Forging process for locomotive sliding fork
A sliding fork and locomotive technology, which is applied in the field of forging technology, can solve problems such as reduced service life, oxide pad damage on the product surface, and excessive loss of molds, so as to improve product quality and stability, avoid manual billet making processes, and improve product surface quality. Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The forging process of the locomotive sliding fork is further described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
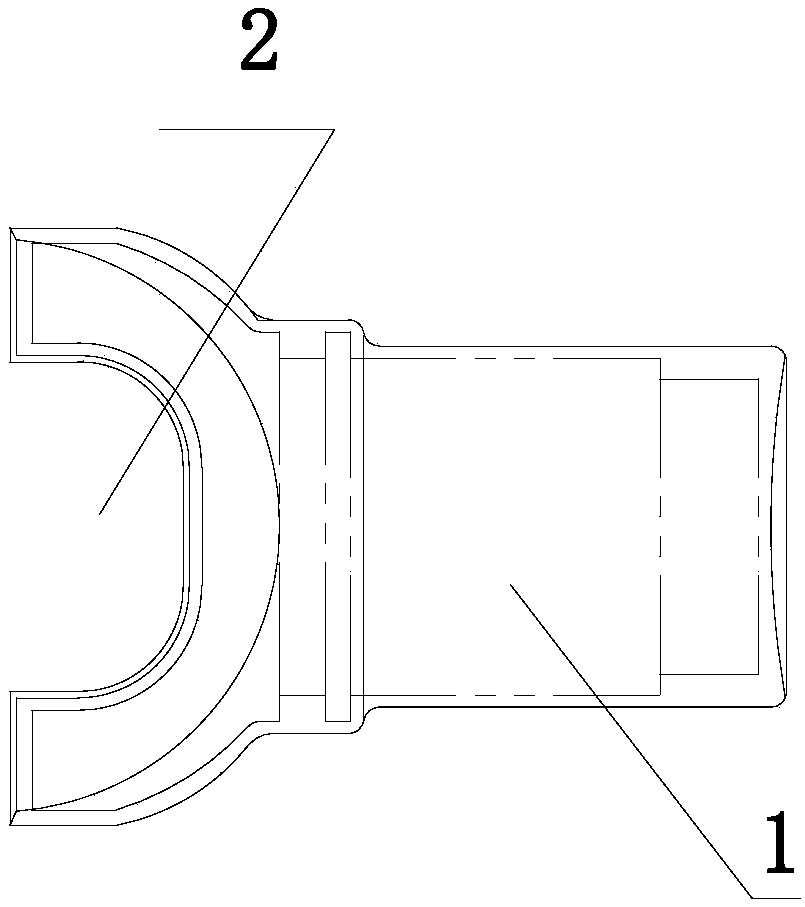
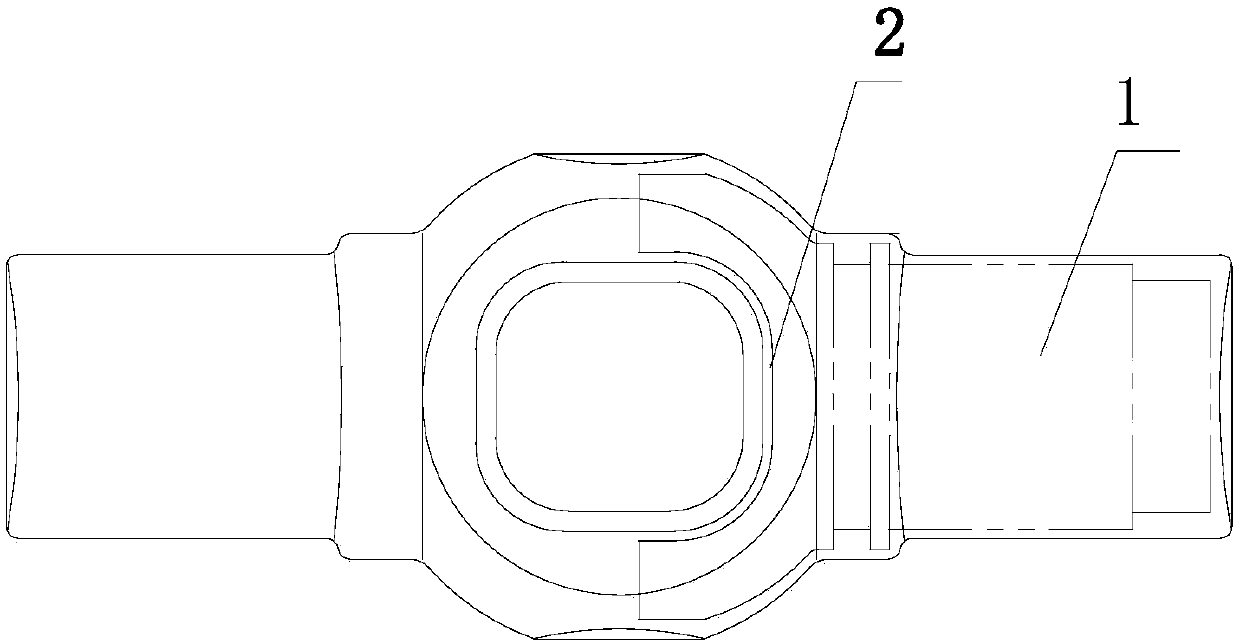
[0030] A, the sliding fork forging process for this locomotive, according to the following steps: blanking: the blanks of two sliding forks 1 are designed so that the two ends of the fork mouth 2 are opposite to form a group of blanks;
[0031] B. Heating: Heating the assembled blanks and keeping them warm after heating;
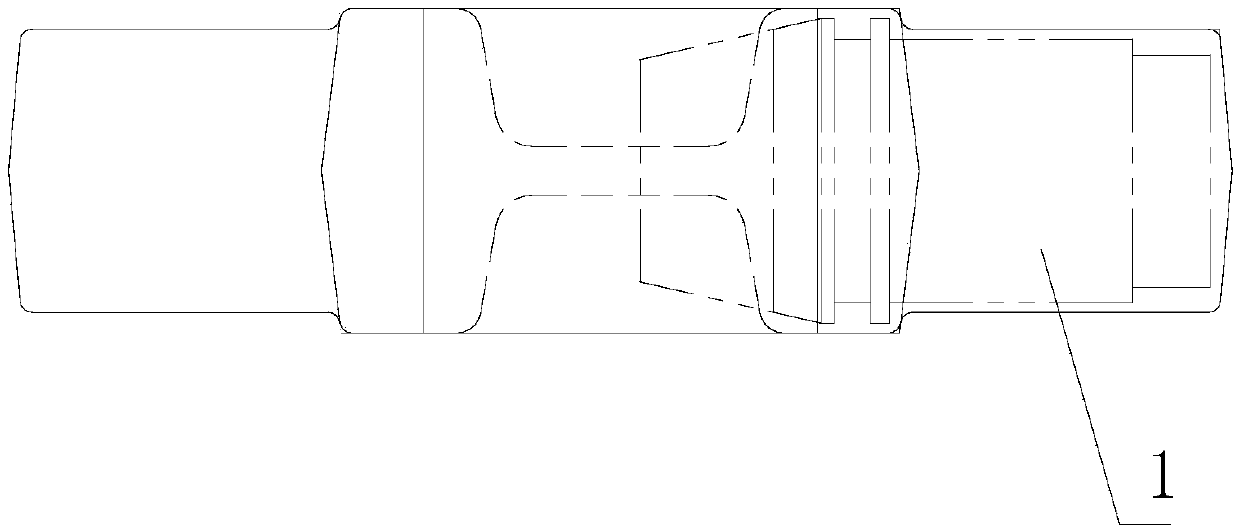
[0032] C, pre-pressing: the blank after heat preservation is put into the pre-pressing mold 3 for pre-pressing and forming, and removes scale at the same time;
[0033] D. Final forging: put the pre-pressed blank into the final forging die for final forging;
[0034] E. Edge trimming: use a press to remove flash from the final forged billet;
[0035] F. Cutting: Cut the cooled billet with flash removed, and divide it into two parts to obtain two sliding forks 1 for locomotives.
[0036] In the described blanking step, the blankin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com