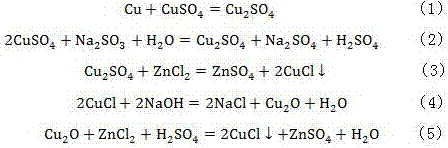Method for removing chlorine in waste zinc electrolyte
A technology for zinc electrolysis waste liquid and waste electrolyte, which is applied in the direction of electrolysis process, electrolysis components, and process efficiency improvement, can solve the problems of increased production energy consumption, high price, and a large amount of waste water, and achieves simple operation and strong practicability. , the effect of improving the recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
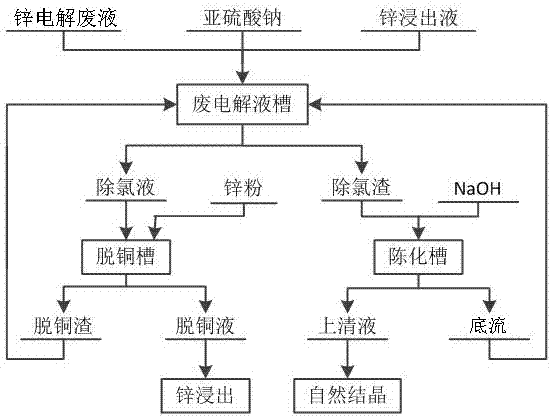
[0022] A method for removing chlorine in zinc electrolysis waste liquid, the method comprises the following steps:
[0023] (1) Add excess sodium sulfite to the waste electrolyte tank containing the zinc electrolysis waste liquid, and the ratio of the mass of chlorine in the zinc electrolysis waste liquid to the mass of sulfurous acid is 1:1, and the stirring and dissolving reaction is carried out for 10 minutes, and the stirring rate is 60r / min, after the sodium sulfite is completely dissolved, add zinc leaching solution to the waste electrolyte tank, the copper content in the zinc leaching solution is 500mg / L, and the ratio of the mass of copper in the solution to the mass of chlorine in the waste electrolyte after adding the zinc leaching solution is 1.5 : 1, the pH value of the control solution is 1, and the reaction temperature is that the reaction is 60 minutes under the condition of 30 ℃, after the precipitation is complete in the waste electrolyte tank, filter to obtain...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A method for removing chlorine in zinc electrolysis waste liquid, the method comprises the following steps:
[0029] (1) Add excess sodium sulfite to the waste electrolyte tank containing the zinc electrolysis waste liquid, the ratio of the mass of chlorine to the mass of sulfurous acid in the zinc electrolysis waste liquid is 5:1, and the stirring and dissolving reaction is carried out for 30 minutes, and the stirring rate is 300r / min, after the sodium sulfite is completely dissolved, add zinc leaching solution to the waste electrolyte tank, the copper content in the zinc leaching solution is 550mg / L, and the ratio of the mass of copper in the solution to the mass of chlorine in the waste electrolyte after adding the zinc leaching solution is 6.5 : 1, the pH value of the control solution is 5, and the reaction temperature is to react for 30 minutes under the condition of 60 ℃, after the precipitation is complete in the waste electrolyte tank, filter to obtain dechlorina...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A method for removing chlorine in zinc electrolysis waste liquid, the method comprises the following steps:
[0035] (1) Add excess sodium sulfite to the waste electrolyte tank containing the zinc electrolysis waste liquid, the ratio of the mass of chlorine to the mass of sulfurous acid in the zinc electrolysis waste liquid is 3:1, and the stirring and dissolving reaction is carried out for 20 minutes, and the stirring rate is 200r / min, after the sodium sulfite is completely dissolved, add zinc leaching solution to the waste electrolyte tank, the copper content in the zinc leaching solution is 600mg / L, and the ratio of the mass of copper in the solution to the mass of chlorine in the waste electrolyte after adding the zinc leaching solution is 4 : 1, the pH value of the control solution is 3, and the reaction temperature is that the reaction is 45 minutes under the condition of 45 ℃, after the precipitation is complete in the waste electrolyte tank, filter to obtain dech...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com