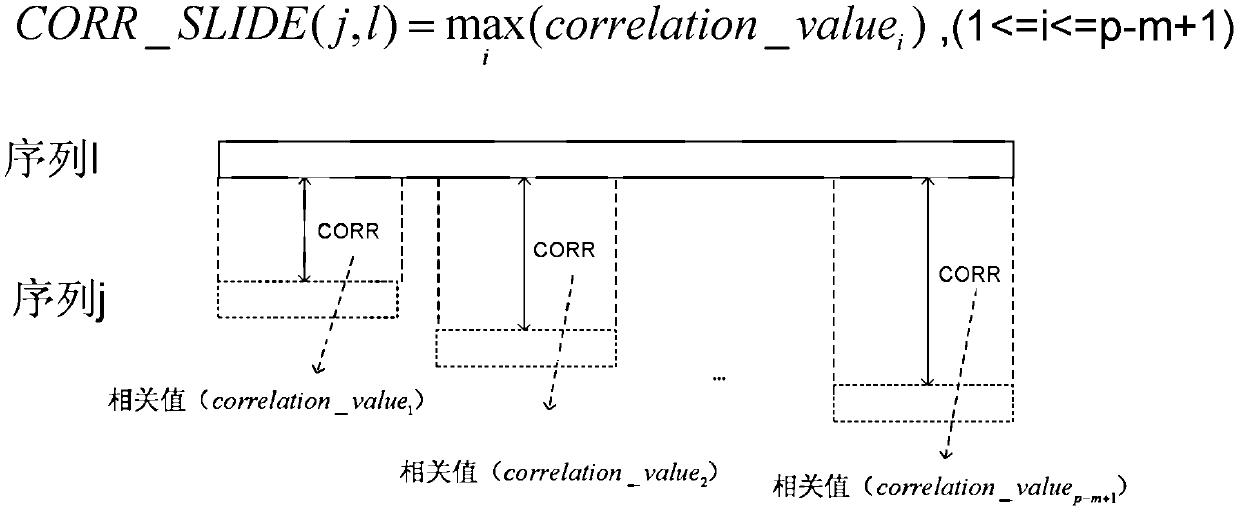
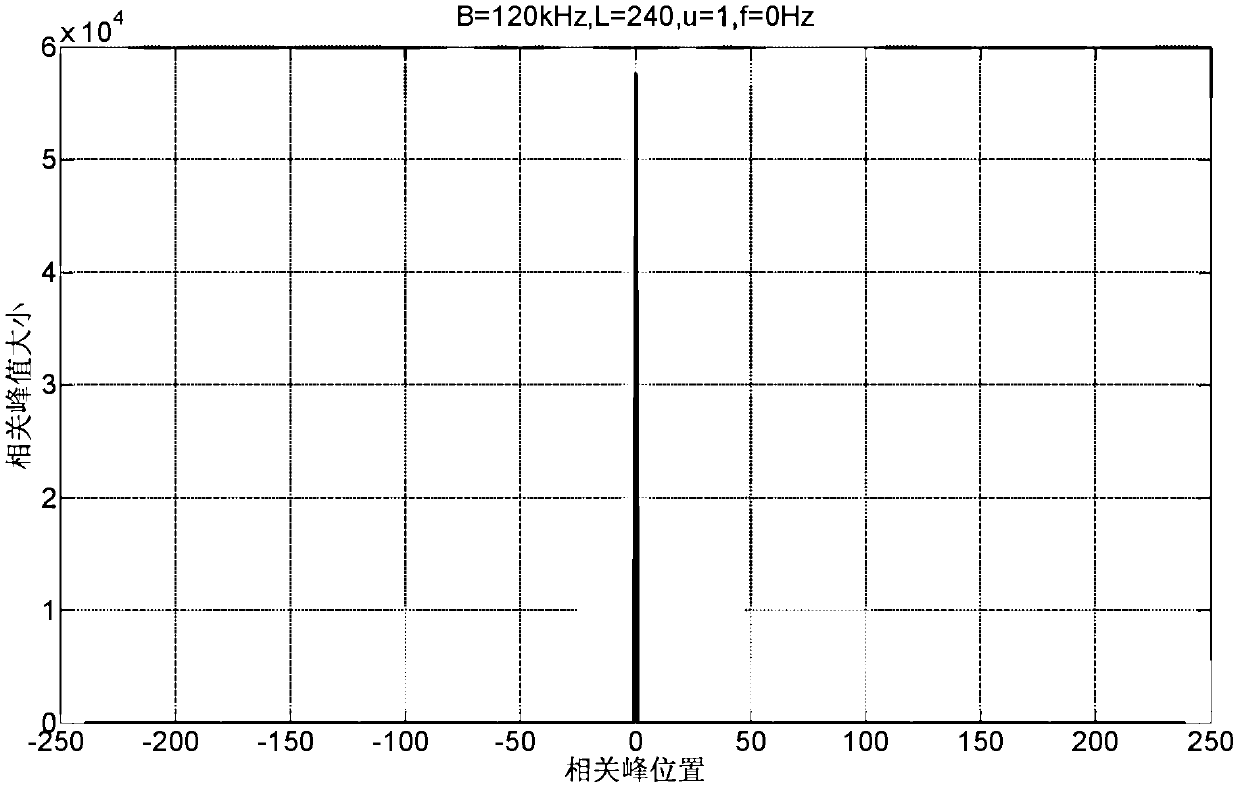
Signal transmitting device, receiving device and method and system for synchronizing symbol timing
A technology for receiving equipment and signals, which is applied in the field of signal sending equipment, receiving equipment and symbol timing synchronization, and can solve the problems of low precision of crystal oscillator, large frequency deviation of terminals, and high complexity of symbol timing synchronization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0268] N1=N2=1, the first signal includes the first generalized ZC sequence with u=1, the second signal includes the second generalized ZC sequence, and the root index of the second generalized ZC sequence is used to distinguish different cells or cell groups.
[0269] For example: the cells in the wireless communication system are divided into 3 groups, the cells of the first group correspond to the second generalized ZC sequence of u=-1, the cells of the second group correspond to the second generalized ZC sequence of u=2, and the cells of the third group correspond to the second generalized ZC sequence of u=2. A cell corresponds to the second generalized ZC sequence for u=-2.
example 2
[0271] Similar to Example 1, N1=N2=1, the first signal includes the first generalized ZC sequence of u=1, the second signal includes the second generalized ZC sequence, and the root index of the second generalized ZC sequence is used to distinguish different A district or group of districts.
[0272] Similarly, the cells in the wireless communication system can be divided into 3 groups. The difference from Example 1 is that: the first group of cells corresponds to the generalized ZC sequence of u=-1, and the second group of cells corresponds to the generalized ZC sequence of u=0.5 , the third group of cells corresponds to the generalized ZC sequence of u=-0.5.
example 3
[0274] The second signal in the synchronization signal includes a plurality of generalized ZC sequences, and the relative positions (time domain positions and / or frequency domain positions) between the plurality of generalized ZC sequences are used to distinguish cells or cell groups, that is, different cells or cell groups Corresponding to different above relative positions.
[0275] For example: when the second signal in the synchronization signal includes three generalized ZC sequences, the root indices of the three generalized ZC sequences are respectively u=1, -1, and 2, and the three generalized ZC sequences are continuously arranged in the time domain.
[0276] like Figure 5D As shown, the cells in the wireless communication system are divided into three groups, and the order of the three generalized ZC sequences corresponding to the cells in the first group is: the generalized ZC sequence with the root index of 1, the generalized ZC sequence with the root index of -1,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com