A small current grounding anti-misselection line method based on five-temporal phase-to-ground incremental current
A technology of small current grounding and line selection method, applied in the direction of fault location, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in distinguishing the difference of transformer excitation inrush current, single temporal signal of grounding characteristics, misjudgment and false alarm, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
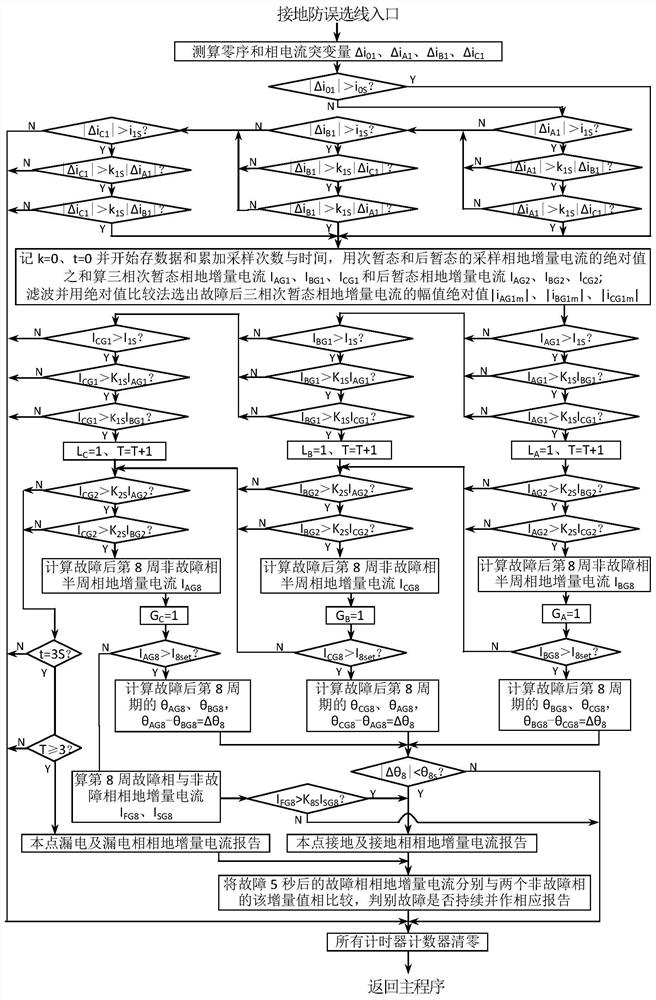
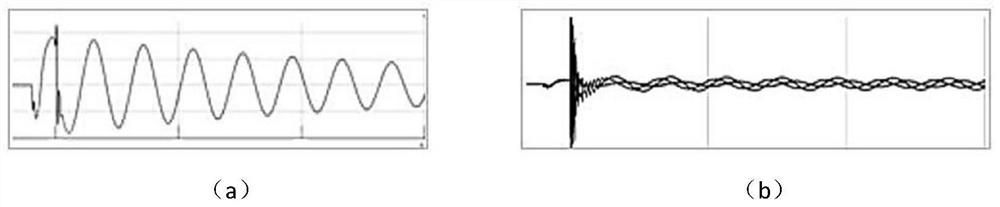
[0039] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0040] 1. Build the small current grounding monitoring system of the present invention:
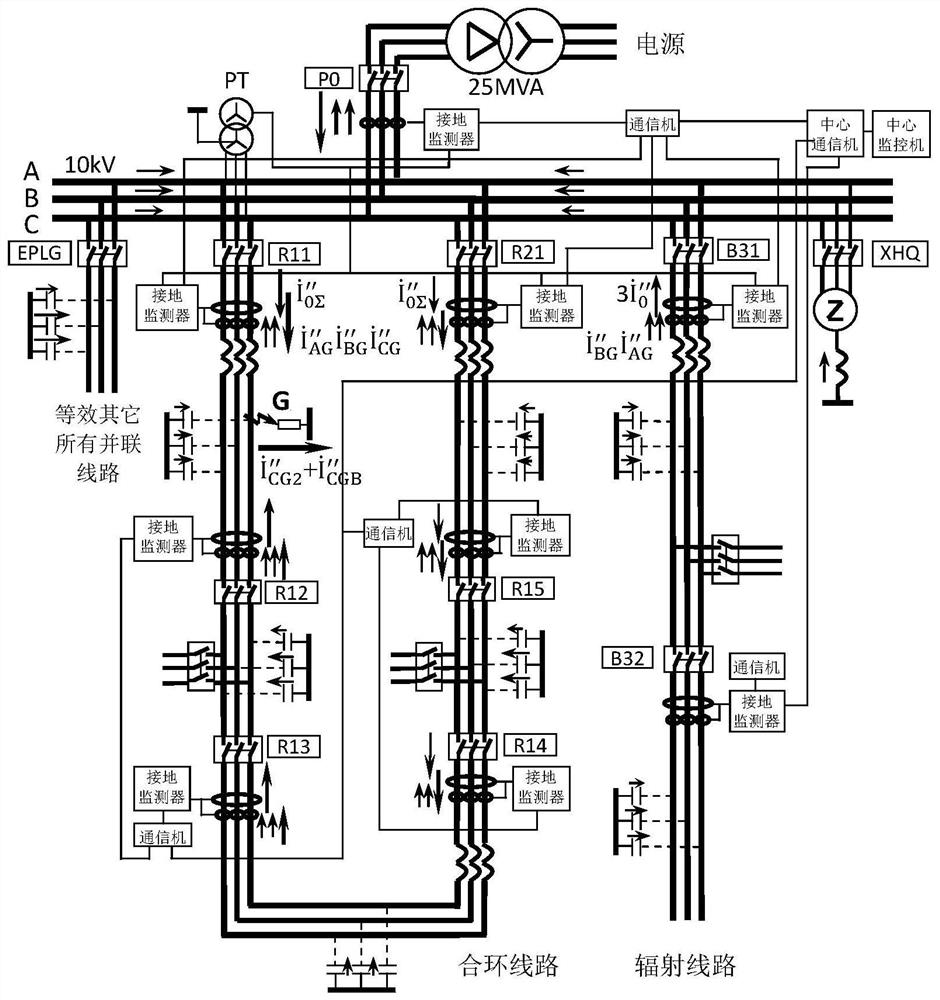
[0041] Such as figure 2 As shown in the distribution network, the matching grounding monitors of the present invention are installed at the monitoring points of each power switch, outlet switch, ring network line switch, and radiation line switch, and the three-phase current transformers and zero-sequence current transformers of each switch The current transformers are respectively connected to the grounding monitors at this place; the grounding monitors at each monitoring point are connected to the common communicator at this place, each communicator is connected to the central communicator, and the central communicator is connected to the central monitor ,composition figure 2 A small current grounding monitoring system for the distribution network shown in .
[0042] 2. Set...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com