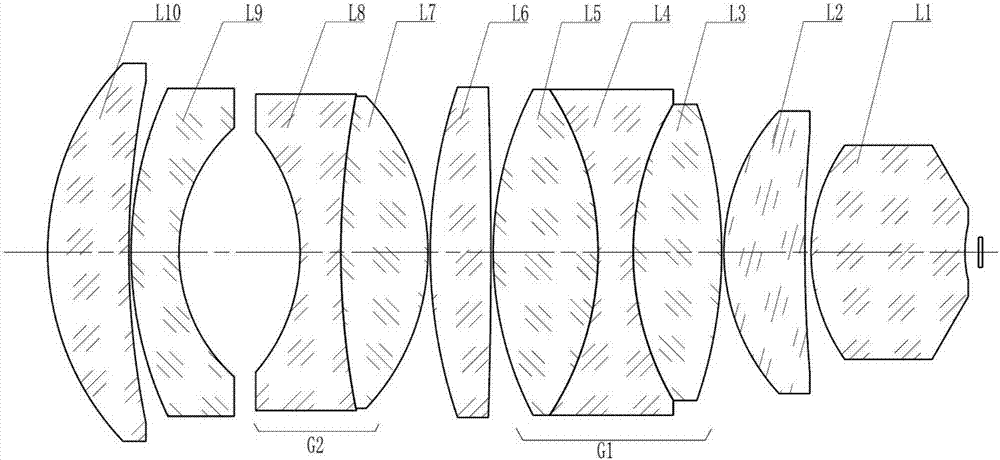
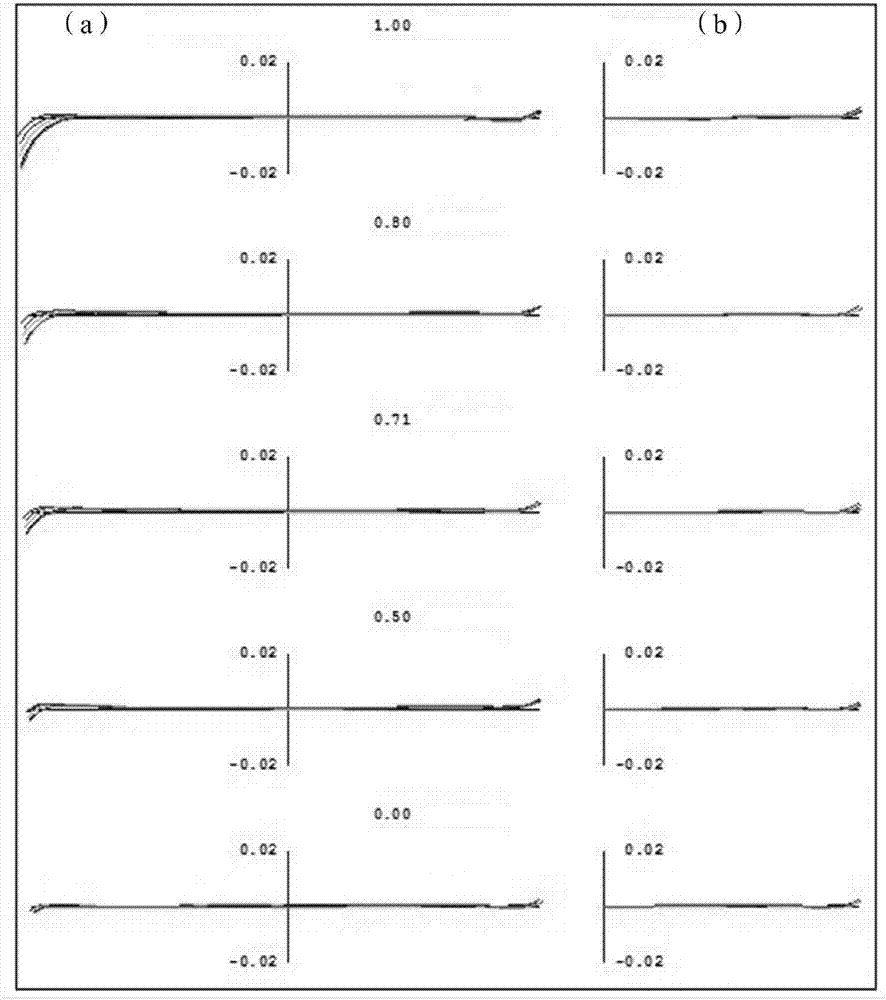
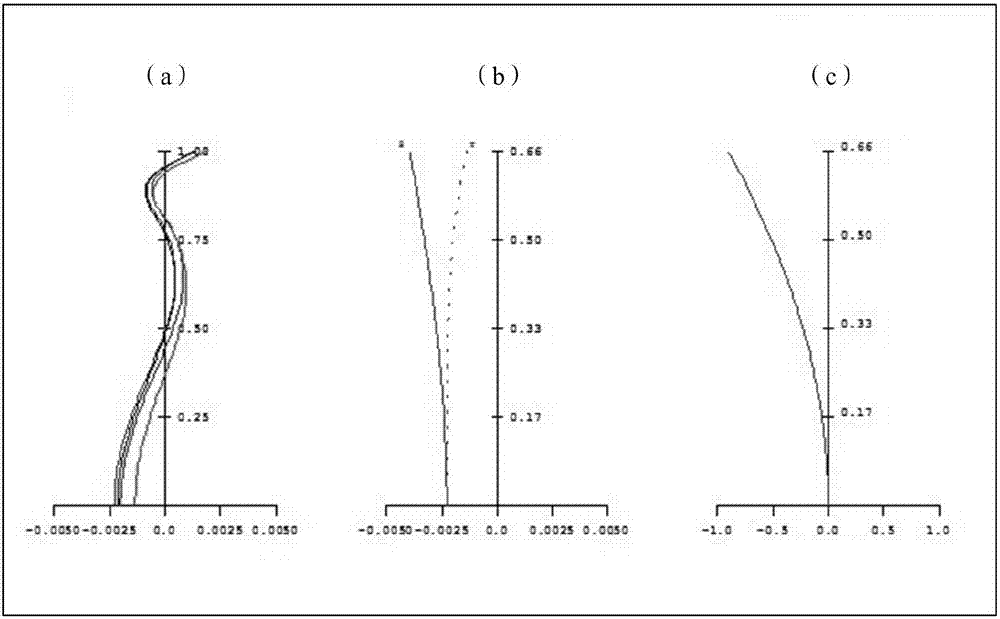
Flat-field apochromatic microscope objective
An apochromatic, microscopic objective lens technology, applied in the optical field, can solve the problems such as the inability to meet the requirements of high imaging quality and large numerical aperture of microscopic objective lenses, and the small numerical aperture of microscopic objective lenses, so as to meet the requirements of mass production, structural Simple, well-designed effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0039] As a specific implementation, the doublet lens group G2 satisfies the following relationship:
[0040] 0.8G2 / f obj <2.5
[0041] Among them, f G2 is the focal length of the doublet lens group G2, f obj is the focal length of the plan apochromatic microscope objective.
[0042] As a specific implementation manner, the ninth lens L9 satisfies the following relationship:
[0043] -3L9 / f obj <-2.1
[0044] Among them, f L9 is the focal length of the ninth lens L9, f obj is the focal length of the plan apochromatic microscope objective.
[0045] As a specific implementation manner, the tenth lens L10 satisfies the following relational expression:
[0046] 2.44L10 / f obj <4.1
[0047] Among them, f L10 is the focal length of the tenth lens L10, f obj is the focal length of the plan apochromatic microscope objective.
[0048] By implementing the above specific implementation methods, the optimization of the plan apochromat microscope objective lens can be reali...
example 1
[0050] Example 1: Starting from the image space of the tenth lens L10, the surfaces of each lens or lens group arranged in sequence from the image space to the object space are numbered. The specific structural parameters are shown in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1
[0052] face number
Radius of curvature / mm
Thickness / mm
1
11.9308
3.4693
1.75
27.58
2
36.1812
0.4449
3
16.9237
2
1.68
31.18
4
7.3102
5.0796
5
-8.1232
1.8
1.73
28.25
6
29.7912
3.893
1.43
95.16
7
-10.1394
0.0996
8
22.4724
2.66
1.75
27.58
9
-149.0062
0.1
10
14.8331
4.7229
1.43
95.16
11
-13.1687
1.5
1.61
44.09
12
13
3.8663
1.43
95.16
13
-19.9569
0.1
14
9.2056
3.594
1.52
76.98
15
55.3775
0.1
...
example 2
[0064] Example 2: Starting from the image space of the tenth lens L10, the surfaces of each lens or lens group arranged in sequence from the image space to the object space are numbered. The specific structural parameters are shown in Table 2.
[0065] Table 2
[0066] face number
Radius of curvature / mm
Thickness / mm
1
14.8203
3.2988
1.75
27.58
2
118.6351
0.1
3
15.0857
2
1.68
31.11
4
7.7327
5.0115
5
-8.2178
1.8
1.73
28.25
6
58
3.6156
1.43
95.16
7
-9.5534
0.9936
8
15.8585
3.132
1.75
27.58
9
31.575
0.5
10
15.1442
5
1.43
95.16
11
-11.7758
1.5
1.61
44.09
12
13
3.4705
1.43
95.16
13
-20.6979
0.1
14
9.7224
2.8077
1.52
76.98
15
94.0141
0.1
16
7.008...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com