A method for degrading chloramphenicol antibiotics in soil or clay
A technology for chloramphenicol and antibiotics, which is applied in the field of degrading chloramphenicol antibiotics in soil or clay, can solve the problems of complicated operation, low degradation rate, high energy consumption, etc., and achieves simple operation, low degradation cost and high removal rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
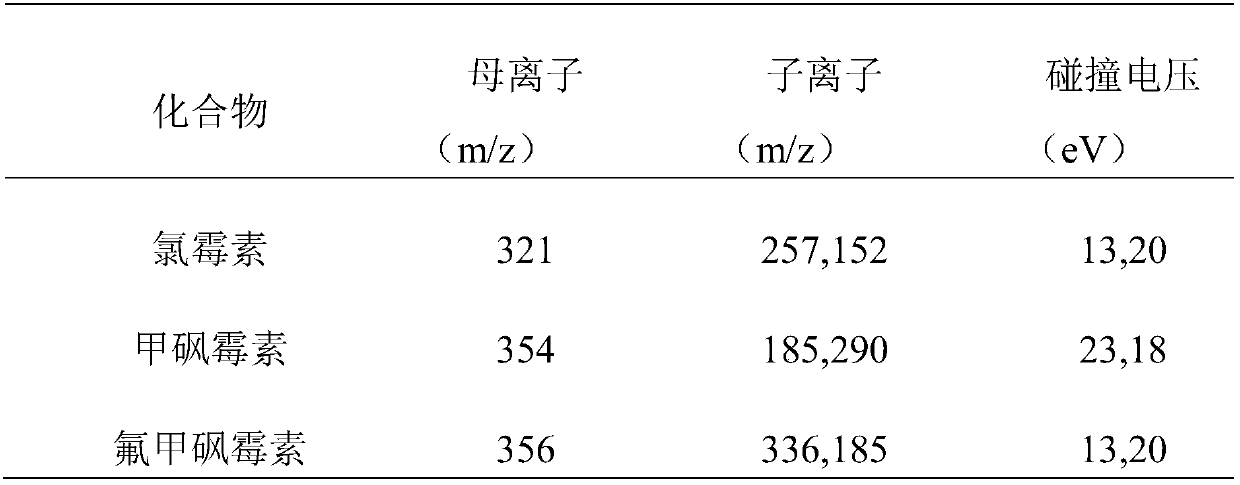
[0059] Test product: take 2 g of the sieved clay sample, add chloramphenicol (3.3*10 -6 mol, thiamphenicol (3.3*10 -6 mol), fluthiamphenicol (3.3*10 -6 mol). Vortex with a vortex mixer for 0.5 to 1 minute; add 2 mL of potassium persulfate aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.1 mol / L, add 2 mL of a ferrous sulfate solution with a concentration of 0.1 mol / L, and vortex with a vortex mixer for 0.5 to 1 minute. Stand still for 4 hours, and detect the chloramphenicol antibiotics in the clay after the reaction according to the sample processing method described in 1.1 and the instrument analysis conditions in 1.2.
[0060] Reference substance: take 2 g of the sieved clay sample, add chloramphenicol (3.3*10 -6 mol), thiamphenicol (3.3*10 -6 mol), fluthiamphenicol (3.3*10 -6 mol); vortex with a vortex mixer for 0.5 to 1 minute; detect the chloramphenicol antibiotics in the reference substance according to the sample processing method described in 1.1 and the instrument anal...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Other operations and methods are the same as in Example 1, the only difference is that the volume of the ferrous sulfate solution added to the test product is 1 mL.
[0072] Experimental results:
[0073]
[0074]
[0075] After testing, the degradation rates of chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol and fluthiamphenicol in the clay sample were 75.3%, 74.4% and 73.8%, respectively. And after degradation, no by-products of benzoic acid are generated, and the measured benzoic acid contains a substance with a benzoic acid structure.
Embodiment 3
[0077] Other operations and methods are the same as in Example 1, the only difference is that the volume of the potassium persulfate aqueous solution added is 4 mL.
[0078] Experimental results:
[0079] Types of antibiotics A As f ω Chloramphenicol 8532 410198 1 97.9% Thiamphenicol 7126 327698 1 97.8% Flumethicone 2361 106960 1 97.8%
[0080] After testing, the degradation rates of chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol and fluthiamphenicol in the clay sample were 97.9%, 97.8% and 97.8%, respectively. And after degradation, no by-products of benzoic acid are generated, and the measured benzoic acid contains a substance with a benzoic acid structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com