Pathogenicity related protein of Verticillium dahliae in cotton and its coding gene, application and mutant
A technology of cotton Verticillium dahliae and pathogenic related genes, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of lack of antigenic materials, lagging of disease-resistant breeding, loss of variety resistance, etc., and achieve good application potential Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1 Construction of Verticillium dahliae T-DNA insertion mutant library of cotton
[0030] Cotton Verticillium dahliae Vd080 isolated from a severely diseased field in Xinji, Hebei, as the starting strain, will carry
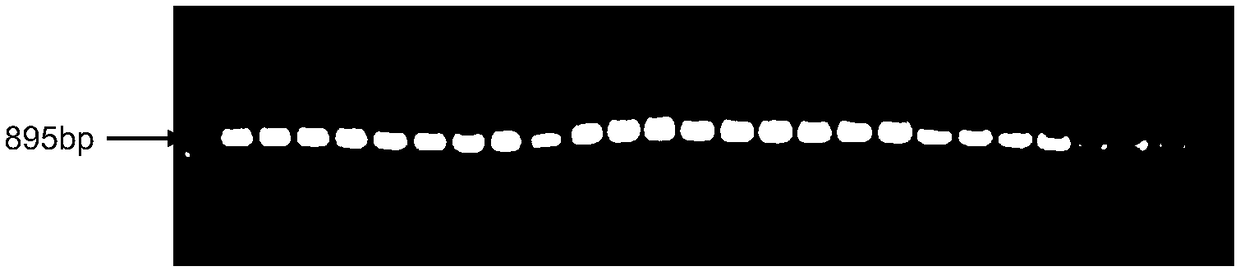
[0031] For the Agrobacterium pCTHyg binary vector, the Agrobacterium-mediated transformation (ATMT) method was used to construct a T-DNA insertion mutant library with a capacity of 3000 carrying hygromycin (HPH) resistance selection markers. Whether there is a hygromycin label is an important basis for screening positive transformants. Use hygromycin-specific primers Hyg-F / Hyg-R (Hyg-F: 5′-GCCAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGTC-3′; Hyg-R: 5′-GCGCTCGAG
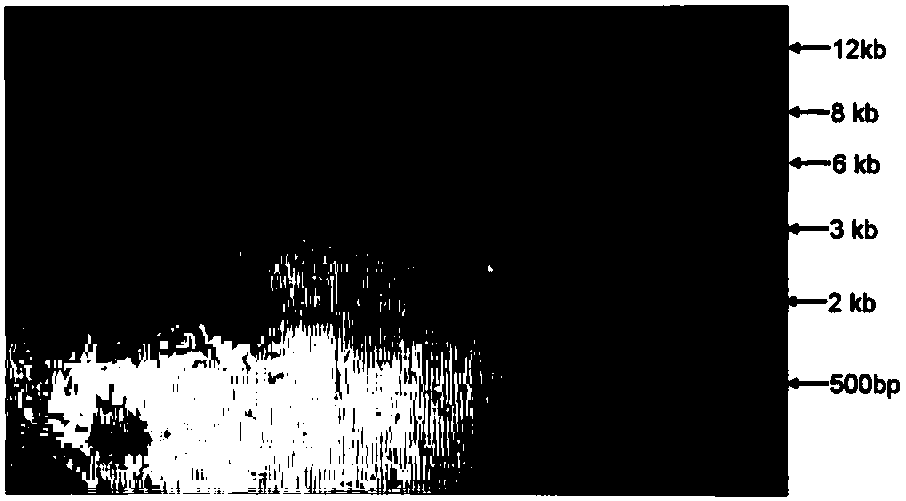
[0032] TCCTCTAGAAAAGAA GGATTAC-3′) amplified to obtain a specific band of 895bp is a positive transformant ( figure 1 ). The Southern hybridization technique was used to detect the copy number of T-DNA insertion in the mutant (Figure 2).
Embodiment 2
[0033] The acquisition of embodiment 2 low pathogenicity mutant T1027 bacterial strain
[0034] The pathogenicity of cotton Verticillium dahliae mutants was determined by using the upland cotton susceptible variety Jimian 11 as the identification host, and using the method of quantitative inoculation in vermiculite sandy soil with bottomless paper pots. After two rounds of primary screening and re-screening, the mutant T1027 with significantly reduced pathogenicity was obtained. Compared with the wild-type relative disease index of 50, the relative disease index of T1027 was only 8.7, and the pathogenicity was greatly reduced. see comparison image 3 .
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Mutant T1027 biological shape analysis
[0036] 3.1 Observation of colony morphology and determination of growth rate
[0037] Take the wild-type strain Vd080 as a control, drop 5 μL of mutant spore suspension with a concentration of 1×107 / mL in the center of the PDA medium, and repeat 5 times for each strain, and culture at a constant temperature of 25°C for 10 days, and record the number of colonies growth form. And at 5d, 7d, 9d and 11d, adopt the cross method to measure the colony growth diameter respectively, and calculate the growth rate.
[0038] The results showed that compared with the wild-type Vd080, the sclerotium production of the mutant T1027 decreased sharply, and the synthesis of melanin also decreased significantly. But the growth rate of the two tends to be the same, both are 4.5mm / d.
[0039] 3.2 Determination of spore production and crude toxin content
[0040] Taking the wild-type strain Vd080 as a control, drop 5 μL of the mutant spor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com