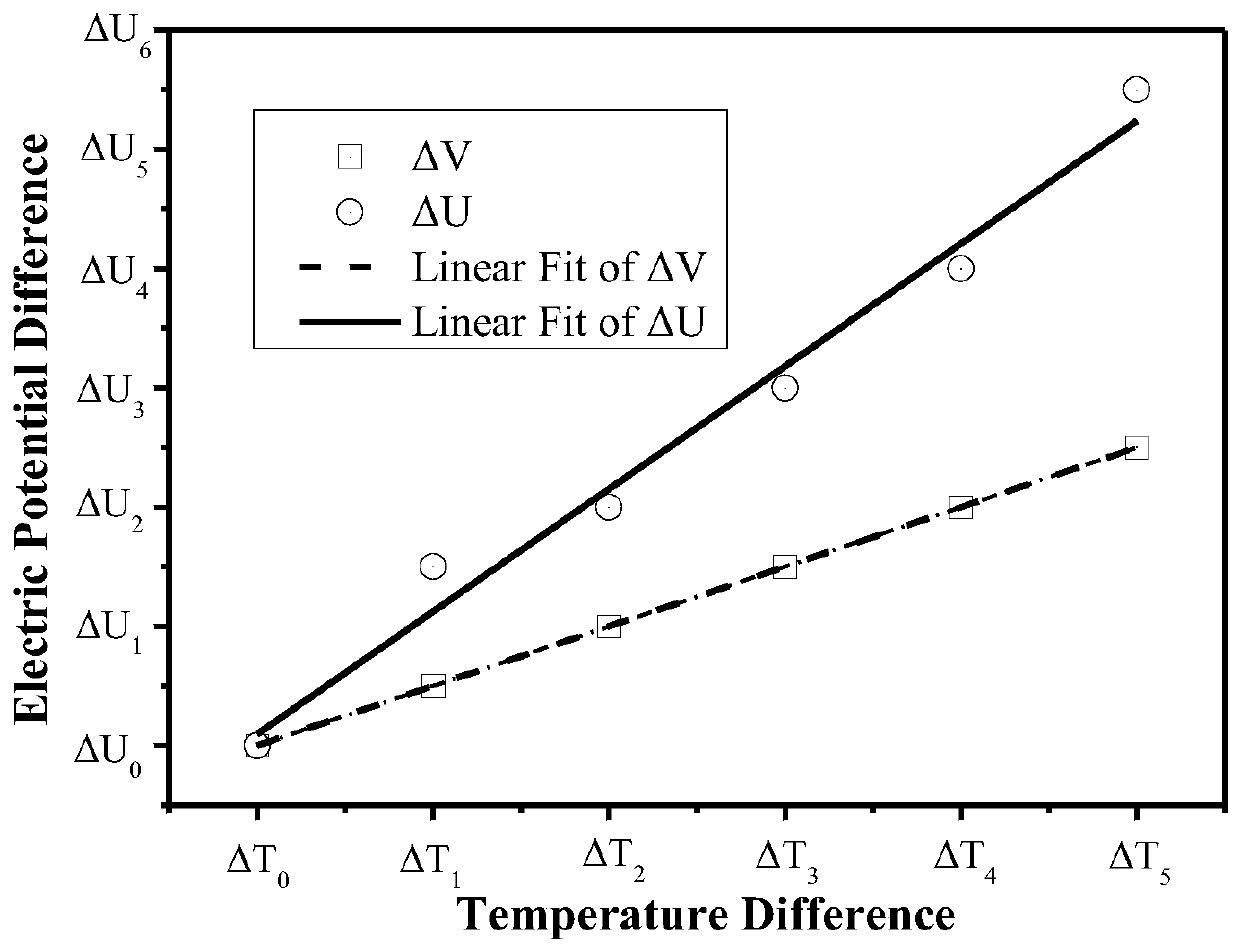
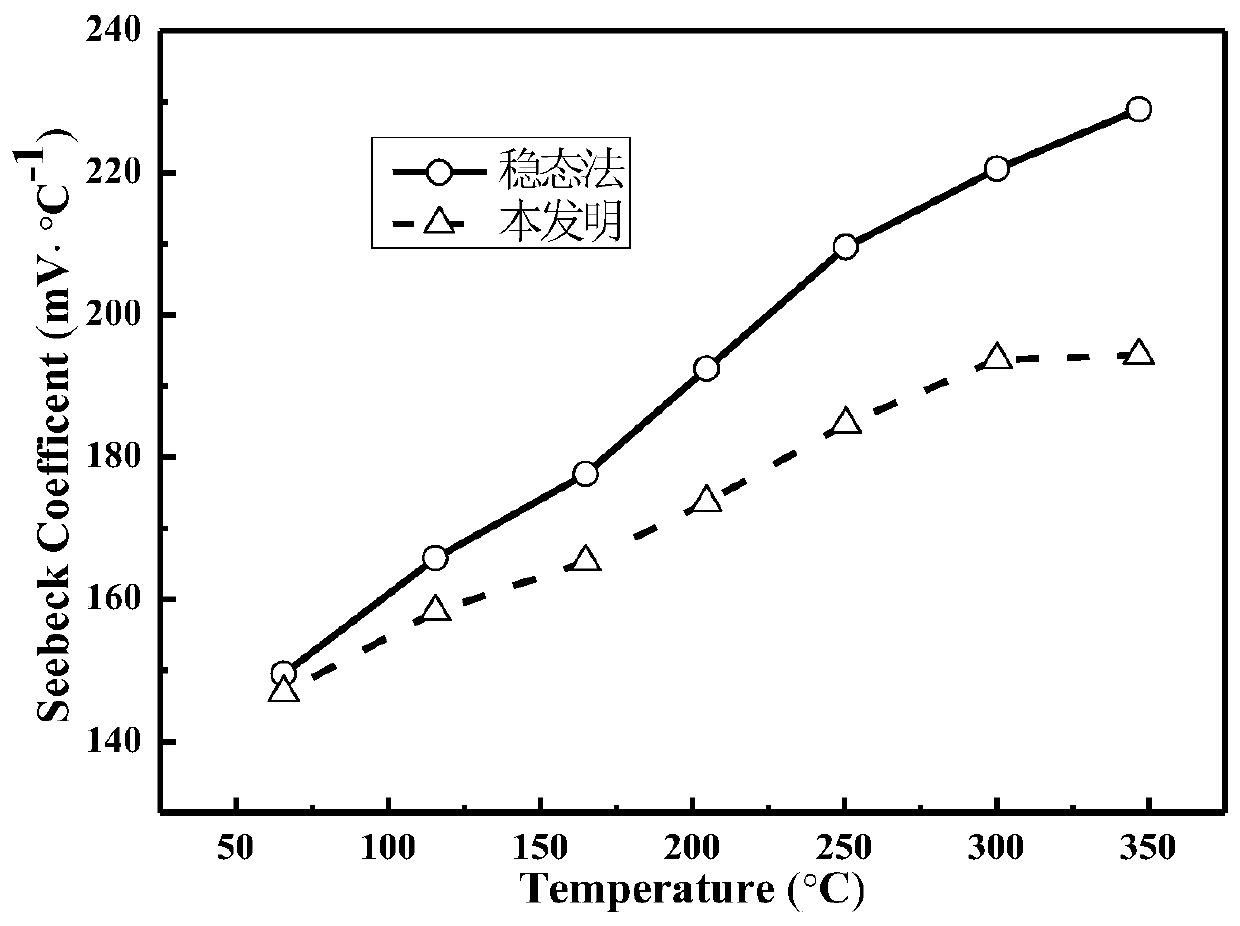
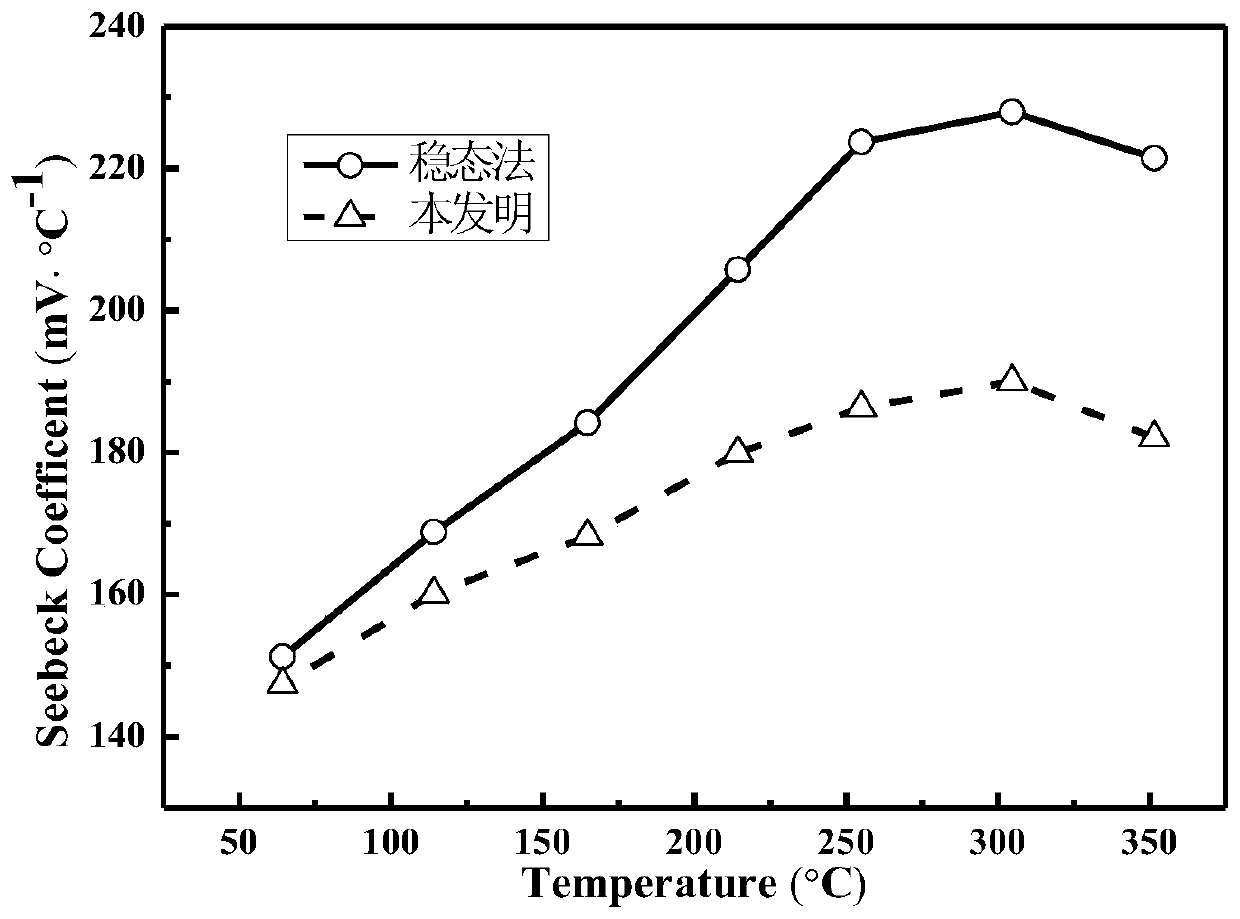
A Test Method for Seebeck Coefficient of Thermoelectric Materials
A technology of thermoelectric materials and testing methods, which is applied in the direction of material analysis, material analysis, and material thermal analysis through electromagnetic means, which can solve problems such as errors in testing, and achieve the effects of reducing requirements, low prices, and eliminating system errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings, but the present invention can be implemented in many different ways defined and covered by the claims.
[0022] At present, the thermoelectric performance of materials is generally measured by the dimensionless thermoelectric figure of merit ZT, and the expression of ZT is shown in formula 1.
[0023] ZT = α 2 ρ -1 kappa -1 T Formula 1.
[0024] Where α is the Seebeck coefficient, ρ is the resistivity, κ is the thermal conductivity, and T is the thermodynamic temperature. α, ρ, and κ are physical parameters of materials and are related to temperature. Therefore, it is of great significance to accurately test the relationship of α, ρ and κ with the change of temperature for judging the thermoelectric properties of materials.
[0025] The determination of the Seebeck coefficient of the material is mainly based on the Seebeck effect, that is, the two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com