HPLC analysis of impurities in dianhydrogalactitol
A technology of dianhydrodulcitol and dulcitol, which is applied in the field of HPLC analysis of impurities in dianhydrodulcitol, and can solve the problem of high incidence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
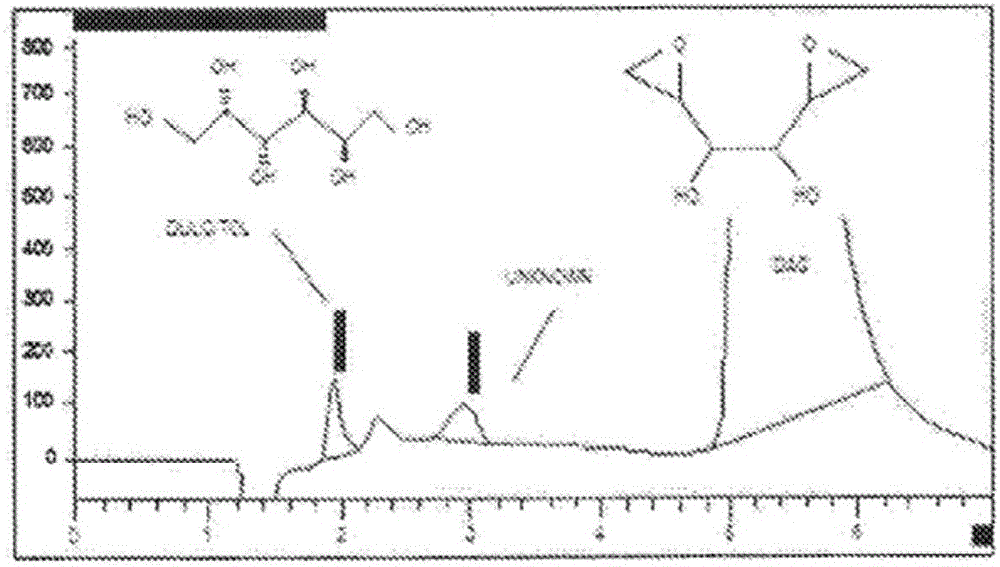
[0083] Example 1. HPLC Analysis of Didehydrodulcitol Preparation Using Isocratic Sodium Hydroxide Elution
[0084] Dulcitol and related impurities in pharmaceutical formulations of didhydrodulcitol were determined by ion-exchange high performance liquid chromatography with differential refractive index detection using the procedure disclosed in this example.
[0085] During this process, the sample was prepared so that the target concentration of dianhydrodulcitol was 5 mg / mL. An anion exchange column (Hamilton RCX-10, 250*4.1 mm, 7 μm), 50 mM NaOH was used as the isocratic mobile phase, and differential refractive index detection were used to separate dulcitol, didhydrodulcitol, and related impurities. The concentration of dulcitol was determined using an external standard, and the amount of related substances was estimated using a DAG reference standard.
[0086] A suitable HPLC system and data acquisition system is an Agilent Technologies 1200 Series HPLC system or equival...
Embodiment 2
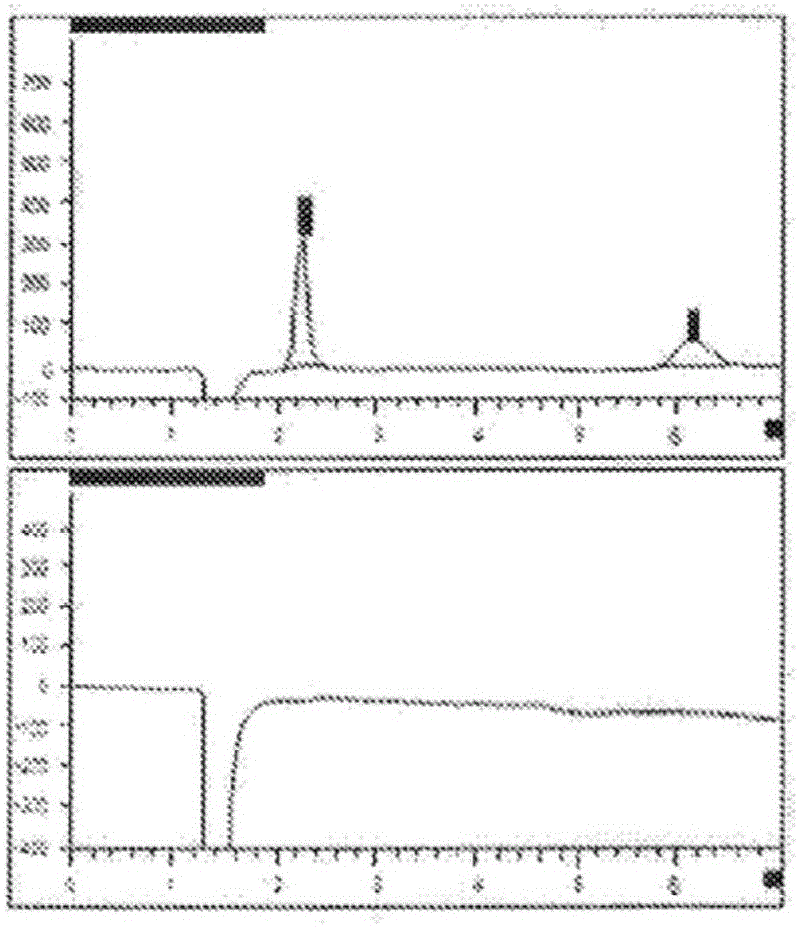
[0108] Example 2. HPLC Analysis with Evaporative Light Scattering Detector and Using Water / Acetonitrile Gradient
[0109] To improve the separation of impurities, another HPLC analysis method was employed in which an evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD) with a water / acetonitrile gradient as detailed below was used.
[0110] Due to the limitations of refractive index (RI) displays, HPLC / RI methods are not specific enough to obtain reliable impurity profile data, potentially creating an unacceptable risk of exposing patients to unknown or incompletely characterized impurities. To solve this problem, a more sensitive detector such as the Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) manufactured by Agilent (Agilent) is used in conjunction with the HPLC system to detect the presence of Dicrol in bulk drug or finished drug. impurities found in.
[0111] For example, analyze a DAG sample by HPLC / ELSD method using a YMC C18 column and the gradient shown in Table 3:
[0112] ...
Embodiment 3
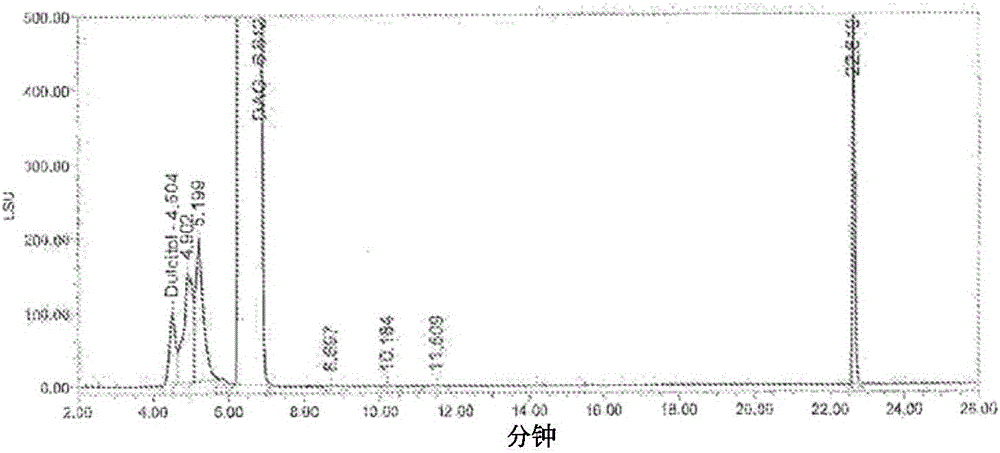
[0118] Example 3. HPLC analysis using an aqueous formic acid / methanol gradient to improve separation of monoepoxide peaks
[0119] To improve the separation of the monoepoxide peak, a new method was developed. This new method employed the following parameters: The column was Atlantis C18, 250 x 4.6 mm, 5 μm. The column temperature was 30°C. The flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. The injection volume was 100 μL. The ELSD detector was operated in cooling mode with a drift tube temperature of 35°C, a gain of 400, 2pps, and 45PSI. Mobile phase A was 0.05% formic acid in water. Mobile phase B was 100% methanol. Gradients are shown in Table 5:
[0120] table 5
[0121]
[0122]
[0123] Better separation of early eluting impurities has been observed (referred to as Figure 5 Chromatogram of the DAG sample below). Peak 2, labeled dulcitol, eluted at a retention time of 6.26 minutes or a relative retention time (RRT) of 0.59. The dianhydrodulcitol eluted at 10.86 minutes.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com