Method for preventing or treating nosocomial pneumonia
An iatrogenic and pneumonia-related technology, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, chemical instruments and methods, antibody medical components, etc., can solve the problems of complicated management of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0085] Example 1: Phase 1 Clinical Trial Study
[0086] Conduct a Phase 1, first-in-human, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-escalation study evaluating the safety and tolerability of single ascending IV doses of MEDI3902 in healthy adult subjects. Among 42 subjects who received MEDI3902 at doses of 250 mg (n=3), 750 mg (n=15), 1500 mg (n=15) or 3000 mg (n=9) and 14 subjects who received placebo , adverse event (AE), PK and ADA data were collected until the last study visit (60 days post-dose / day 61). All AEs in both the MEDI3902 group and the placebo group were Grade 1 or 2 in severity. The most frequently reported adverse events were grade 1 or 2 infusion-related reactions (15 / 42 subjects [35.7%] in the overall MEDI3902 group; none in the placebo group) and grade 1 or 2 headache (across the 6 / 42 subjects [14.3%] in the MEDI3902 group; 2 / 14 subjects [14.3%] in the placebo group). Adverse events of special interest (AESI) included infusion-related reactions ...
example 2
[0089] Example 2: Phase 2b Clinical Trial Study
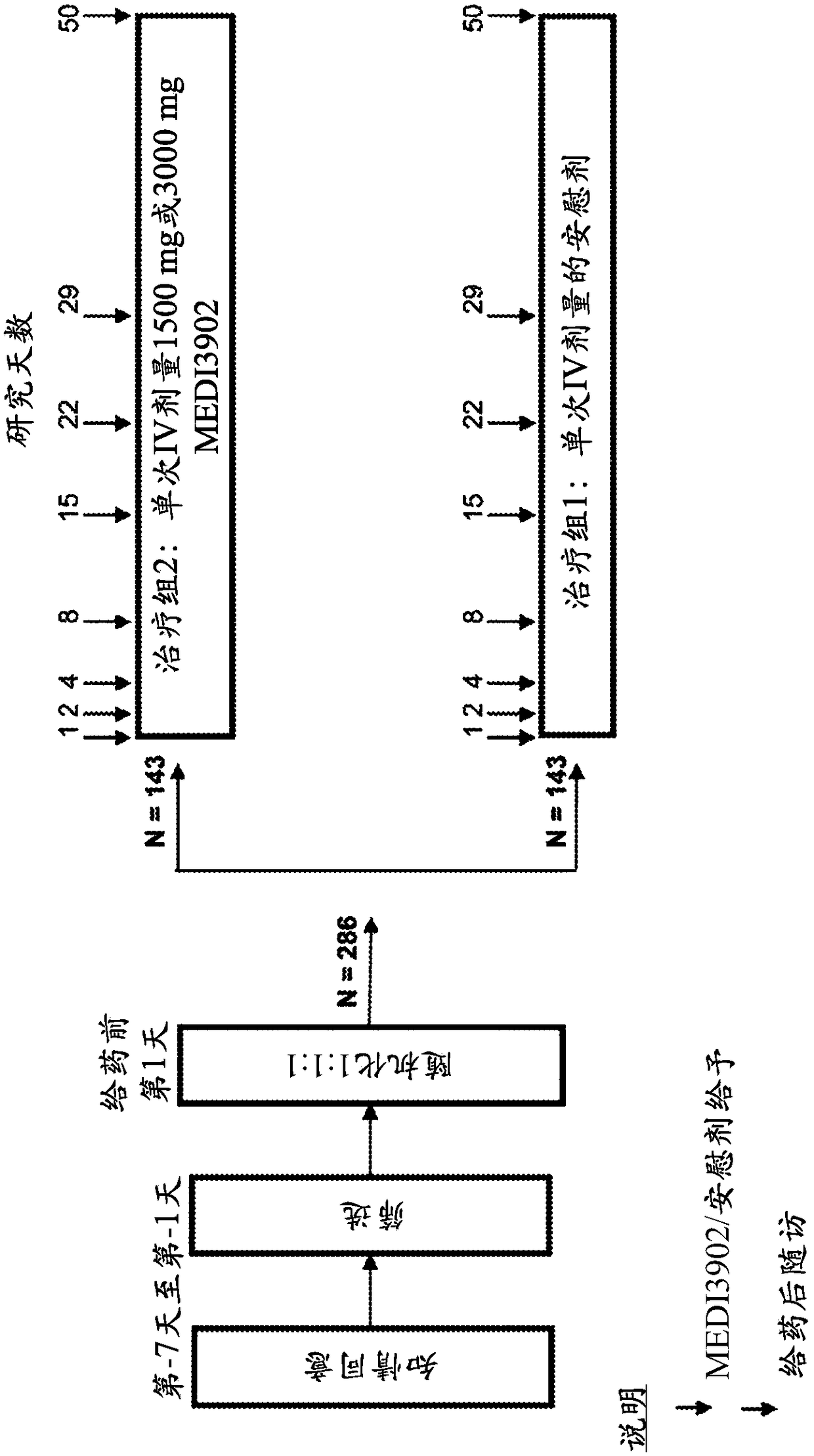
[0090] Approximately 429 subjects were recruited and administered at approximately 120 sites primarily in Europe in a Phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-dose, dose-ranging proof of concept. Subjects will be randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive a single IV dose of 1500mg or 3000mg MEDI3902 or placebo. The dosing regimen may also become randomized 1:1 between a single IV dose of 1500 mg (or 3000 mg) MEDI3902 or placebo. Randomization will be stratified by geographic region and by whether subjects have received anti-P. aeruginosa antibiotic therapy (duration ≤72 hours) within 96 hours prior to randomization. Subjects will be followed until Day 50 (49 days after study product administration) ( figure 1 ).
[0091]For enrollment, subjects were required to be 18 years of age or older, in an intensive care unit, currently intubated and mechanically ventilated, and expected to remain intubated and...
example 3
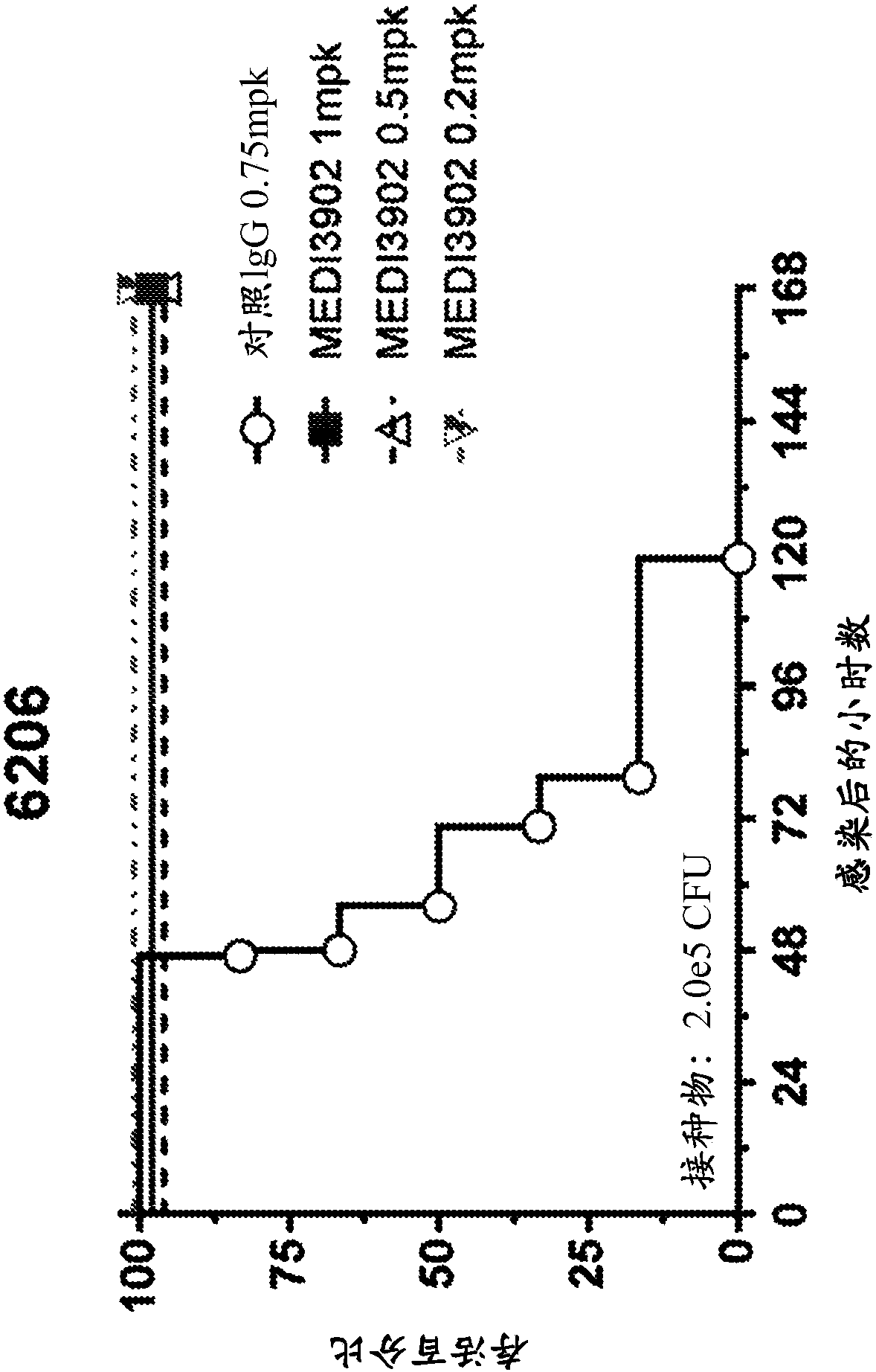
[0143] Example 3: MEDI3902 reduces lethality in an acute pneumonia model under lower bacterial burden
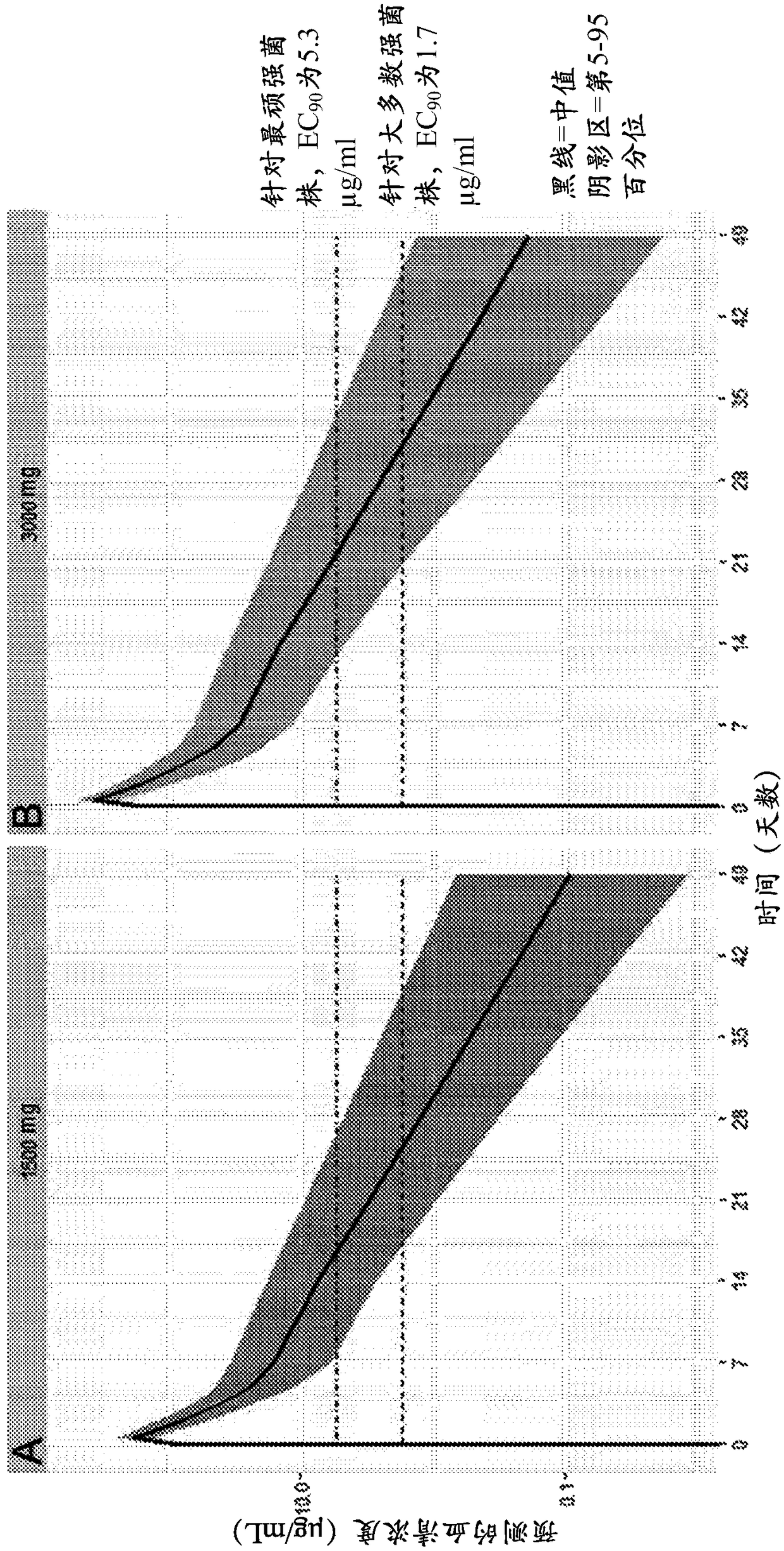
[0144] The in vivo effects of MEDI3902 administration were studied in mice using an acute pneumonia model. Groups of mice (n=6) were injected intraperitoneally (IP) with decreasing concentrations of MEDI3902 (1.0 mg / kg, 0.5 mg / kg, or 0.2 mg / kg) or an isotype control IgG antibody (negative control, 0.75 mg / kg). ). Twenty-four hours after treatment, all mice were treated with 2 × 10 5 CFU Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 6206 (1×LD 100 ) for intranasal infection. Such as image 3 As shown, all control-treated animals died of infection at 120 hours post-infection. However, MEDI3902 showed complete protection at all doses, even at 1×LD 100 The same is true below, suggesting that a lower target serum level of 1.7 μg / mL in humans would provide protection against most Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com