Limited angle CT image reconstruction algorithm based on boundary-preserving diffusion and smoothing
A CT image, limited-angle technology, applied in the field of limited-angle CT image reconstruction algorithms, can solve the problems of limited-angle CT imaging, blur, and undiscovered patent publications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A limited-angle CT image reconstruction algorithm based on boundary-preserving diffusion and smoothing, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific process is described as follows:
[0045] Step 1. Input variables: finite-angle CT scan data set p, finite-angle CT scan geometric parameter set G;
[0046] Step 2. Initialization: Determine the coordinate system of the reconstructed image according to the scanning angle range; initially estimate the image u (0) , the iteration termination threshold ε or the upper limit of the number of iterations N;
[0047] Step 3. Assume that the estimated image u has been obtained (k) , with u (k) As the initial value, use the limited-angle CT scan data set p to update the estimated image u (k+1 / 3) =R G (p,u (k) ), where R G Represents the image reconstruction operator related to the scanning geometry parameter set G;
[0048] Step 4, for the image u (k+1 / 3) Perform boundary-preserving diffusion correction in the x-axis direction to...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Step 1. Input variables: finite-angle CT scan data set p, finite-angle CT scan geometric parameter set G;
[0053] Step 2. Initialization: Determine the coordinate system of the reconstructed image according to the scanning angle range; initially estimate the image u (0), the iteration termination threshold ε or the upper limit of the number of iterations N;
[0054] wherein the coordinate system of the reconstructed image makes the projection angle range symmetrical about the y-axis;
[0055] Step 3. Assume that the estimated image u has been obtained (k) , with u (k) As the initial value, use the limited-angle CT scan data set p to update the estimated image u (k+1 / 3) =R G (p,u (k) ), where R G Represents the image reconstruction operator related to the scanning geometry parameter set G;
[0056] The image reconstruction operator R related to the scanning geometry parameter set G G Defined by the following optimization problem:
[0057]
[0058] where A is...
Embodiment 3
[0073] In order to better reflect the advantages of a limited-angle CT image reconstruction algorithm based on boundary-preserving diffusion and smoothing in the reconstruction effect of the present invention, the algorithm described in the present invention and existing typical algorithms are combined below in conjunction with a specific embodiment, including SART algorithm, TV regularization algorithm, gradient l 0 Compare the regularization algorithm and the DART algorithm.
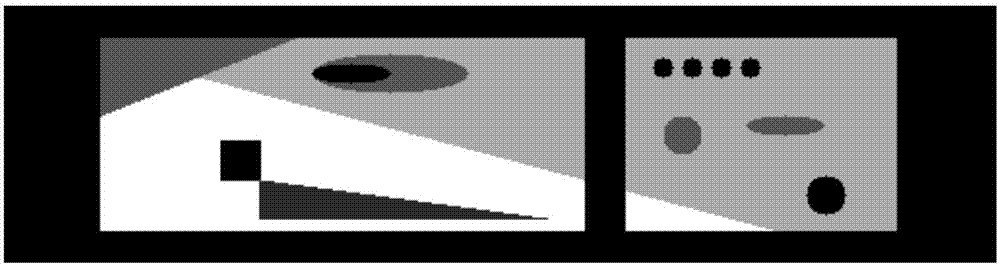
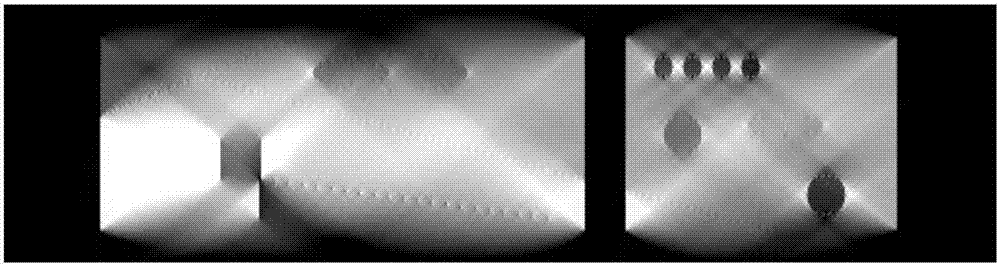
[0074] This embodiment adopts the two-dimensional tomographic fan-beam scanning mode, the limited-angle scanning range is [π / 4,3π / 4], and the scanning phantom is as figure 2 As shown, the number of detector units is 512, the unit size is 0.3mm, the distance from the ray source to the rotation center is 300mm, the distance from the detector is 600mm, and the number of angular samples in the scanning range is 181.
[0075] Using SART algorithm, TV regularization algorithm, gradient l 0 Regularization ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com