A 3d printed ink bag
A 3D printing and ink bag technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low efficiency, strict storage and transportation conditions, complicated processes, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding unexpected mixing, simple preparation process and good uniformity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 3D printing bio-ink, including the following raw materials in mass percentage:
[0027] Extracellular Vesicle Suspension 10%
[0028] Pig dermal soft tissue derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder 5%
[0029] Hydrochloric acid 1%
[0030] Ultrapure water balance.
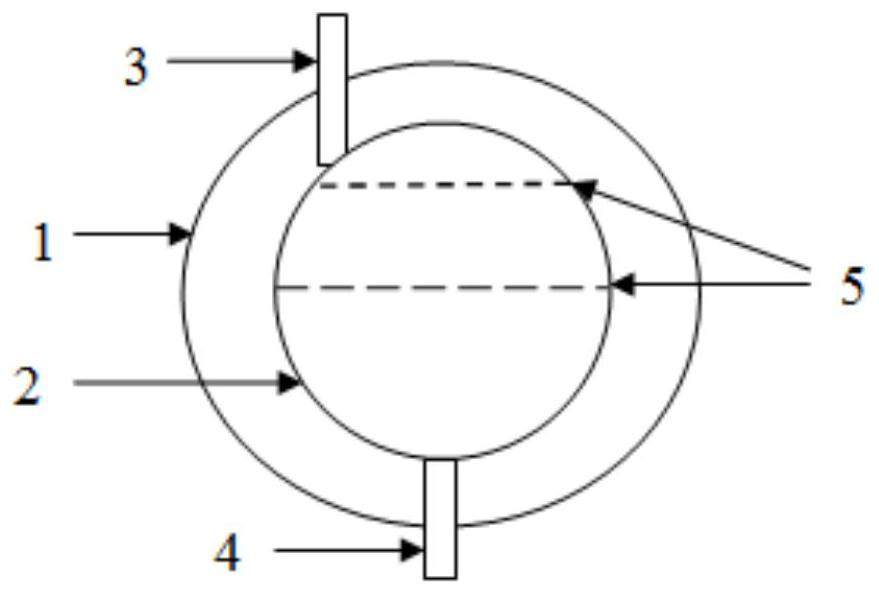
[0031] A 3D printed ink bag, see figure 1 , comprising an inner bag 2 and an outer bag 1, the inner bag 2 is divided into three chambers by a partition 5, the porcine dermal soft tissue-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber micropowder is packed into the inner bag under low vacuum, and then vacuum-sealed to form a chamber 1; refill extracellular vesicle suspension, seal to form chamber 2, finally fill in water and hydrochloric acid mixed solution, seal to form chamber 3, the upper part of the inner bag is provided with an inlet 3, and the lower part is provided with an outlet 4, the inlet and The outlets are all sealed and extend out of the outer bag, and the outer bag vacuum-seals the inner bag. ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The 3D printing bio-ink with a pH of 6.5 is made of the following raw materials in mass percentage:
[0036] Extracellular Vesicle Suspension 10%
[0037] Pig dermal soft tissue derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder 5%
[0038] Hydrochloric acid 1%
[0039] Sodium bicarbonate amount
[0040] Ultrapure water balance.
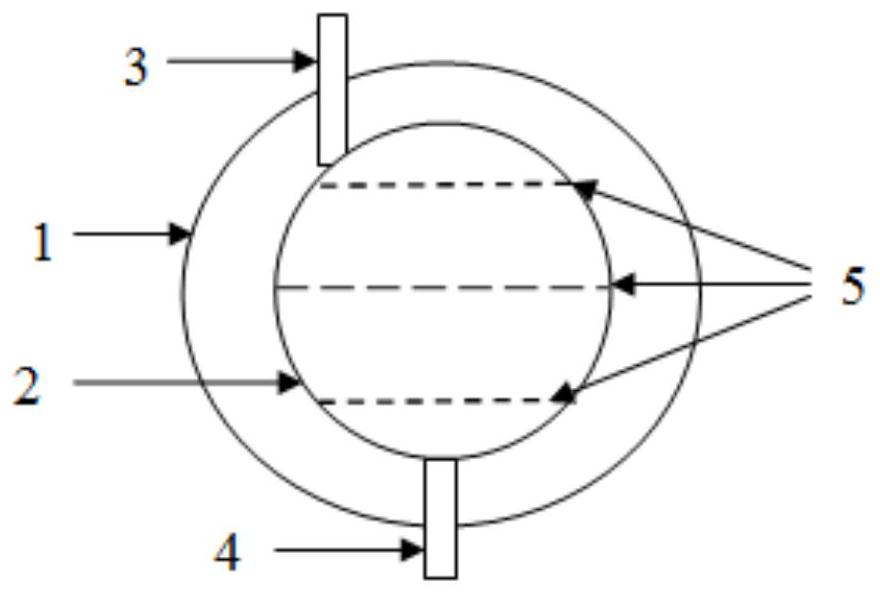
[0041] A 3D printed ink bag, see figure 2 , including an inner bag 2 and an outer bag 1, the inner bag 2 is divided into four chambers by a partition 5, the upper part of the inner bag is provided with an inlet 3, and the lower part is provided with an outlet 4, the outlet is sealed, and the pig dermis soft tissue is loaded from the inlet under vacuum Derived extracellular matrix nanofiber micropowder is then heat-sealed to form chamber 1, then filled with extracellular vesicle suspension and heat-sealed to form chamber 2, then filled with water and hydrochloric acid and heat-sealed to form chamber 3, and finally filled to make the mixed biolo...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The 3D printing bio-ink with a pH of 6.9 is made of the following raw materials in mass percentage:
[0046] Extracellular Vesicle Suspension 30%
[0047] Pig dermal soft tissue derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder 9%
[0048] Acetic acid 1%
[0049] Sodium bicarbonate amount
[0050] Ultrapure water balance.
[0051] A 3D printing ink bag, including an inner bag and an outer bag, the inner bag is divided into three chambers by a partition belt, filled with porcine dermis soft tissue-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber micropowder and acetic acid under low vacuum and then vacuum-sealed to form chamber 1, Then put water and sodium bicarbonate into it to vacuum-seal to form chamber 2, and finally put extracellular vesicle suspension into it to vacuum-seal to form chamber 3. The upper part of the inner bag is provided with an inlet, and the lower part is provided with an outlet, and the inlet and outlet are sealed and sealed. Stretch out the outer bag, whic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com