Method for improving security of physical layer of collaborative network by using energy collection
A physical layer security and energy harvesting technology, applied in the direction of advanced technology, reducing energy consumption, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of improving energy utilization efficiency, saving power, and improving physical layer security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
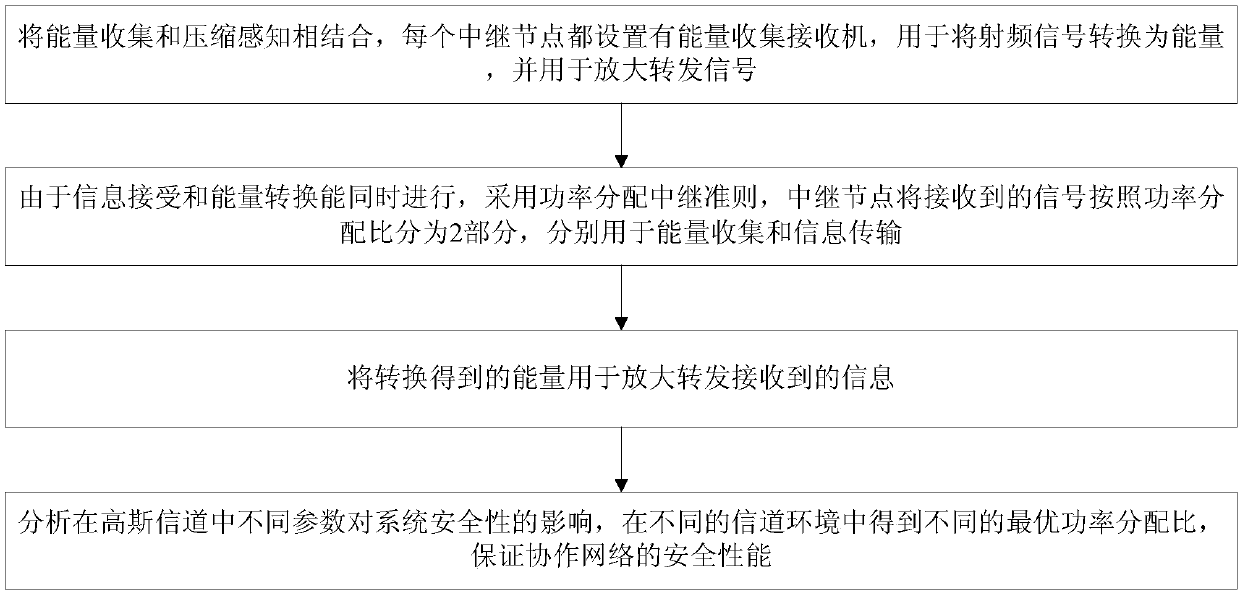
[0032] An approach to using energy harvesting to improve the physical layer security of collaborative networks, see figure 1 , the method includes the following steps:
[0033] 101: Combining energy harvesting and compressed sensing, each relay node is equipped with an energy harvesting receiver for converting radio frequency signals into energy and amplifying and forwarding signals;
[0034] 102: Since information reception and energy conversion can be performed at the same time, the power distribution relay criterion is adopted, and the relay node divides the received signal into two parts according to the power distribution ratio, which are used for energy collection and information transmission respectively;
[0035] 103: Using the energy converted in step 101 to amplify and forward the received information;
[0036] 104: Analyze the impact of different parameters on system security in Gaussian channels, and obtain different optimal power allocation ratios in different ch...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Combine below figure 1 , figure 2 And concrete calculation formula, example are further introduced to the scheme in embodiment 1, see the following description for details:
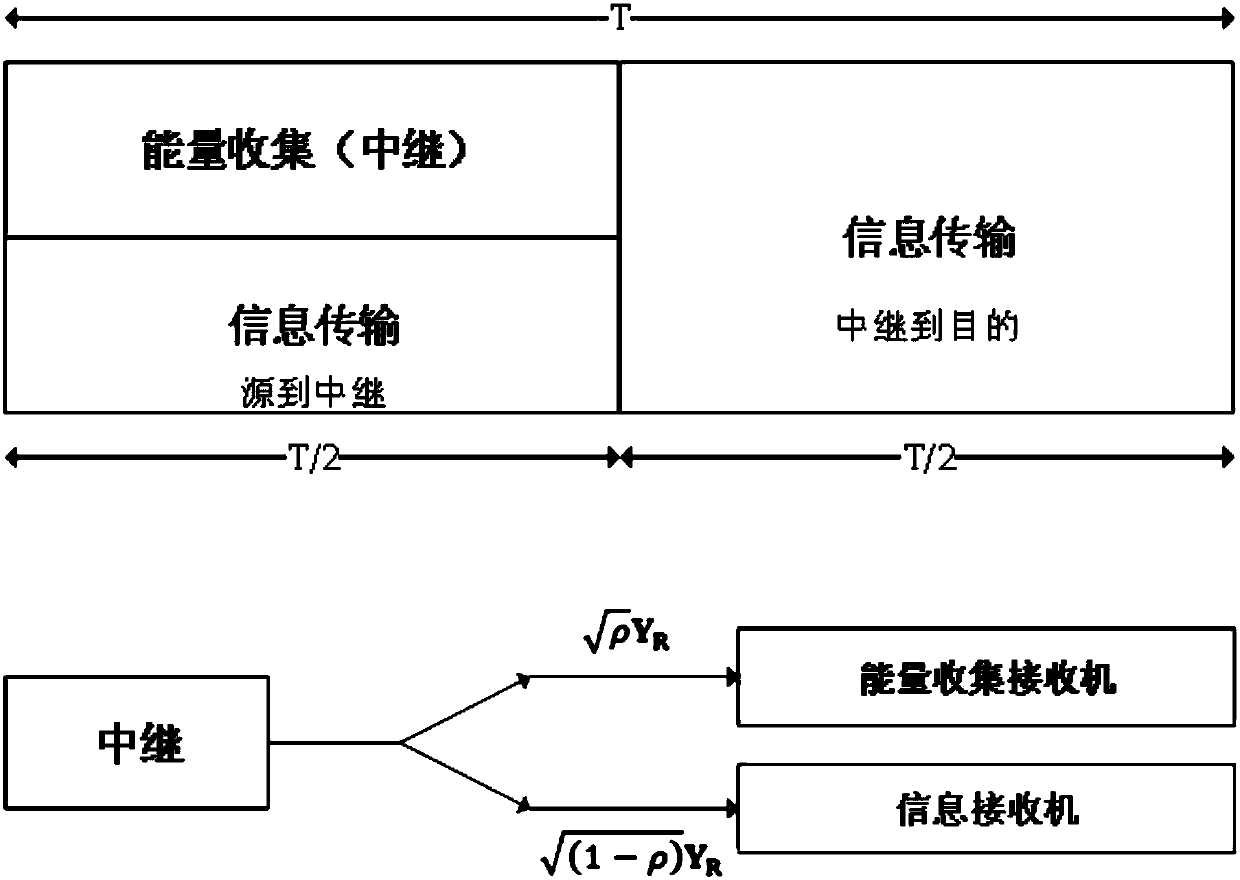
[0040] Among them, the working mechanism of the energy harvesting network provided by the embodiment of the present invention is:
[0041] 1) In the first time slot, all source nodes S send information to the relay node R at the same time, and the relay node R divides the received signal into two parts according to the power allocation ratio, and the first part is used for energy collection (converted into energy) , the second part as information;
[0042] 2) In the second time slot, the relay node R uses the collected energy (the first part) to amplify the received information (the second part), and forwards it to the destination node D.
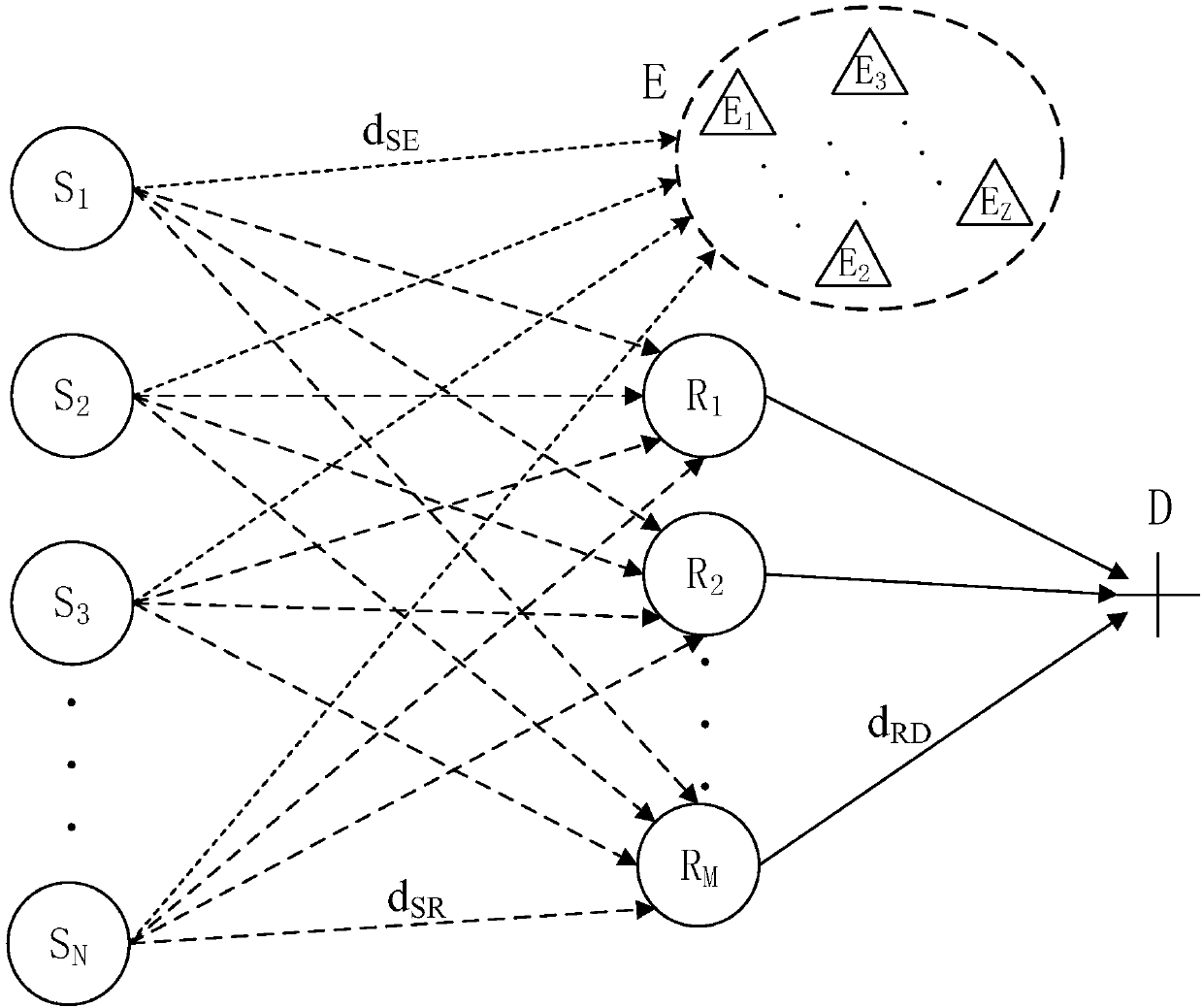
[0043] 201: Construct a compressed sensing collaborative network model based on energy harvesting;
[0044] Among them, see figure 1 , assuming that there...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Combined with the specific experimental data, Figure 4 The scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
[0077] There are 15 source nodes S, 4 relay nodes R, 2 eavesdropping nodes E, and 1 destination node D in the network. The distance between the source node and the relay node is normalized, that is, d SD = d SR +d RD = 1, the energy harvesting mechanism only needs to provide power P for the source node S S , the non-energy harvesting mechanism needs to provide the power P of the source node S S and relay power P R , then the sum of the power provided by the non-energy harvesting mechanism is P=P S +P R =10 -2 W.
[0078] Figure 4 It shows that the distance between the relay node R and the source node S is d SR =0.3, the total power P of non-energy harvesting is fixed (P=10 -2 W), the power P of the source node S of the two mechanisms S At the same time, the safe capacity varies with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com