Magnetron sputtering cavity and semiconductor processing device for silicon through hole filling
A technology of magnetron sputtering and through-silicon vias, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, sputtering plating, ion implantation plating, etc., can solve the problem of low deposition rate, increase filling rate, and increase film coverage Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
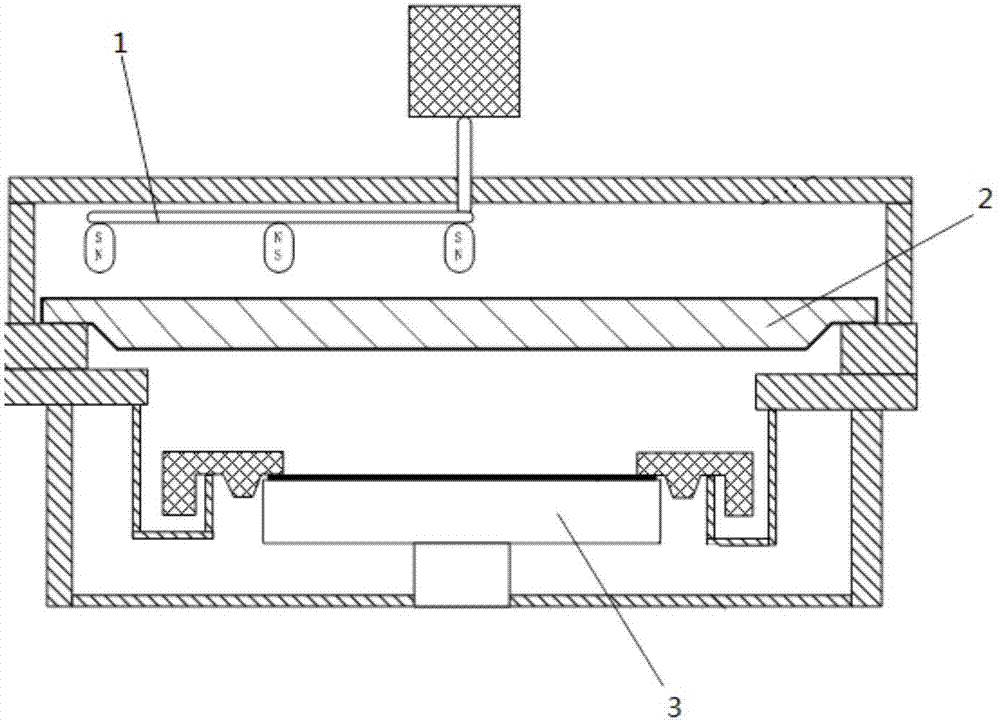
[0038] This embodiment provides a magnetron sputtering chamber for filling through-silicon vias, including: a chamber, a target disposed on the top of the chamber, a magnetron disposed above the target, and a magnetron disposed on the chamber. The base inside and under the target, the projected area of the magnetron on the target is less than one-fifth of the target area, so as to increase the ionization rate of the medium gas, thereby increasing the filling rate of the through-silicon holes.
[0039] In the prior art, the projected area of the magnetron on the target is generally 1 / 2 of the area of the target, while the projected area of the magnetron on the target used in the magnetron sputtering chamber provided by the present invention is less than One-fifth of the target area. Under the same power condition, the ionization rate of the medium gas will increase, thereby increasing the filling rate of the TSV.
[0040] Wherein, the projected area of the magnetron ...
Embodiment 2
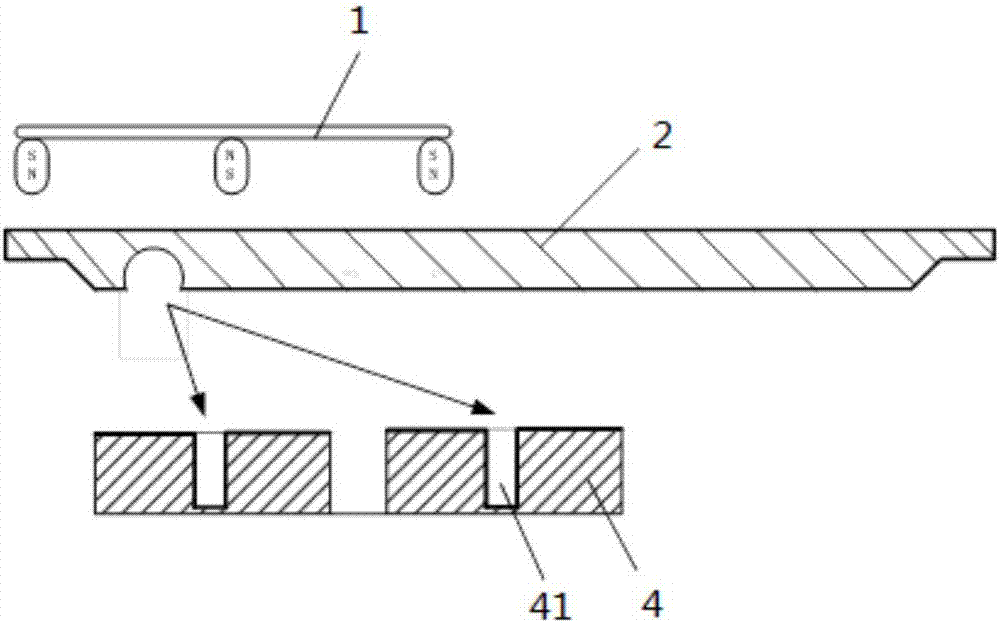
[0042] Other settings in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. The difference is that a magnetron includes magnetically opposite outer poles and inner poles surrounded by outer poles.
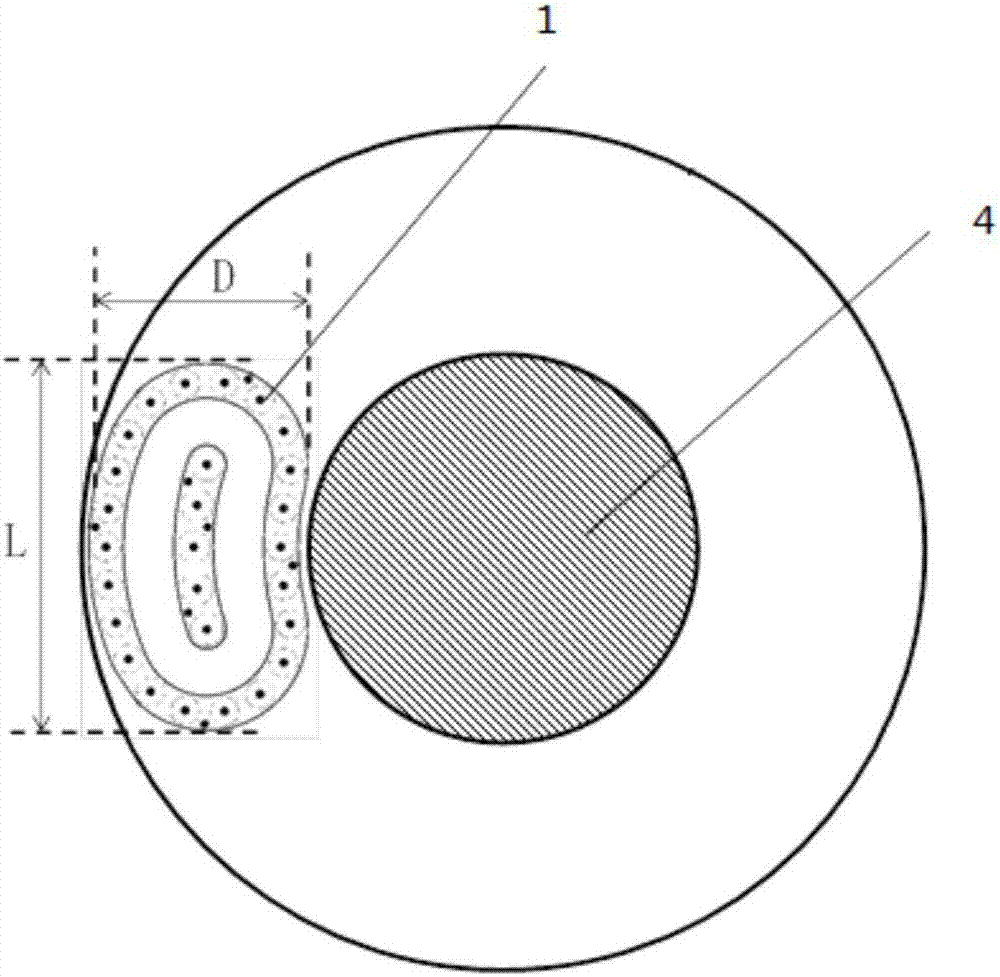
[0043] The magnetron in the magnetron sputtering chamber of the present invention includes magnetically opposite outer magnetic poles and inner magnetic poles, and the inner magnetic poles are surrounded by outer magnetic poles, further preferably as image 3 The kidney-type magnetron 1 is shown, and the magnetron can better ionize the medium gas. In addition, the outer magnetic pole of the magnetron 1 can be circular, rectangular or elliptical. Wherein, the outer magnetic pole has a long diameter L and a short diameter D, and the short diameter D is preferably less than or equal to 1 / 2 of the difference between the inner diameter of the chamber and the diameter of the wafer 4, that is, the short diameter D is less than or equal to the radius of ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Other settings in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here.
[0047] Its difference is that the magnetron sputtering chamber of this embodiment also includes a rotating mechanism, such as Figure 4As shown, the rotating mechanism 5 includes a rotating shaft 51, a first rotating arm 52 and a second rotating arm 53; one end of the first rotating arm 52 is fixedly connected to the rotating shaft 51, and the other end is connected to one end of the second rotating arm 53. The other end of the two rotating arms 53 is fixedly connected with the magnetron 1; there is an included angle between the first rotating arm 52 and the second rotating arm 53; the rotating shaft 51 drives the first rotating arm 52 and the second rotating arm 53 to rotate, thereby Drive the magnetron 1 to rotate.
[0048] Wherein, the connection mode between the first rotating arm 52 and the second rotating arm 53 can be a fixed connection or a flexible connect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com