Method for establishing in-vitro model capable of simulating barrier functions of pulmonary epithelial cells and capillary endothelial cells during acute lung injury
An endothelial cell barrier, lung epithelial cell technology, applied in vascular endothelial cells, epidermal cells/skin cells, artificial cell constructs, etc., can solve problems that do not involve barrier function, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
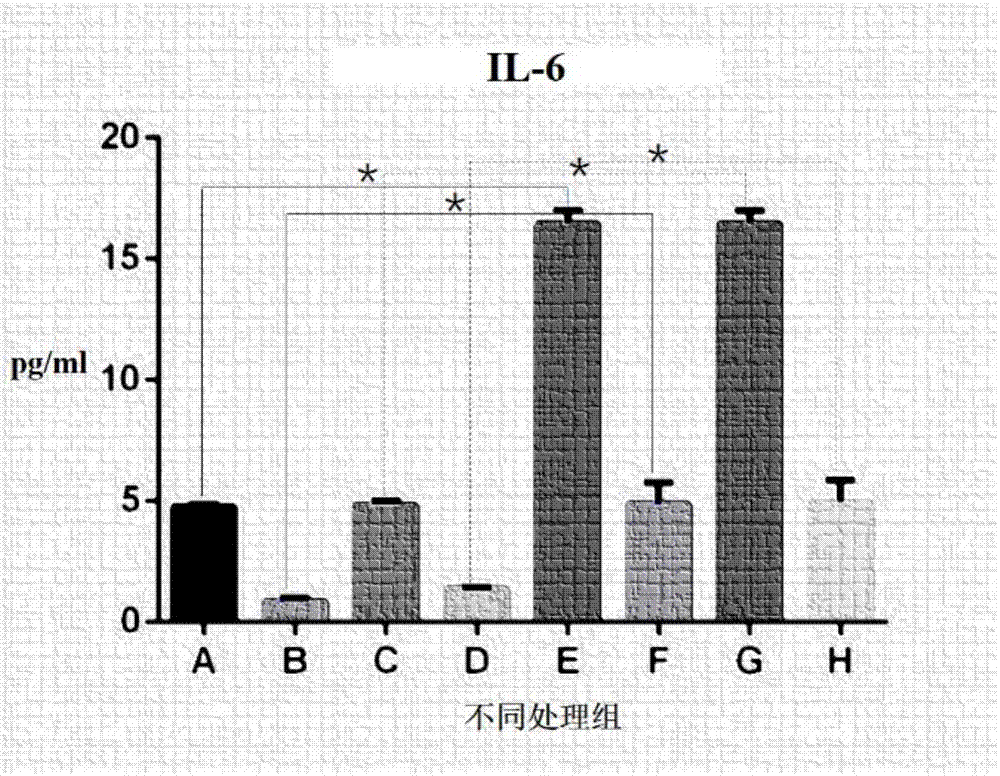
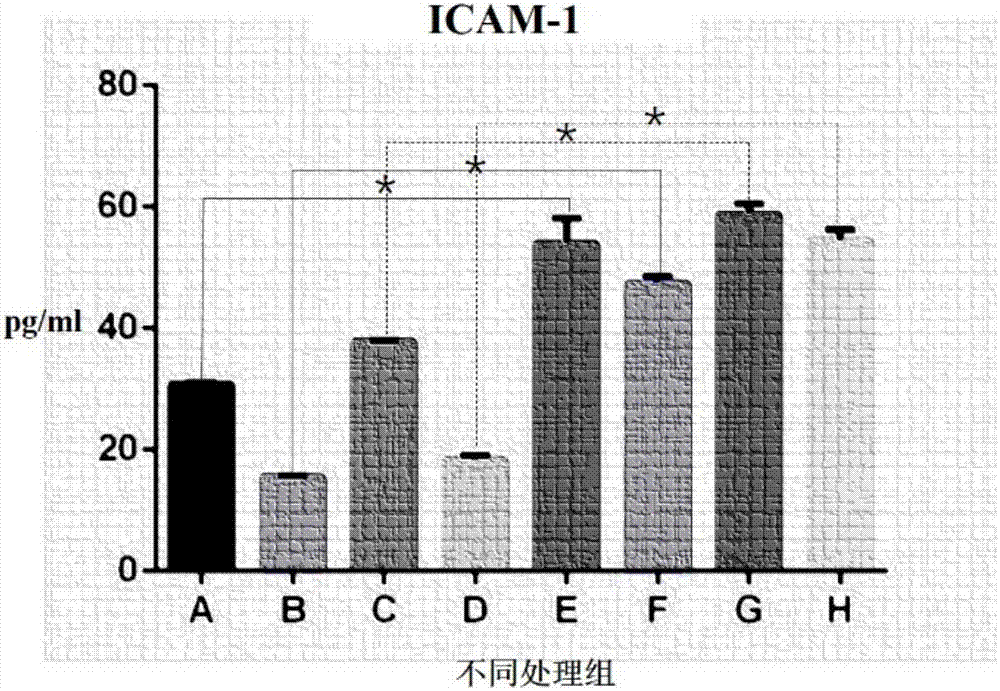
[0021] In this example, a co-culture model of mouse TC-1 lung epithelial cells and mouse C3H / 10T1 / 2 microvascular endothelial cells was made in the Transwell co-culture system, and the lung epithelial cells / microvascular endothelial cells were co-cultured by adjusting the cell culture environment. The culture model can express inflammatory cytokines (IL6) and inflammatory cell infiltration-associated protein (ICAM-1) under endotoxin stimulation.
[0022] The process of making a lung epithelial cell / microvascular endothelial cell co-culture model is as follows:
[0023] Using the Transwell co-culture system, the mouse C3H / 10T1 / 2 microvascular endothelial cell line infected with 1ug / mL LPS was mixed with 4 × 10 4 / cm 2 The concentration of 1.5mL was inoculated on the lower layer of the Transwell chamber, and cultured for 5h. The mouse-derived TC-1 lung epithelial cell line was mixed with 2×10 4 / cm 2 Inoculate 1mL on the upper layer of the small chamber. The lower cell cult...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Changing the concentration of LPS
[0032] After pre-experimental exploration, it was found that the cells in the co-culture system induced by the final concentration of 0.8-1.2 μg / mL LPS could survive and grow well. Concentrations below 0.8 μg / mL will result in failure to cause damage or a large gap between the degree of damage and the situation of acute lung injury in vivo. Above 1.2μg / mL, it will lead to cell death.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3 Changing the lower cell culture medium
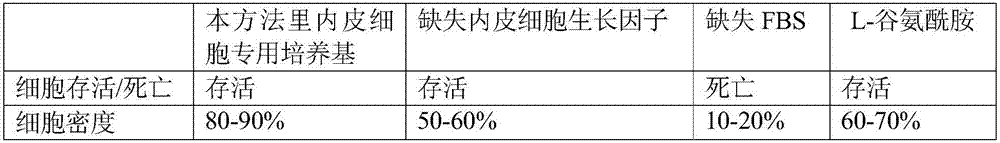
[0034] The established lower medium is the most suitable culture environment for the growth of endothelial cells. Changing the components in the medium, or missing a certain component, or changing the amount and ratio of components will lead to low survival rate of endothelial cells, slow proliferation, or even death. The cell density required for the co-culture of the two types of cells could not be reached, and the cell culture results are shown in Table 1.
[0035] Table 1
[0036]
[0037] Typically, cells die the next day when no FBS is added. In the absence of 90-95U / mL heparin, there is little effect on cell viability and density. Too high concentrations of penicillin sodium and streptomycin sulfate may cause cell death, and too low concentrations may cause bacterial contamination.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com