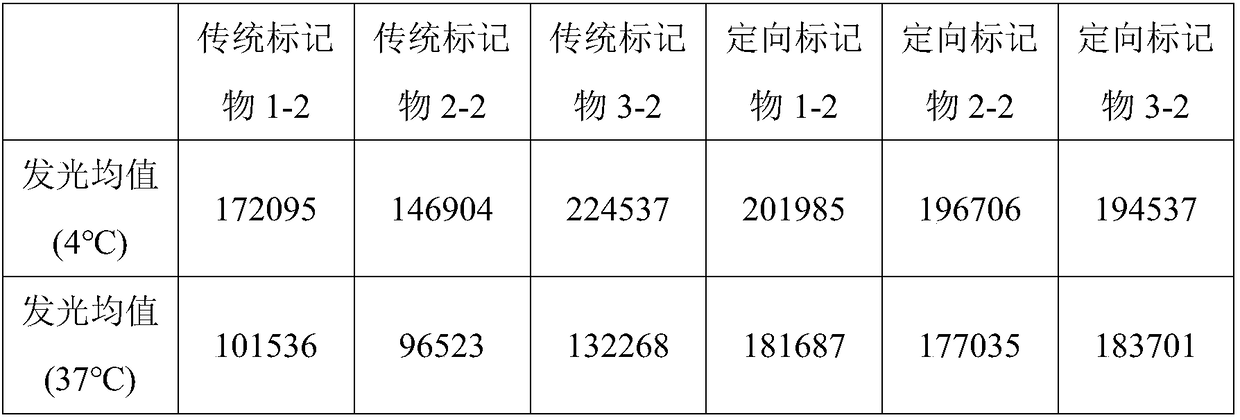
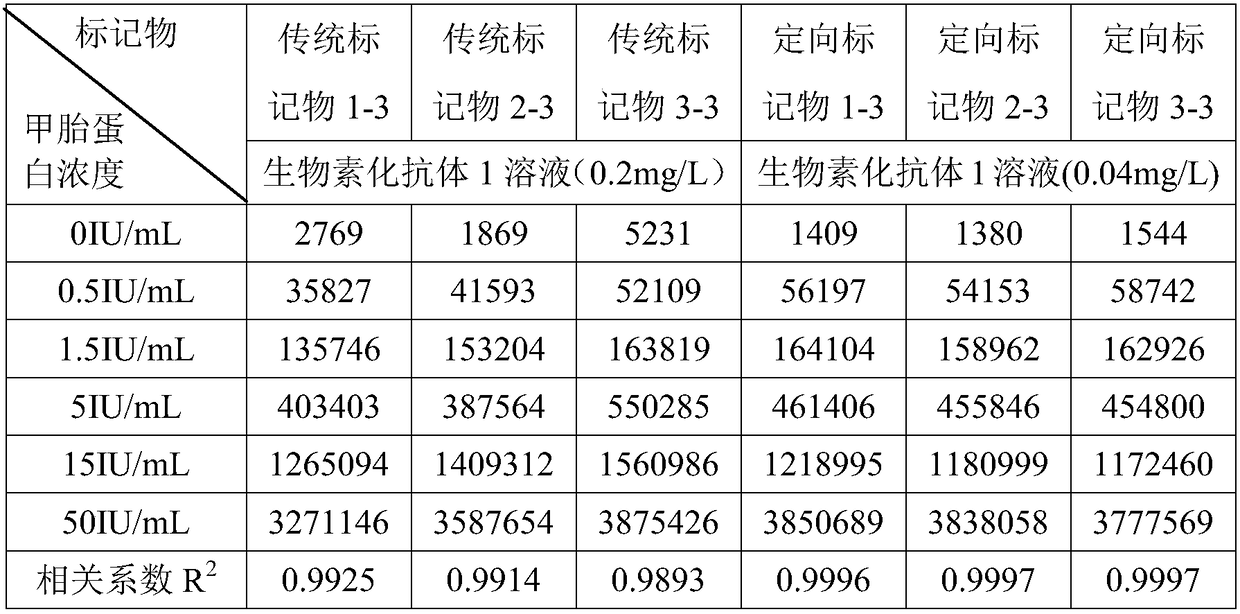
[0039]This embodiment provides a method for biotin-specific labeling of anti-alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)-specific monoclonal antibody 1 to obtain biotinylated anti-alpha-fetoprotein-specific monoclonal antibody 1. The specific steps are:
[0040] The expression plasmid with Leu-Pro-Leu-Thr-Gly is cloned at the Fc end of the anti-alpha-fetoprotein specific monoclonal antibody 1, and the expression plasmid is transfected into Escherichia coli for expression, and the polypeptide fragment Leu can be connected to the end of the HIV antigen -Pro-Leu-Thr-Gly, the modified anti-alpha-fetoprotein specific monoclonal antibody 1;
[0041] Dissolve biotin activated by N-hydroxysuccinimide in DMF to obtain a biotin solution; add diethanolamine solution to the biotin solution to adjust the pH to 8-9, and react at room temperature for 2 hours; add acrylic acid solution to adjust the pH to 6.5-7.5, then add sulfo-SMCC, react at room temperature for 1 hour; add diethanolamine solution to adjust th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com