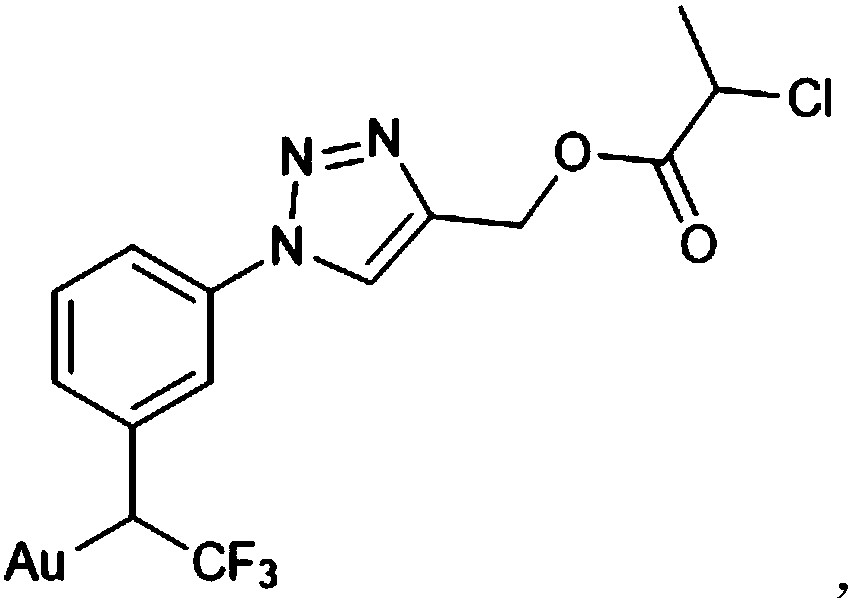
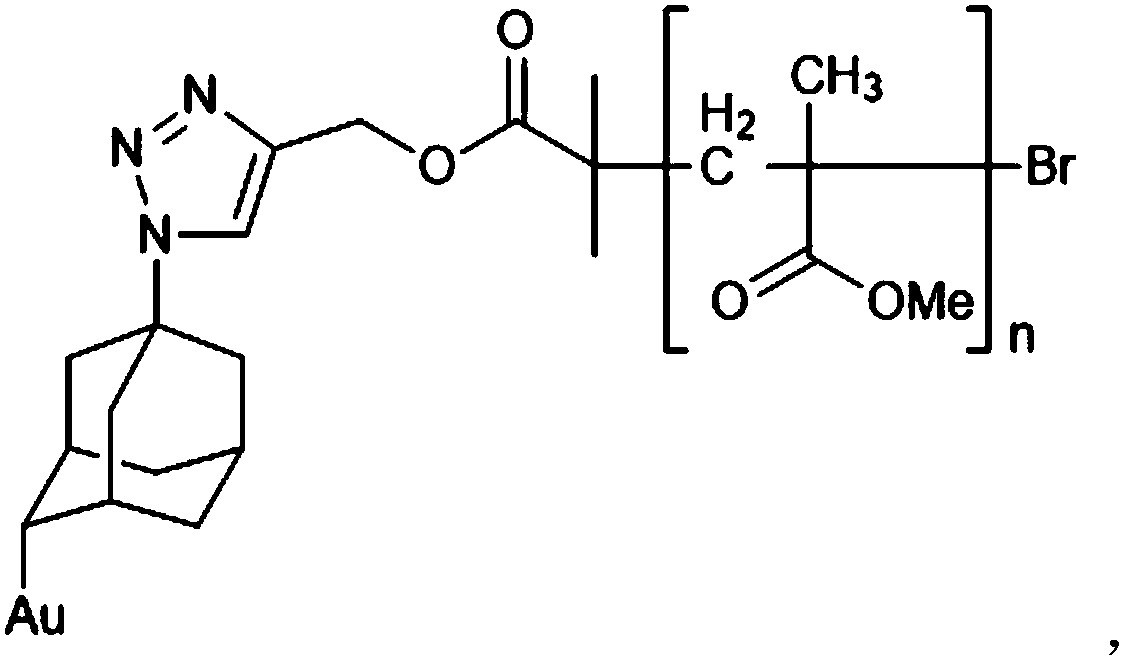
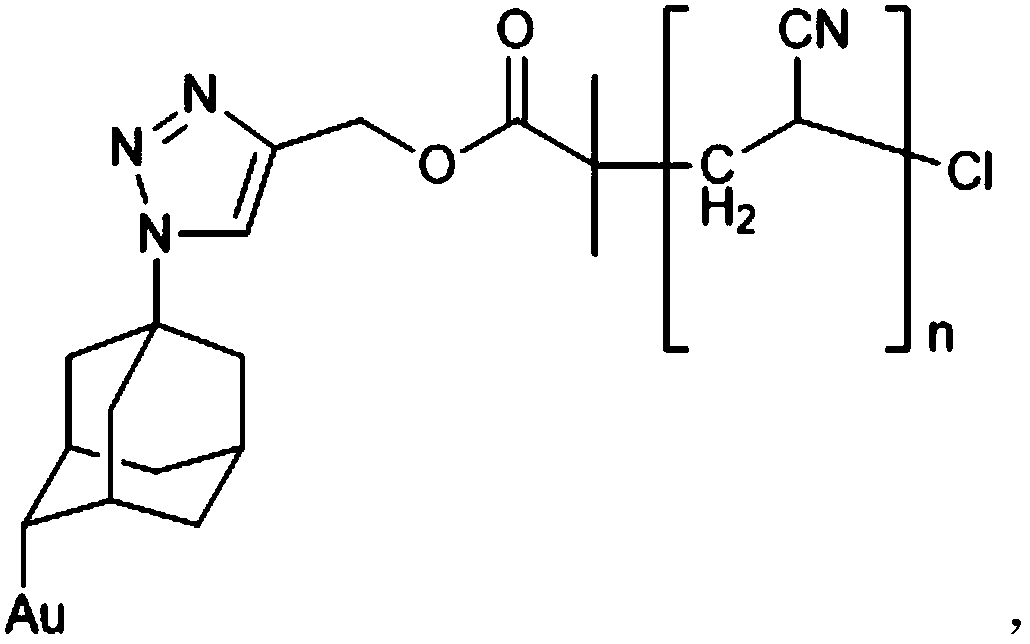
Gold surface initiator grafting method, gold surface polymer brush and preparation method thereof
A surface grafting and polymer brush technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of unfavorable promotion and harsh preparation conditions, and achieve the effect of simple operation and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The embodiment of the present invention also provides a preparation method of a gold surface polymer brush, which includes:
[0037] The second intermediate is prepared by adopting the above-mentioned method of grafting the initiator on the gold surface; and the second intermediate is mixed with the olefin polymer monomer to undergo free radical polymerization.
[0038] Preferably, the olefin polymer monomer includes at least one of acrylate compounds, acrylamide compounds, acrylonitrile compounds and vinylpyridine compounds.
[0039]The embodiment of the present invention also provides a polymer brush on a gold surface, which is prepared by the above method for preparing a polymer brush on a gold surface. The polymer brush on the gold surface has strong stability and controllable graft density, and has good application value.
Embodiment 1
[0042] This embodiment provides a kind of azidodiaziridine compound A, its chemical formula is Its preparation method is as follows:
[0043] 5-Bromo-2-adamantanone (1.16 g) was dissolved in 25% (w / v) ammonia in methanol and stirred at -10°C for 45 min. 1 g of hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid was dissolved in 10 ml of methanol solution and added dropwise to the above solution of 5-bromo-2-adamantanone. The reaction was continued for 18 h under stirring at 4 °C. The solvent was removed and the remaining solid was extracted twice with dichloromethane solvent (2 x 20ml). The dichloromethane solvents were combined and extracted three times (3×20 ml) with 2N sulfuric acid solution at 4°C, and the aqueous layer was collected and made basic with 2N sodium hydroxide solution at 4°C. It was extracted again with dichloromethane, and the organic layer was dried with potassium carbonate, filtered, and rotary evaporated to obtain a diaziridine intermediate (1.34 g, yield 82%).
[0044] T...
Embodiment 2
[0047] This embodiment provides a kind of azidodiaziridine compound B, its chemical formula is Its preparation method is as follows:
[0048] Dissolve 1-(3-bromophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethan-1-one (1.35 g) in 25% (w / v) ammonia in methanol and stir at -10°C 60min. 1 g of hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid was dissolved in 10 ml of methanol solution and added dropwise to the above 1-(3-bromophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethan-1-one solution. The reaction was continued for 18h under stirring at 4°C. The solvent was removed and the remaining solid was extracted twice with dichloromethane solvent (2 x 20ml). The dichloromethane solvents were combined and extracted three times (3×20 ml) with 2N sulfuric acid solution at 4°C, and the aqueous layer was collected and made basic with 2N sodium hydroxide solution at 4°C. It was extracted again with dichloromethane, and the organic layer was dried with potassium carbonate, filtered, and rotary evaporated to obtain a diaziridine intermediate (0.79...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com