Protease-resistant streptavidin
A technology of streptavidin and trypsin, applied in the field of streptavidin molecules, can solve problems such as large full-length proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
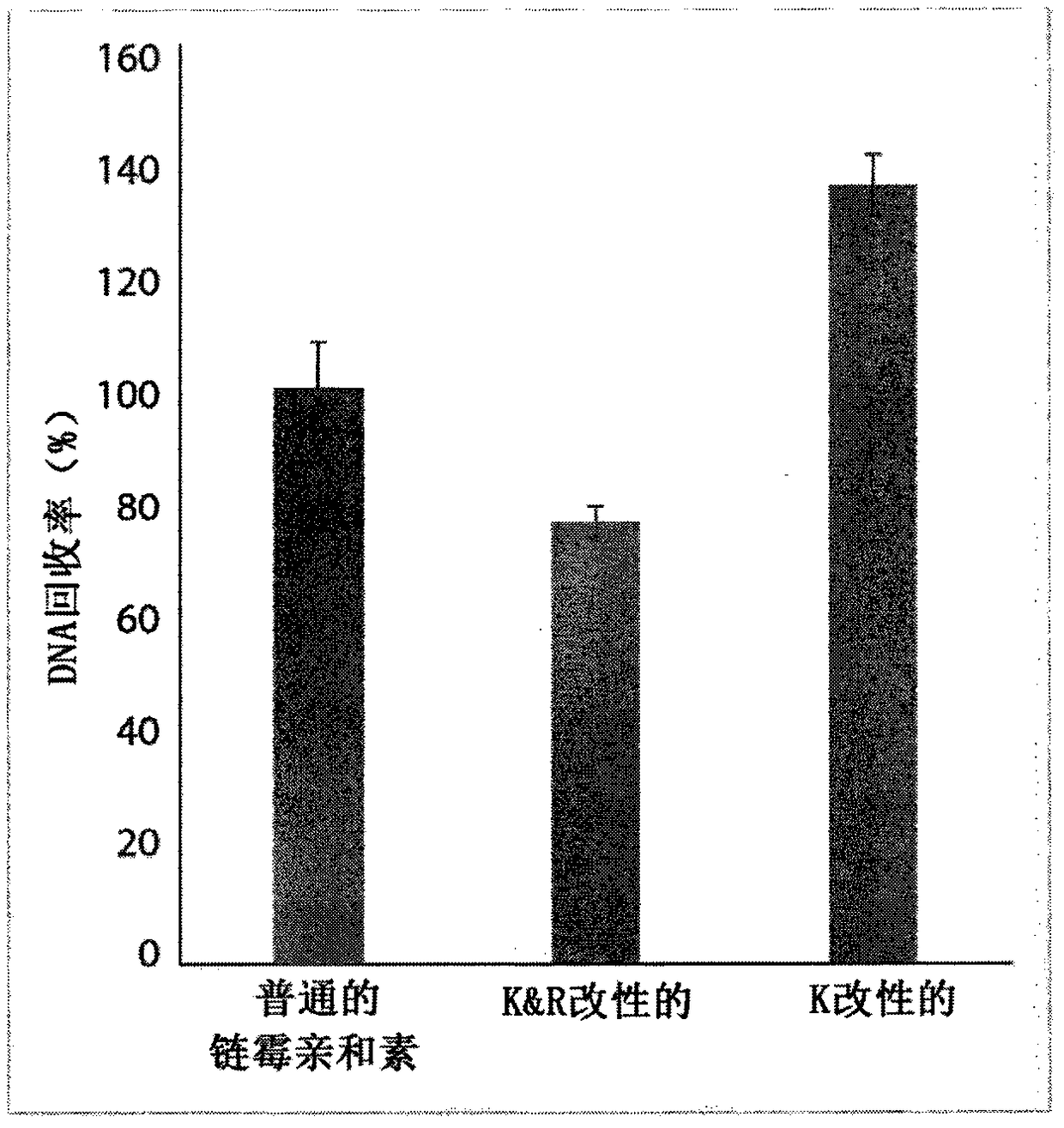
[0241] Example 1: Reductive methylation of lysine residues in streptavidin
[0242] The chemistry used to block lysine residues is based on the reductive methylation method described by Boersema et al., the modification described in Boersema P.J. et al. (2009) Nat.Protoc.4(4):484-94.
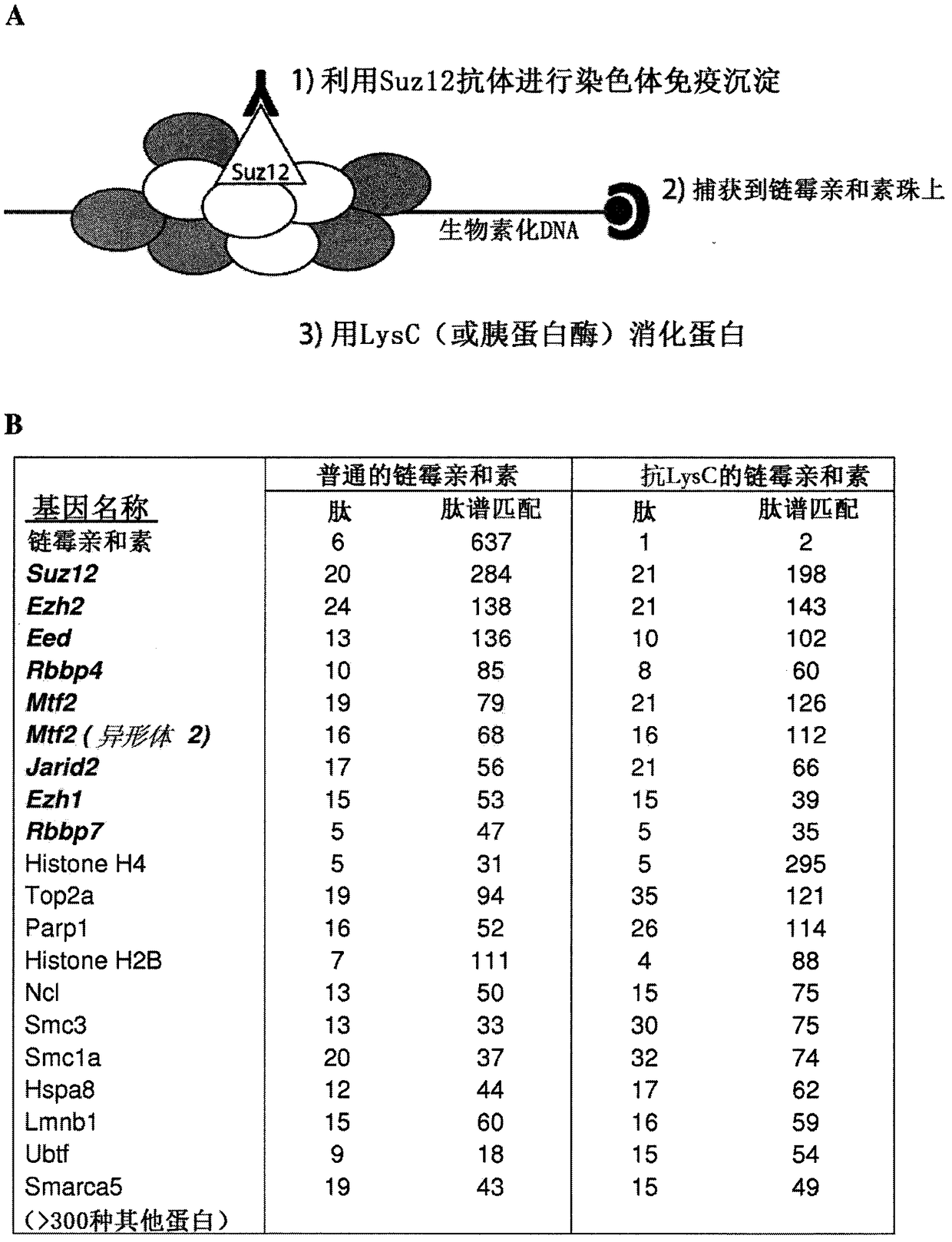
[0243] This blocking reaction is performed with streptavidin already attached to the beads. Subsequently, the biotinylated protein is bound to blocked streptavidin, and the sample is digested with LysC protease, which cleaves the bound protein at lysine residues without exposure to streptavidin.
[0244] Reagent
[0245] 4.5ml of 50mM pH 7.5 Sodium Phosphate Buffer
[0246] 600mM NaBH 3 CN 250μl
[0247] · 4% formaldehyde 250μl
[0248] Acetic acid (Merck, catalog number 1.00063)
[0249] Acetonitrile (ACN) (Biosolve, catalog number 75-05-8)
[0250] · Ammonia solution (25% (vol / vol), Merck, Cat. No. 1.05432)
[0251] · Formaldehyde (CH 2 O) (37% (v / v), Sigma, Cat. No. 252549)
[0252]...
Embodiment 2
[0272] Example 2: Identification of peptides from streptavidin before and after chemical blocking of arginine and lysine
[0273]The lysine and arginine residues in streptavidin are blocked by subsequent reductive methylation and reaction with cyclohexanedione, respectively. The blocking reaction was performed on streptavidin already attached to the beads. Subsequently, the streptavidin beads were trypsinized. The obtained peptides were analyzed by LC-MS.
[0274] Table 1: Tryptic peptides produced by unmodified streptavidin
[0275]
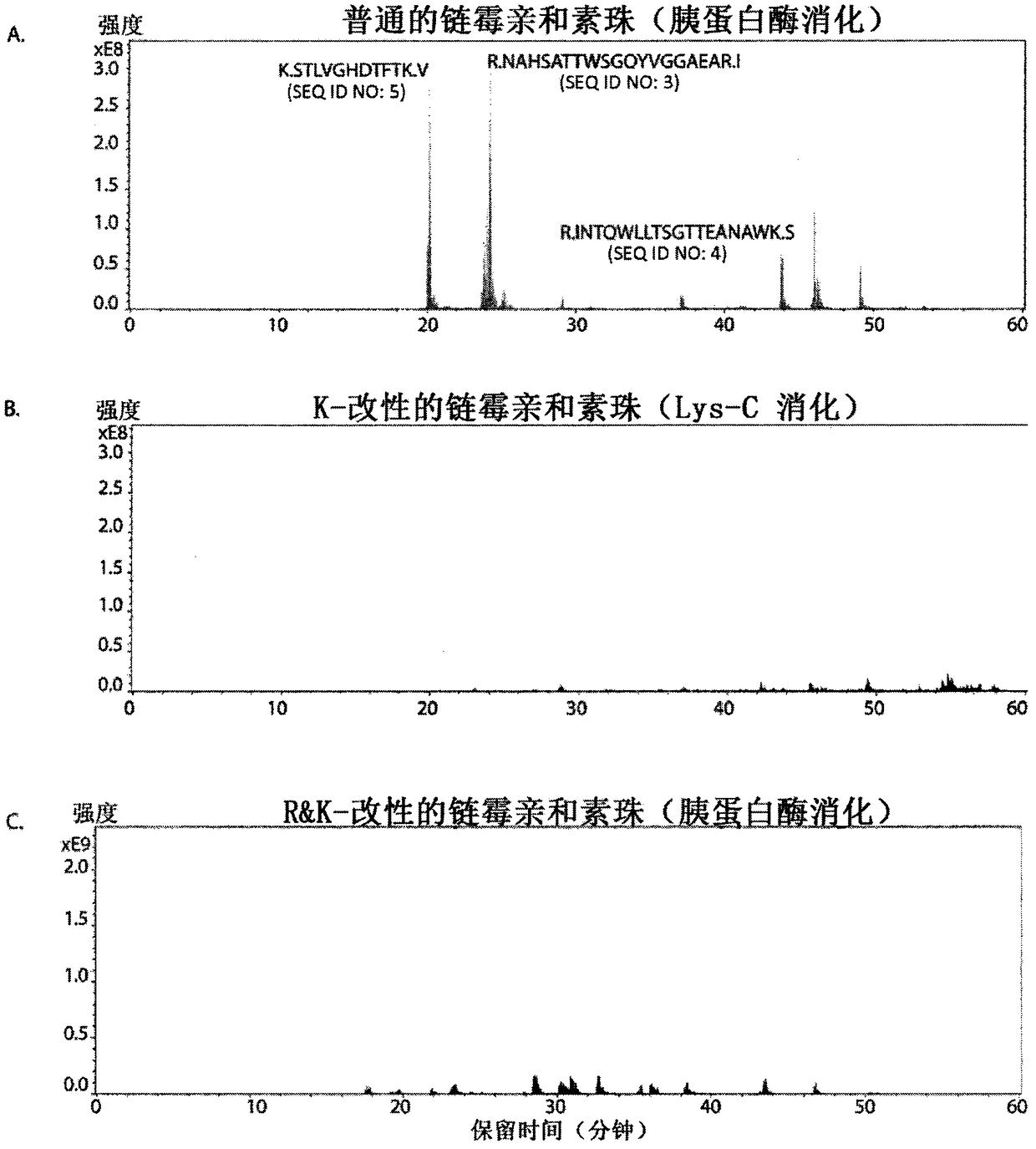
[0276] Tryptic digestion of unmodified streptavidin beads followed by LC-MS analysis identified multiple peptides (see also figure 1 A). A total of 411 profiles were recorded, most of them multiples, indicating their high abundance (Table 1).
[0277] Table 2: Tryptic peptides produced by streptavidin after chemical blocking of K's and R's
[0278]
[0279] After blocking lysine and arginine (by reductive methylation and reaction wit...
Embodiment 3
[0280] Example 3: Identification of peptides from streptavidin before and after chemical blocking of lysine and enzymatic conversion of arginine to citrulline
[0281] The enzyme peptidyl arginine deiminase (Peptidyl arginine deiminase, PAD) can convert arginine to citrulline ( Figure 4 ), while citrulline is not a substrate for trypsin, conferring resistance to proteolytic cleavage.
[0282] This was confirmed by chemically blocking lysine in streptavidin (as in Example 2), followed by enzymatic treatment with PAD to convert arginine to citrulline. This is in stark contrast to the 411 profiles observed after digestion of unmodified trypsin (Table 1), which resulted in the identification of 2 peptides out of a total of 7 profiles (Table 3), and indicated that Chemically modified streptavidin exhibited similar levels of protease resistance (Table 2). Notably, after PAD treatment (Table 3), the arginine-flanked peptide R.NAHSATTWSGQYVGGAEAR.I (SEQ ID NO : 3) The number of sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com