Dynamic clustering underwater acoustic network routing method based on two-dimensional virtual grids
A virtual grid and underwater acoustic network technology, applied in network topology, data exchange network, power management, etc., can solve problems such as sensor node failure, node energy consumption, and network survival time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
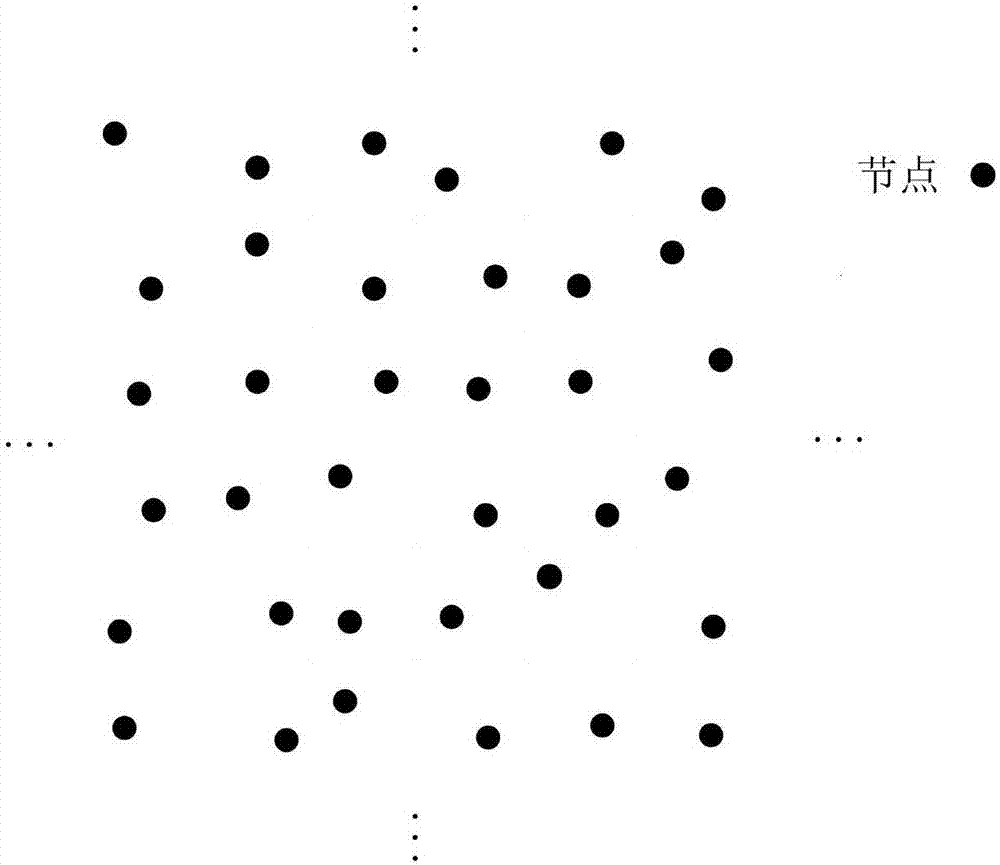
[0041] The first step: the deployment of underwater sensor network nodes, the underwater sensor network nodes are anchored by the anchor chain, the range of motion is relatively fixed, the nodes are approximately evenly distributed, and each node is assigned a unique ID;
[0042]Step 2: According to the actual distribution of nodes in the sensor network, fabricate a grid graph composed of small squares that can cover the entire sensor network. Each small square in the virtual grid graph corresponds to a node, and the size is the same as that of the node Consistent range of motion;
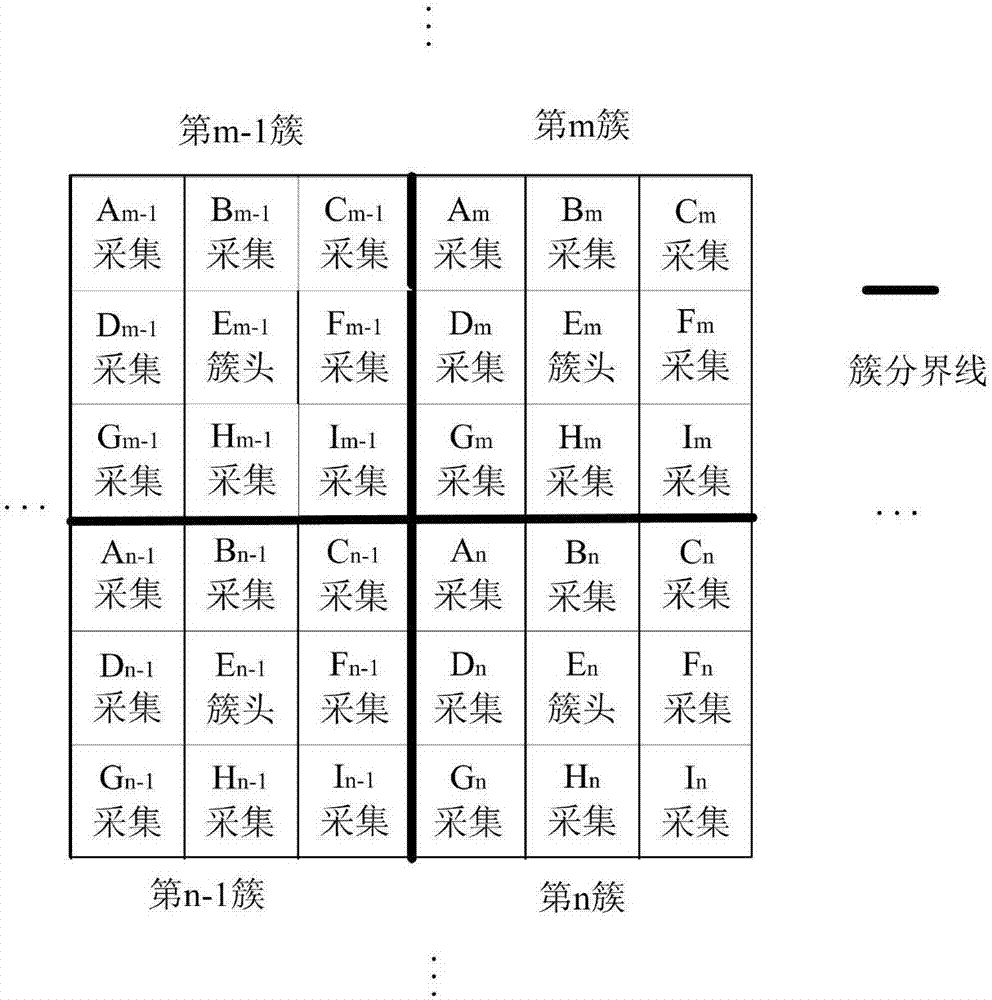
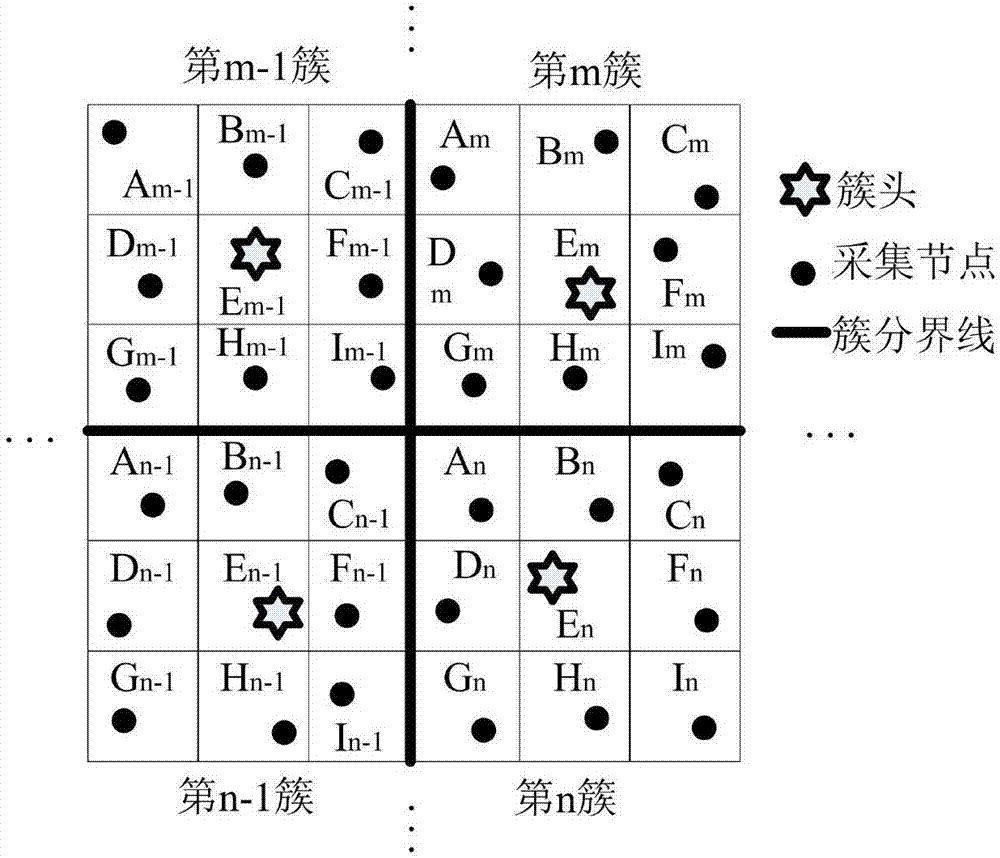
[0043] Step 3: Divide the adjacent small squares in the virtual grid graph into different cluster units, determine the size of the clusters according to the scale of the virtual grid graph, the number of nodes in all clusters is 9, and the cluster head is in each The central position of the cluster unit, the cluster unit at this ti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com