Polyalkoxylated polyamine oxide defoaming compositions
A technology of polyalkoxylation and polyalkoxylated polyethyleneimine, which is applied in the direction of coating, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the effectiveness of defoaming additives, and achieve the effect of reducing air voids and high barrier properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] (Synthetic Amine Oxide)
[0049] Polypropoxylated diethylenetriamine having a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 2,550 (100 g, 0.039 mole), n-propanol (50 mL) and acetic acid (0.2 g) were charged to the reaction vessel. The mixture was heated to 50°C with stirring, and then a 30% by weight aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution (4.54 g, 0.04 mol) was added dropwise to the mixture at 50-55°C over 40 minutes. After addition of hydrogen peroxide, the mixture was kept at 60-65° C. for 18 hours with stirring. The resulting amine oxide product (sample AO1) was collected by removing the n-propanol solvent using a rotary evaporator.
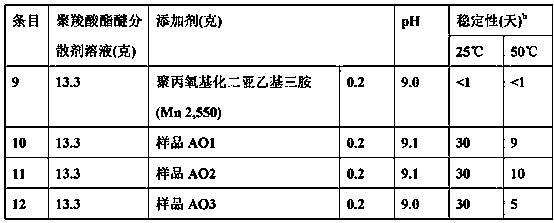
[0050] Amine oxide samples AO2 and AO3 were synthesized in a similar manner with increasing amounts of hydrogen peroxide (Table 1).
[0051] Table 1
[0052] (synthetic amine oxides)
[0053] Amine oxide products
Embodiment 2
[0055] (preparation stability)
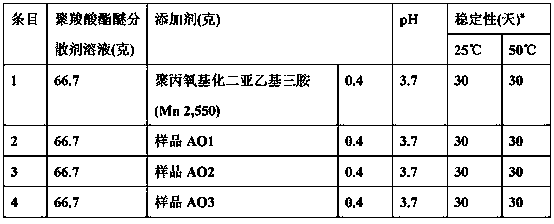
[0056] In this example, the stability of different defoamer additives in low pH blends containing polycarboxylate ether dispersants was evaluated. Admixtures containing defoamers were prepared according to the recipe in Table 2. Water (32.9 grams), Sample AO1 (0.40 grams) and 60% aqueous polycarboxylate dispersant solution (66.7 grams) were added to the beaker with stirring, and the mixture was stirred until it became homogeneous. The pH of the mixture was adjusted to 3.5-4.0 with acetic acid. The mixture was kept in a 50 ml cylinder in an oven at 25°C and 50°C while its stability was monitored visually for 30 days or until phase separation occurred.
[0057] Table 2
[0058] (Admixture Stability Test)
[0059]
[0060] a Stability is expressed by the time before phase separation is observed for a maximum of 30 days.
[0061] As can be seen from Table 2, the amine oxide defoamer additives AO1, AO2 and AO3 are as stable in the admixture u...
Embodiment 3
[0063] (preparation stability)
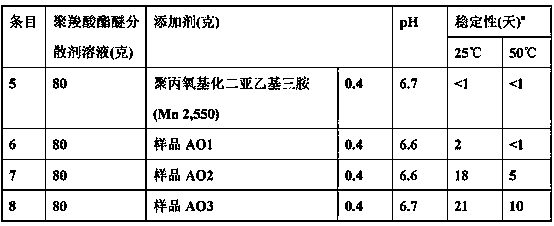
[0064] In this example, the stability of different defoamer additives in a neutral pH blend containing a polycarboxylate ether dispersant was evaluated. Admixtures containing defoamers were prepared according to the recipe in Table 3. Water (19.6 grams), Sample AO1 (0.40 grams) and 50% aqueous polycarboxylate ether dispersant solution (80 grams) were added to the beaker with stirring, and the mixture was stirred until it became homogeneous. The resulting mixture had a pH of 6.25 to 7.0. The admixture was kept in a 50 ml cylinder in an oven at 25°C and 50°C and its stability was monitored visually for 30 days or until phase separation occurred.
[0065] table 3
[0066] (Admixture Stability Test)
[0067]
[0068] a Stability is expressed by the time elapsed before phase separation is observed for a maximum of 30 days.
[0069] As shown in Table 3, the amine oxide antifoam additives are more stable in the admixture under neutral pH cond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com