Magnetic nano material capable of improving intravenous thrombolysis treating efficiency and preparation method thereof
A magnetic nanometer and intravenous thrombolysis technology, applied in the direction of medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, wave energy or particle radiation treatment materials, etc., can solve tPA difficulties, effective combination restrictions, increase cranial Internal hemorrhage rate and other issues, to achieve the effect of short half-life, reduce dosage, and increase the rate of intracranial hemorrhage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
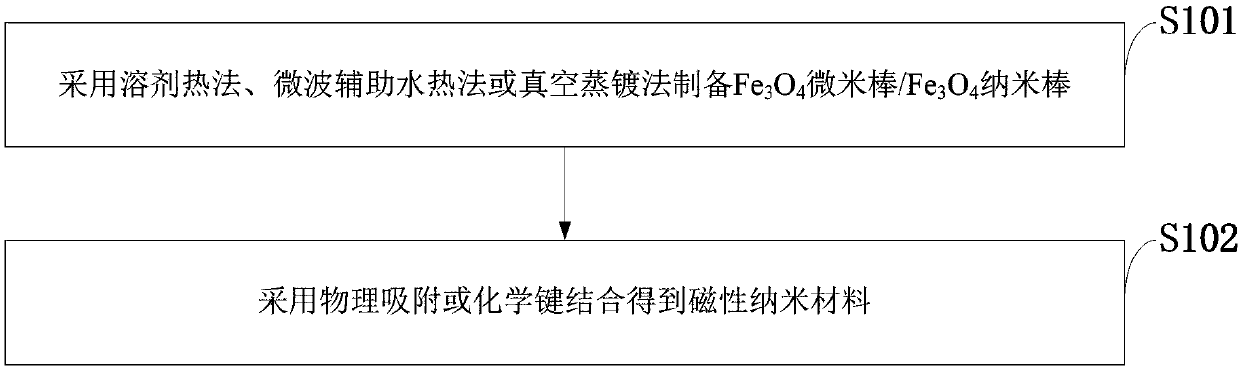
[0049] Such as figure 1 As shown, the preparation method of magnetic nanomaterials for improving the efficiency of intravenous thrombolytic therapy provided by the embodiments of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0050] S101: Prepare Fe by solvothermal method, microwave-assisted hydrothermal method or vacuum evaporation method 3 o 4 Microrod / Fe 3 o 4 Nano stave;
[0051] S102: Obtain magnetic nanomaterials by physical adsorption or chemical bonding.
Embodiment 1
[0054] The Fe provided by the embodiments of the present invention 3 o 4 The preparation method of microrod comprises the following steps: (solvothermal method)
[0055] (1) Stir 0.6-0.8g ferric nitrate nonahydrate, 0.3-0.5g glucose and 75mL ethylene glycol at room temperature for 45 minutes to form a uniform mixture;
[0056] (2) Transfer the mixed solution to a 100mL high-pressure synthesis reactor, and react at 220°C for 12 hours;
[0057] (3) The reactant is purified with alcohol and dried at 70°C;
[0058] (4) Calcining the dried product in an alcohol-nitrogen or pure nitrogen atmosphere at 350°C for 1 to 3 hours to obtain porous Fe with a length of 1.0 to 1.4 microns. 3 o 4 -C microrods.
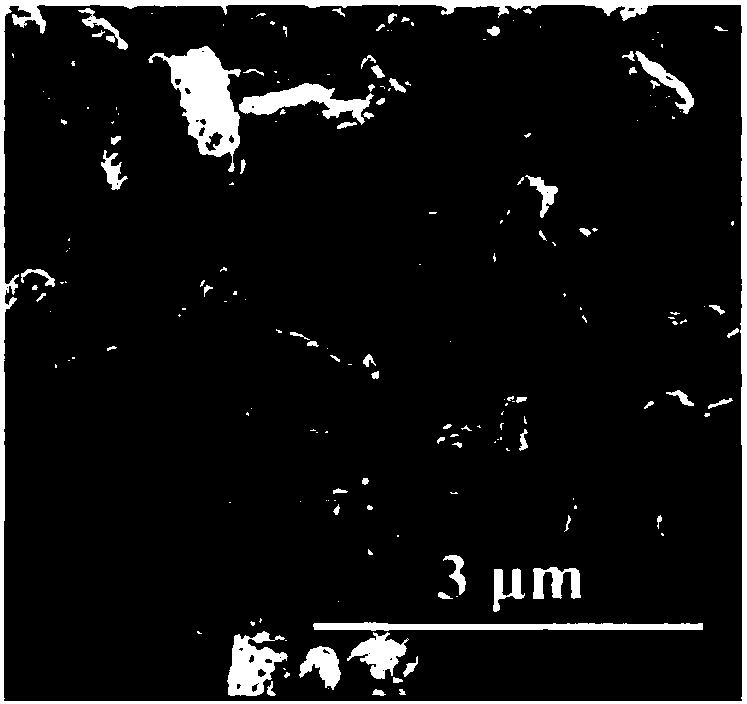
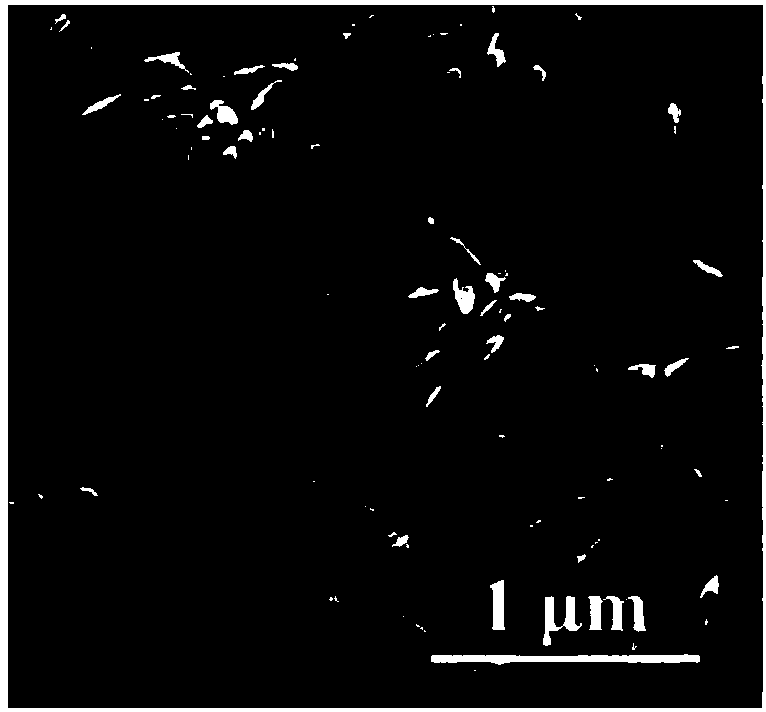
[0059] (5) Fe 3 o 4 -C microrods are calcined in air at 600°C for 2 hours, and then placed in an alcohol-nitrogen atmosphere and calcined at 350°C for 30 minutes to obtain porous Fe with a length of 1.0-1.4 microns and a width of 0.4-0.7 microns 3 o 4 Microrods (such as figu...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The Fe provided by the embodiments of the present invention 3 o 4 The preparation method of nanorod comprises the following steps: (microwave-assisted hydrothermal method)
[0062] (1) Stir 20mM~4mM ferric chloride hexahydrate, 0.45mM~0.08mM sodium dihydrogen phosphate and 10mL deionized water at room temperature for 45 minutes to form a uniform mixture;
[0063] (2) Transfer the mixed solution to a 30mL microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis reactor, and react at 160°C for 30min;
[0064] (3) Purify the reactant with deionized water and dry it at 70°C;
[0065] (4) Calcining the dried product at 350° C. for 30 minutes under an alcohol-nitrogen atmosphere to obtain Fe with a length of 50 to 400 nanometers and a width of 30 to 70 nanometers. 3 o 4 Nanorods (such as image 3 shown).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com