Numerical computation method for predicting flue gas recirculation sintering mass-heat coupling process
A flue gas circulation and numerical calculation technology, applied in the field of iron ore sintering, can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting emission and energy consumption standards, too empirical randomization, and lack of theoretical basis for parameter values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
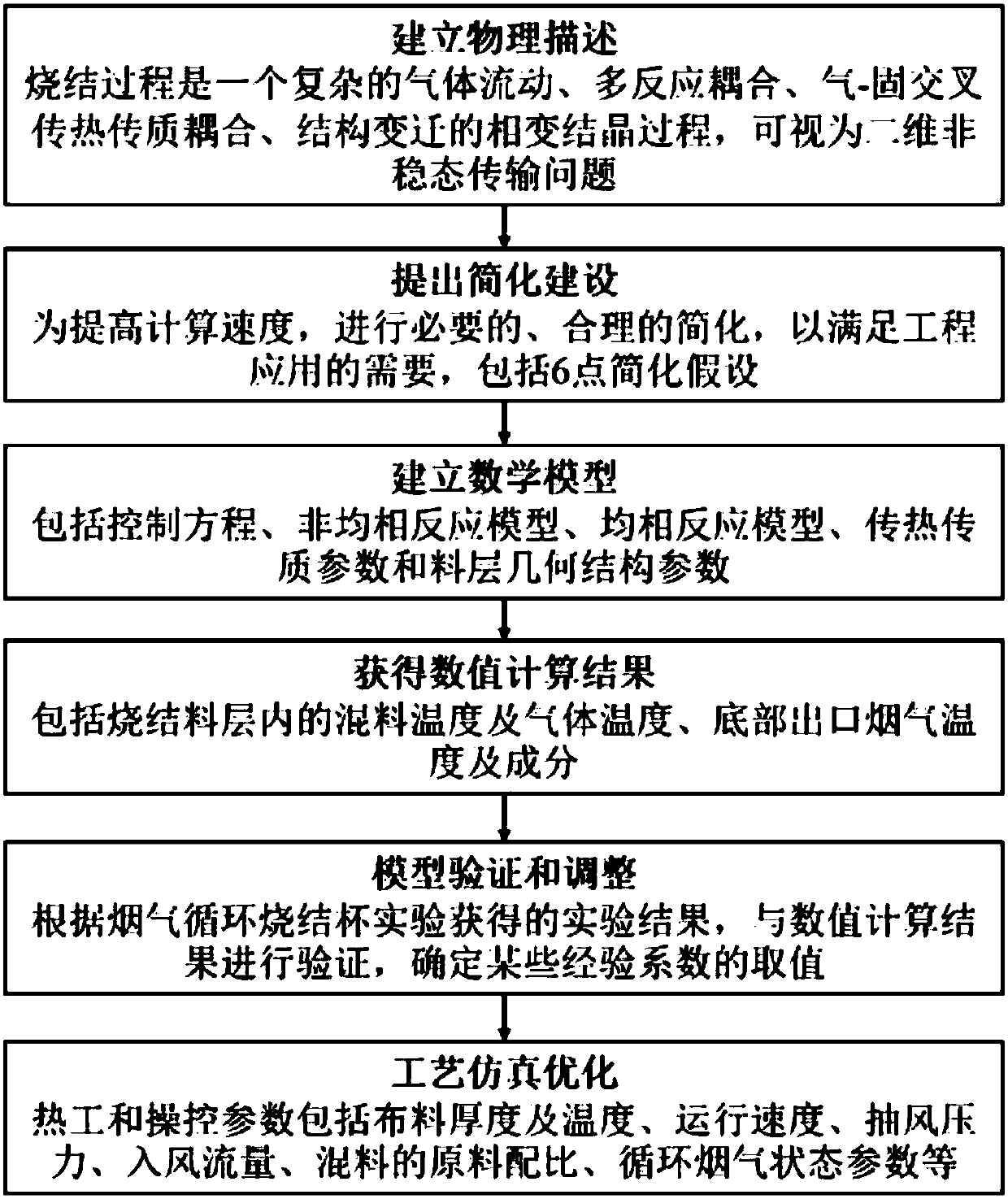
[0249] Example 1, such as figure 1 Shown, the concrete implementation process of the present invention is as follows:
[0250] Step 1, establish a physical description of the traditional sintered mass-thermal coupling process:
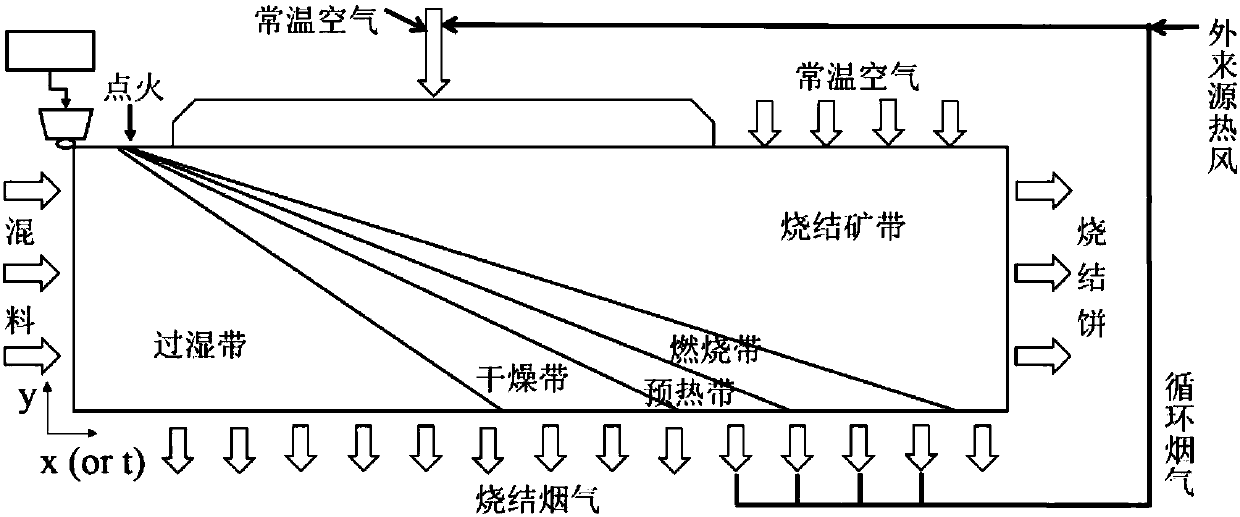
[0251] Such as figure 2 The schematic diagram of the sintering process of flue gas circulation sintering is shown. According to the temperature and physical and chemical changes, the sintering material layer can be divided into sintering zone, combustion zone, preheating zone, drying zone and over-humidity zone from top to bottom. After ignition, five zones appeared one after another, moved downward continuously, and finally all became sinter zones.
[0252] In traditional sintering, room-temperature air is extracted as sintering gas after ignition, while flue gas circulation sintering uses part of the hot flue gas generated by the sintering machine as sintering gas. In this way, the volume of circulating flue gas, the level of temperature, the ch...
Embodiment 2
[0338] This implementation provides a numerical calculation method for predicting the mass-thermal coupling process of the flue gas circulation sintering process, at least including establishing a homogeneous reaction model and solving the reaction rate of the homogeneous reaction. The homogeneous reaction model includes CO secondary combustion model, CO 2 Disproportionation reaction model, CH4 Combustion model, H 2 Combustion model, water gas reaction model and CO 2 reduction reaction model,
[0339] Among them, the calculation formula of CO secondary combustion reaction rate is:
[0340]
[0341] CO 2 The calculation formula of disproportionation reaction rate is:
[0342] CH 4 The formula for calculating the combustion reaction rate is:
[0343] h 2 The formula for calculating the combustion reaction rate is:
[0344] The formula for calculating the water gas reaction rate is:
[0345] CO 2 The formula for calculating the reduction reaction rate is: ...
Embodiment 3
[0347] As the specific scheme of embodiment 2, the method also includes the following steps:
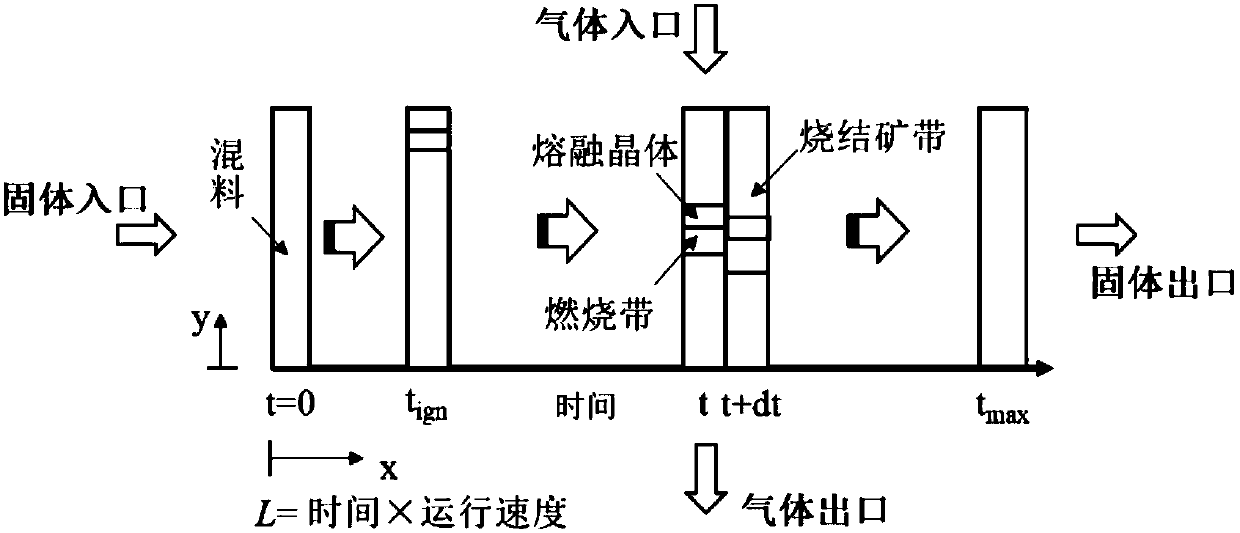
[0348] (1) Establish a mathematical model of the mass-thermal coupling process of the sintering material layer in the sintering machine, the mathematical model is a two-dimensional unsteady model, which is used to describe the flow of cross heat exchange between the sintering material layer and the gas in the sintering machine, Heat transfer combustion and chemical reaction, that is, the sintering process is simplified to a two-dimensional transport process in the thickness direction of the material layer and the running direction of the sintering machine, and a heterogeneous reaction model is established at the same time; wherein, the two-dimensional unsteady sintered mass - The governing equations for the mathematical model of the thermally coupled process include:
[0349] (1.1) Gas mass conservation equation:
[0350] (1.2) Mixed mass conservation equation:
[0351] (1.3) G...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com