Vibration cutting process diagnostic device
A vibration cutting and diagnosis device technology, which is applied in the direction of automatic control devices, metal processing equipment, metal processing machinery parts, etc., can solve problems such as vibration, mechanical inherent vibration, and reduced processing accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
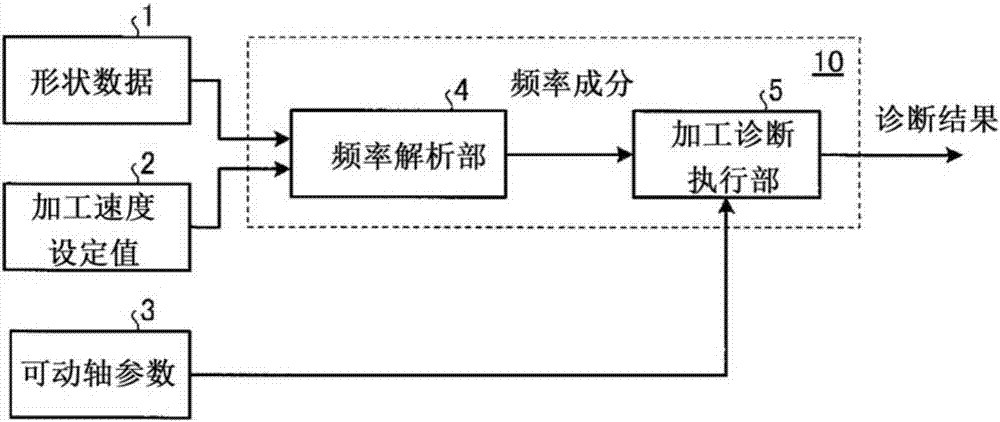
[0023] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the vibration cutting machining diagnosis device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. figure 1 The vibration cutting machining diagnosis device 10 shown is for diagnosing whether the vibrating cutting machining in which the cross-sectional shape of the object to be machined is processed into a non-circular shape by the reciprocating motion of the linear feed axis of the tool post 14 as the movable axis is performed. The vibration cutting machining diagnosis device 10 has a frequency analysis unit 4 that reads the shape data 1 and the machining speed setting value 2 of the object to be machined, and based on them, analyzes the frequency included in the position command signal of the movable shaft. components; and a processing diagnosis execution unit 5, which diagnoses whether the machining speed setting value 2 can be performed according to the shape data 1 based on the frequency components calcu...
Embodiment approach 2
[0032] The difference between the configuration of the second embodiment and the configuration of the first embodiment is that the control system of the movable axis, that is, the linear feed axis of the tool post, is a control system composed of feedback control and a notch filter. The position response characteristic of the control system of the tool post drive unit 13 is the characteristic of a band-stop filter in which the gain of the frequency band specified by the parameter of the notch filter is attenuated. The cut-off frequency band of the band-stop filter is included in the movable axis parameter 3. Here, the lower limit of the cut-off frequency band of the band-stop filter is set to F min [Hz], set the upper limit to F max [Hz]. In addition, it is assumed that the frequency component displaced in the radial direction of the cross-sectional shape of the workpiece 12 to be machined includes a harmonic component twice the rotational frequency of the turning spindle 11...
Embodiment approach 3
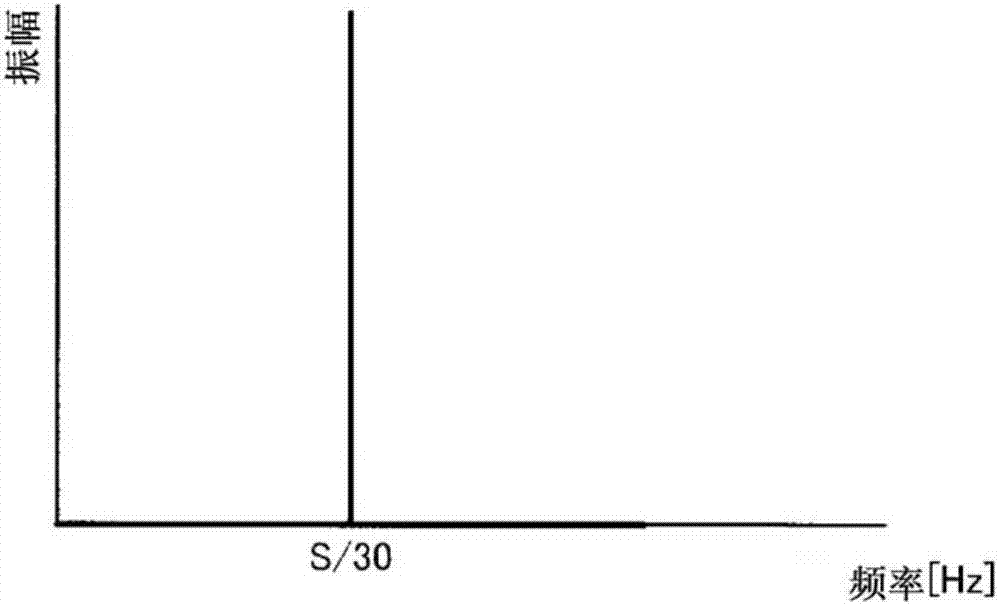
[0036] The structure of the third embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that there is mechanical anti-resonance in the shaft feed system of the linear feed shaft of the tool post which is a movable shaft. The position response characteristic of the linear feed axis is that the gain decreases at the anti-resonance frequency. In addition, the cross-sectional shape of the workpiece processed in the third embodiment is the same as that in the first embodiment, and the frequency components included in the position command signal are assumed to be as follows: image 3 shown.
[0037] The anti-resonance frequency of the mechanical system is included in the movable axis parameter 3, and the anti-resonance frequency is set to F a [Hz]. In Embodiment 3, if the anti-resonant frequency of the linear feed axis of the tool post 14, that is, F a [Hz] and the frequency S / 30[Hz] match, the machining diagnosis execution unit 5 diagnoses that machining is not possible, and if they d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com