Method for positioning ground faults of distributive small current
A small current grounding and fault location technology, applied in the field of barcode reading, can solve the problems of low sensitivity of line selection and location, poor safety, small grounding current, etc., and achieve the effect of setting sensitivity, preventing missed reports, and preventing false reports
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0062] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
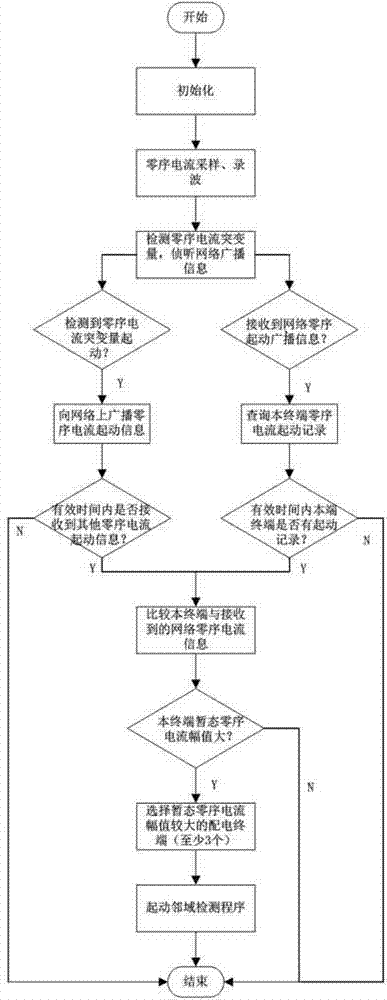
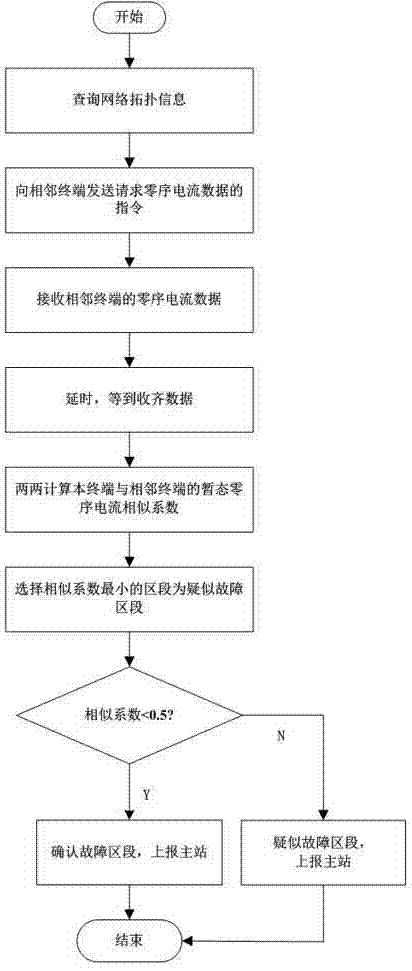
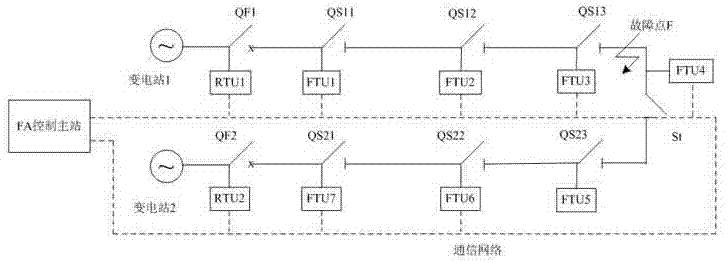
[0063] This embodiment provides a distributed small current grounding fault location method, the method is as follows figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0064] Step S1: The power distribution terminal is started with a sudden change in the transient zero-sequence current. After the start of the sudden change in the power distribution terminal, the zero-sequence current waveform is recorded, and at the same time, the transient zero-sequence information detected by the terminal is broadcast;
[0065] Step S2: After receiving the transient zero-sequence information broadcast on the network, the terminal inquires whether there is a start-up record of the sudden change within the effective time of the terminal, and if so, compares the network transient zero-sequence current with the local transient zero-sequence current Amplitude, judging the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com