Monocrystalline semiconductor wafer and method for producing semiconductor wafer
A single crystal semiconductor, semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, etc., can solve problems such as inability to achieve flatness, inability to achieve long-wavelength roughness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
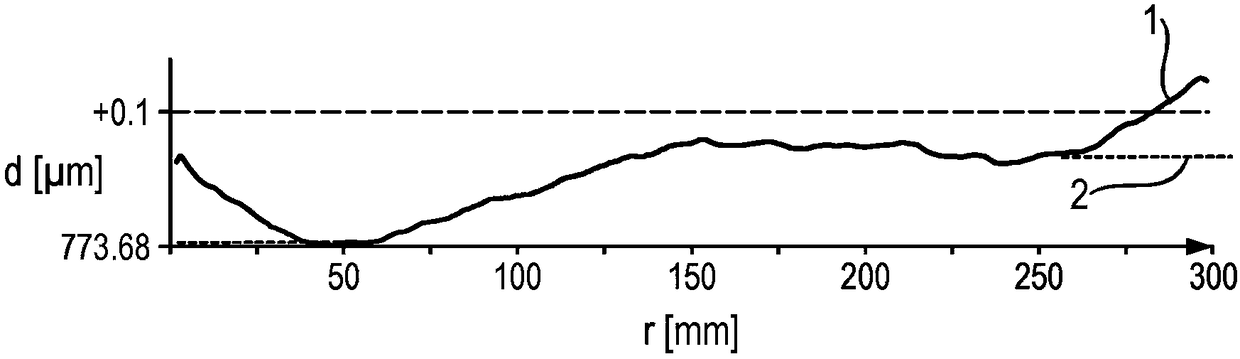
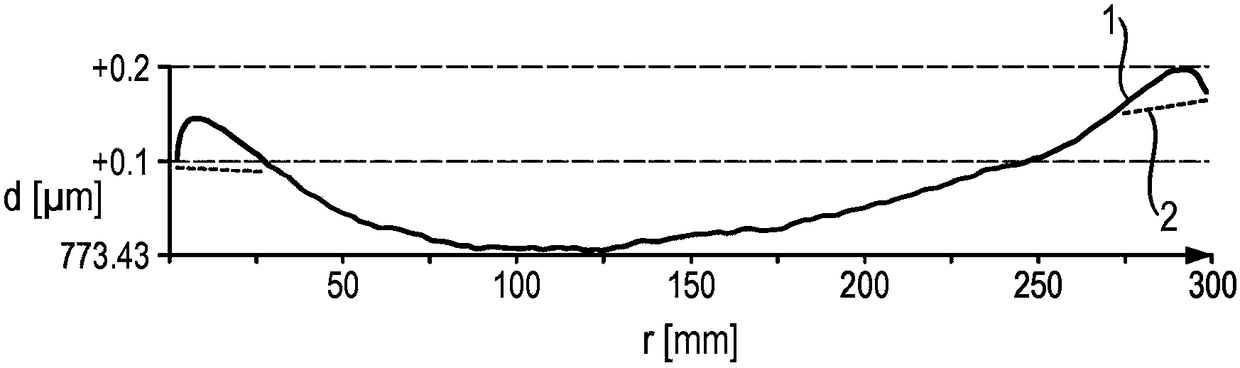
[0021] The semiconductor wafer according to the invention is characterized by a roughness R of 0.8 nm or less, preferably 0.5 nm or less a ("average roughness"), which is typical of polished semiconductor wafers. The stated values relate to the average roughness determined by white light interferometry at a cut-off wavelength of 250 μm. At the same time, however, the semiconductor wafer according to the invention has a value ESFQR of 8 nm or less, preferably 5 nm or less avg - characterizes the flatness in the edge region. Roughness R as low as 0.2 nm or even 0.1 nm can be achieved by means of fog-free polishing according to the state of the art a .
[0022] The semiconductor wafers according to the invention are thus much less rough than after PACE processing and, on the other hand, are significantly flatter at the edges than after double-sided and single-sided polishing according to the prior art.
[0023] Preferably, the semiconductor wafer according to the invention ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com