Microorganism strain for degrading petroleum hydrocarbon and combined repairing agent
A technology of microbial agent and combined repair, applied in the direction of microorganisms, microorganisms, and methods based on microorganisms, can solve the problems of chemical repair that is difficult to fully meet the repair requirements, low comprehensive utilization, and unsatisfactory repair effects, etc., to achieve significant economic benefits. Benefits and social benefits, long-lasting environmental disturbances, effects of high utility value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The preparation of embodiment 1 microbial bacterial agent
[0025] (1) Acquisition of microbial strains
[0026] The strain was derived from the oily soil near the Jiyuan Oilfield in Shaanxi. Using crude oil as the only carbon source, a strain with high oil degradation ability was finally isolated and screened by screening enrichment separation method. The identification results are shown in Table 1.
[0027] Table 1 strain identification results
[0028]
[0029] The strain obtained by the screening was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection CCTCC on June 19, 2017. The preservation address is: Wuhan University, No. 299 Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2017347.
[0030] (2) Inoculation and activation of microbial strains
[0031] Under sterile conditions, inoculate Pseudomonas mendocina PM (Pseudomonas mendocina PM) CCTCC NO: M2017347 into the Erlenmeyer flask containing nutrient b...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The remediation experiment of embodiment 2 microbial bacterial agents to oily soil
[0035] One, the laboratory degradation experiment of microbial bacterial agent of the present invention to n-alkane, horane, aromatic hydrocarbon:
[0036] The experiment was divided into two groups: blank oil sample group and PM oil sample experimental group.
[0037] The experimental process of the PM oil sample experimental group is as follows:
[0038] Under aseptic conditions, get the microbial bacterial agent 1.5ml that embodiment 1 prepares, insert the Erlenmeyer flask of 20ml inorganic salt medium, culture medium contains 10mg crude oil (inorganic salt medium formula: NH 4 NO 3 3g / L, K 2 HPO 4 1.6g / L, KH 2 PO 4 3g / L, trace element solution 6mL, distilled water 1000mL; trace element solution (g / L): MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.15, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.18, CuSO 4 0.15, anhydrous CaCl 2 0.02, Na 2 EDTA·2H 2 O 0.02, pH 7.1, 121°C high-pressure steam sterilization for 20min), 30°C s...
Embodiment 3
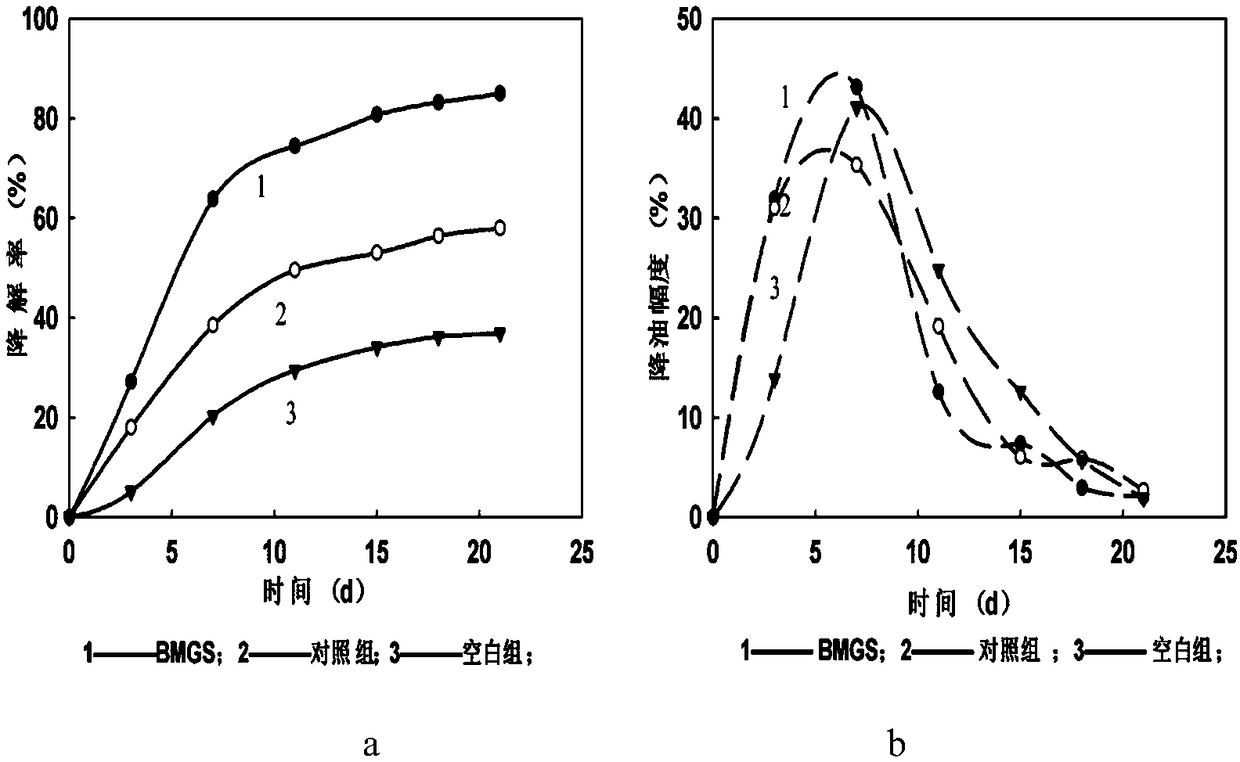
[0058] Example 3 Combined remediation experiment of microbial agent and oil-absorbing material on oily soil
[0059] Generally, oil-absorbing materials can be classified into inorganic mineral materials, synthetic organic materials, and natural organic materials. Inorganic mineral materials (such as clay, silica, vermiculite, etc.) have low oil absorption capacity and poor oil-water selectivity, which limits their wide application in the environment; synthetic organic materials (such as polyurethane) have high oil absorption properties, but there are There are many problems such as high synthesis cost, many by-products of oil absorption, and difficulty in handling after oil absorption. Compared with this, natural organic materials (such as corn) have great advantages, not only cheap and easy to obtain, but also can be completely removed from oily soil after oil absorption, with less environmental hazards; can be used in combination with other methods (such as microbial remedia...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Oil absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com