Chlamydia-activated B cell platforms and methods thereof
A technology of B cells and chlamydia, which is applied in the direction of chlamydia antigen components, animal cells, non-animal cells, etc., and can solve problems such as inapplicability to clinical applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
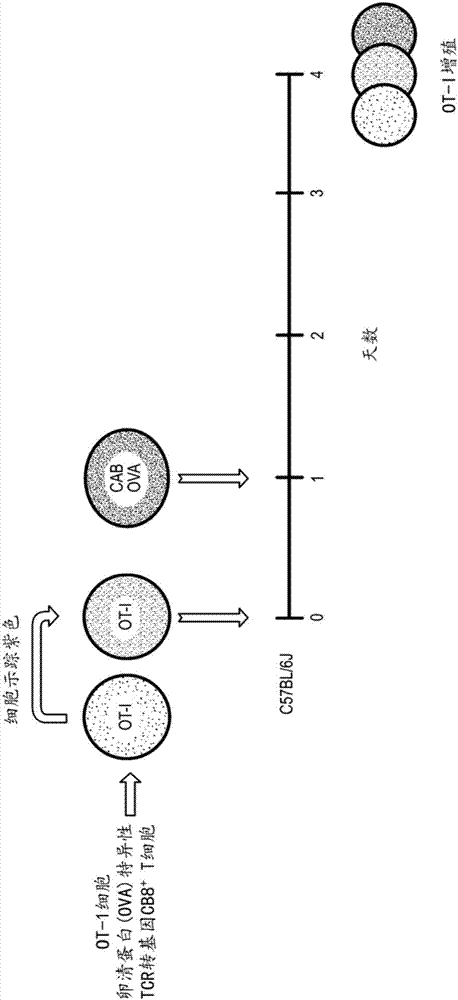
[0112] Example 1: Methods of making and using Chlamydia-activated B cells
[0113] B cells for use with the methods and platforms disclosed herein can be obtained from a variety of sources, including monocytes from peripheral blood and primary and secondary lymphoid organs such as bone marrow and lymph nodes, respectively. For example, in humans, B cells make up approximately 1% to 15% of total peripheral blood leukocytes, 20% to 25% of lymph node cells, and up to 50% of spleen cells. If desired, the frequency of B cells can be expanded in vivo by administering appropriate cytokines and recruitment growth factors (eg, IL-4, GM-CSF, and IL-3) to the patient prior to obtaining peripheral blood. Mononuclear cells are obtained from these tissues, e.g., from peripheral blood using density gradient centrifugation, while lymph node cells can be isolated from intact tonsils, e.g., by mincing the tissue and then obtaining a single cell suspension by straining . Preferably, monocyte...
Embodiment 2
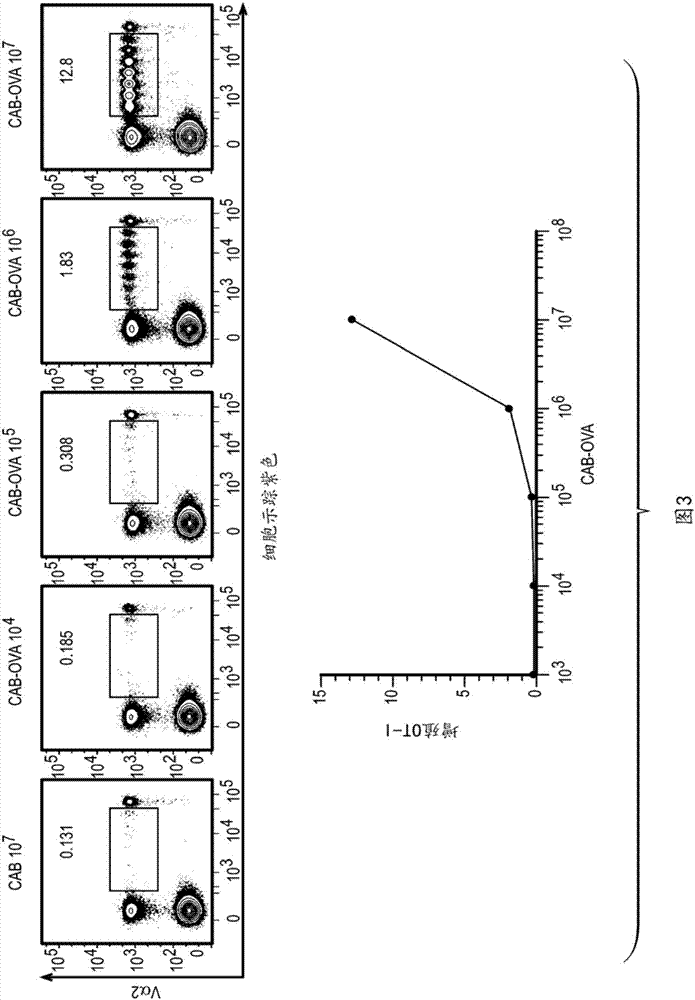
[0116] Example 2: Method of Conjugating Antigens to Chlamydia Activated B Cells
[0117] CAB was prepared as shown in Example 1. Fresh or frozen CABs can be conjugated or cross-linked with the desired antigen (protein or peptide) just prior to administration to the subject. Conjugation or crosslinking can be performed, for example, using the zero-length crosslinker 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDAC). The CAB was washed with PBS (pH 6.0) and washed with 2 × 10 8 / ml resuspension, then EDAC was added to the cell suspension, followed by the addition of sufficient concentration of antigen (protein or peptide), mixed well and incubated at 4°C for 1 hour. After incubation, the antigen-crosslinked cells are washed with PBS (pH 7.4) and can be further processed or can be prepared for administration. This procedure can be performed regardless of the source of the CAB (autologous or allogenic). Other types of crosslinkers can be used, depending on the nature of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com