Non-local-oscillator low-phase-noise microwave signal optical frequency-doubling generation device and method
A microwave signal and optical frequency doubling technology, which is applied in electromagnetic wave transmission systems, electromagnetic network arrangements, ring electromagnetic networks, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in balancing the frequency multiplication factor and frequency tunable range, and achieve excellent phase noise performance and large frequency Range tunable to improve the effect of frequency range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
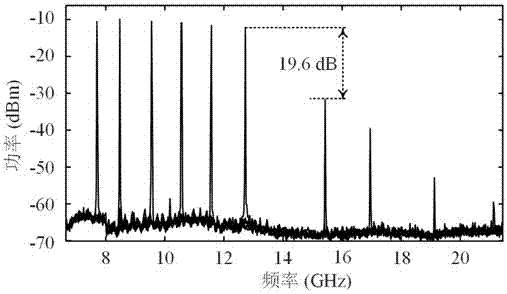
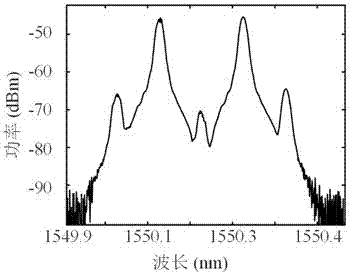
[0058]In this embodiment, the bandwidth of the PS-FBG reflection spectrum is 50GHz, the position of the extremely narrow depression on the reflection spectrum is 1549.99nm, and the bandwidth is 40MHz. increase to generate resonant signals of different frequencies. The half-wave voltage of the DP-QPSK modulator is 3.5V. The polarization controller is adjusted so that the directions of the two main axes of the polarization beam splitter and the directions of the two main axes of the DP-QPSK modulator are respectively consistent. The two sub-DP-MZMs of the DP-QPSK modulator are set as follows: the two sub-MZMs of the sub-DP-MZM constituting the optoelectronic oscillator loop are respectively biased at the maximum transmission point and the minimum transmission point, and the main MZM is biased at the orthogonal point , in another sub-DP-MZM, the sub-MZM of the input RF signal is biased at the minimum transmission point, and the sub-MZM without input sets the bias voltage so that...
Embodiment 2
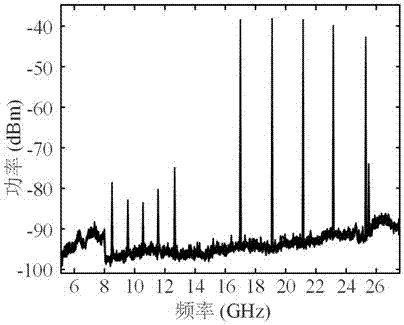
[0060] In this embodiment, the bandwidth of the PS-FBG reflection spectrum is 50GHz, the position of the extremely narrow depression on the reflection spectrum is 1549.99nm, and the bandwidth is 40MHz. increase to generate resonant signals of different frequencies. The half-wave voltage of the DP-QPSK modulator is 3.5V. The polarization controller is adjusted so that the directions of the two main axes of the polarization beam splitter and the directions of the two main axes of the DP-QPSK modulator are respectively consistent. The two sub-DP-MZMs of the DP-QPSK modulator are set as follows: the two sub-MZMs of the sub-DP-MZM constituting the optoelectronic oscillator loop are respectively biased at the maximum transmission point and the minimum transmission point, and the main MZM is biased at the orthogonal point , in another sub-DP-MZM, the sub-MZM of the input RF signal is biased at the maximum transmission point, and the sub-MZM without input sets the bias voltage so tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com