Nucleic acid probe of specific marker nosema bombycis and in-vivo fluorescence hybridization detection method of nucleic acid probe
A technology for nucleic acid probes and microsporidia, which is applied in the field of nucleic acid probes for specific labeling of microsporidia and its in situ fluorescence hybridization detection. Problems such as training and research foundation are weak, and the results are intuitive and reliable, easy to operate, and simple and convenient to operate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1 probe design
[0030] According to the DNA sequence of N.b large ribosomal RNA subunit (LSU rRNA) and its secondary structure model, combined with FISH probes, the design and screening of FISH probes was carried out. The nucleic acid probe designed by the technical solution can specifically bind the ribosomal RNA outside the nucleus, while the general probe can only bind the DNA in the nucleus and cannot achieve the purpose of distinguishing the microsporidia of silkworms in different stages. The requirements for the FISH probe are: the length is about 18nt, and the Tm value is 48-60°C. If the Tm value is greater than 60°C or less than 48°C, the length of the probe can be adjusted appropriately. According to the above principles, two nucleic acid probes were designed, the sequences of which are as follows:
[0031] Table 1 Nucleic acid probes for specific labeling of N. silkworm
[0032] serial number name sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 NbLSU-...
Embodiment 2
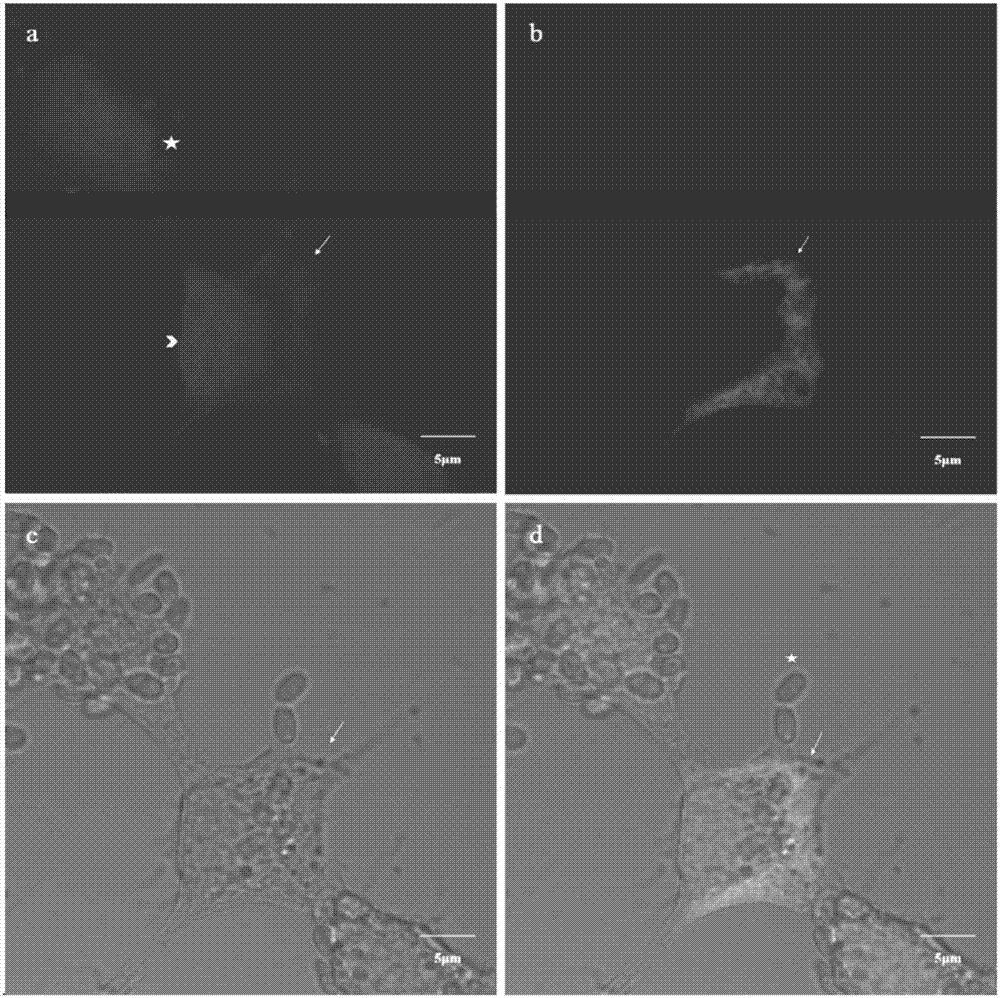
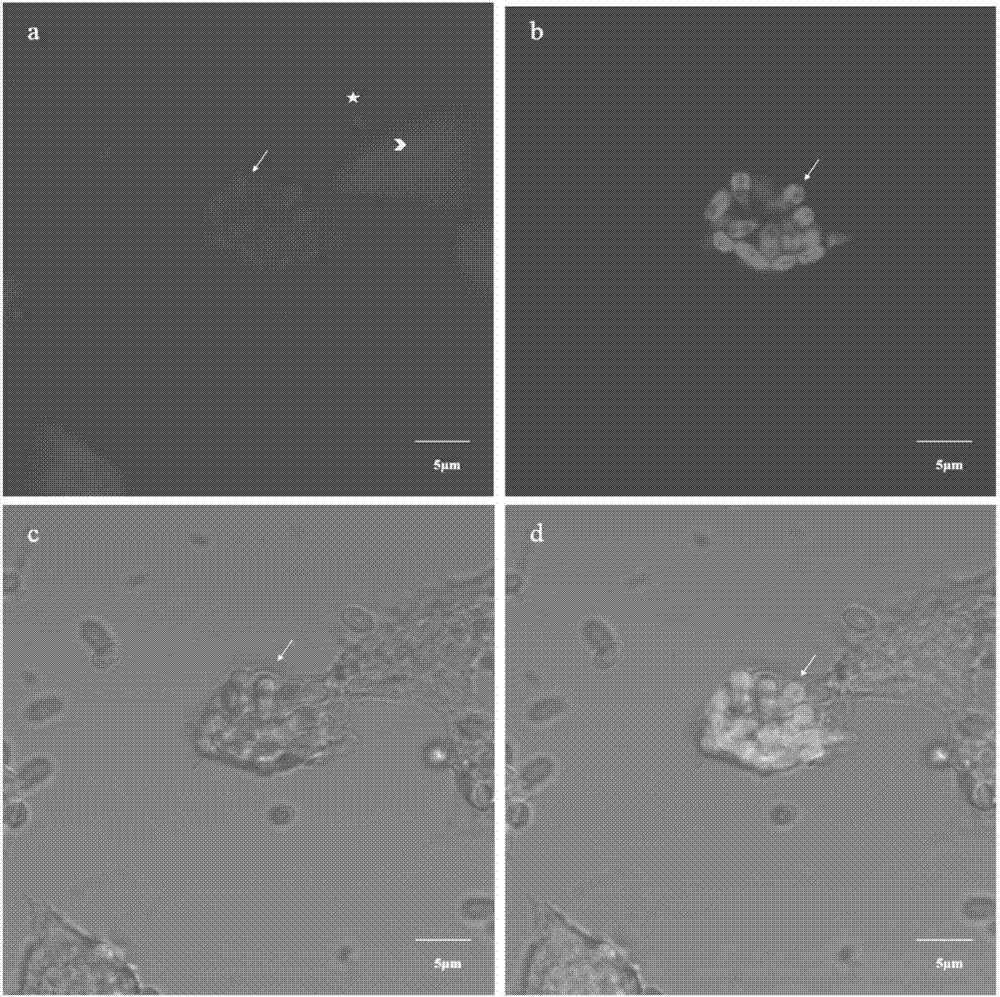
[0037] The method and result of embodiment 2NbLSU-1-Cy3 in situ hybridization experiments
[0038] 1) Preparation of silkworm BmE cells infected with N.b
[0039] Normal silkworm embryo cells (BmE) were counted according to 1X10 6 Sub-power climbing sheet (diameter 20mm), meanwhile, under aseptic conditions, get the silkworm chrysalis blood that infects Nosema bombycis (Nosema bombycis, N.b), the N.b spore wherein is counted, after counting with N.b:cell=10: The ratio of 1 was used to infect BmE cells, and the medium was changed after 6 hours of infection.
[0040] 2) FISH probe labeling of silkworm BmE intracellular hybridization N.b
[0041] 45 hours after N.b infected BmE cells, the BmE cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and the NbLSU-1-Cy3 probe was diluted with hybridization solution (900mM NaCl, 20mM Tris[pH 7.5], 0.01%SDS), The final concentration was 5ng / μL, and the hybridization was carried out at 46°C for 12 hours. After the hybridization, the non-specifi...
Embodiment 3
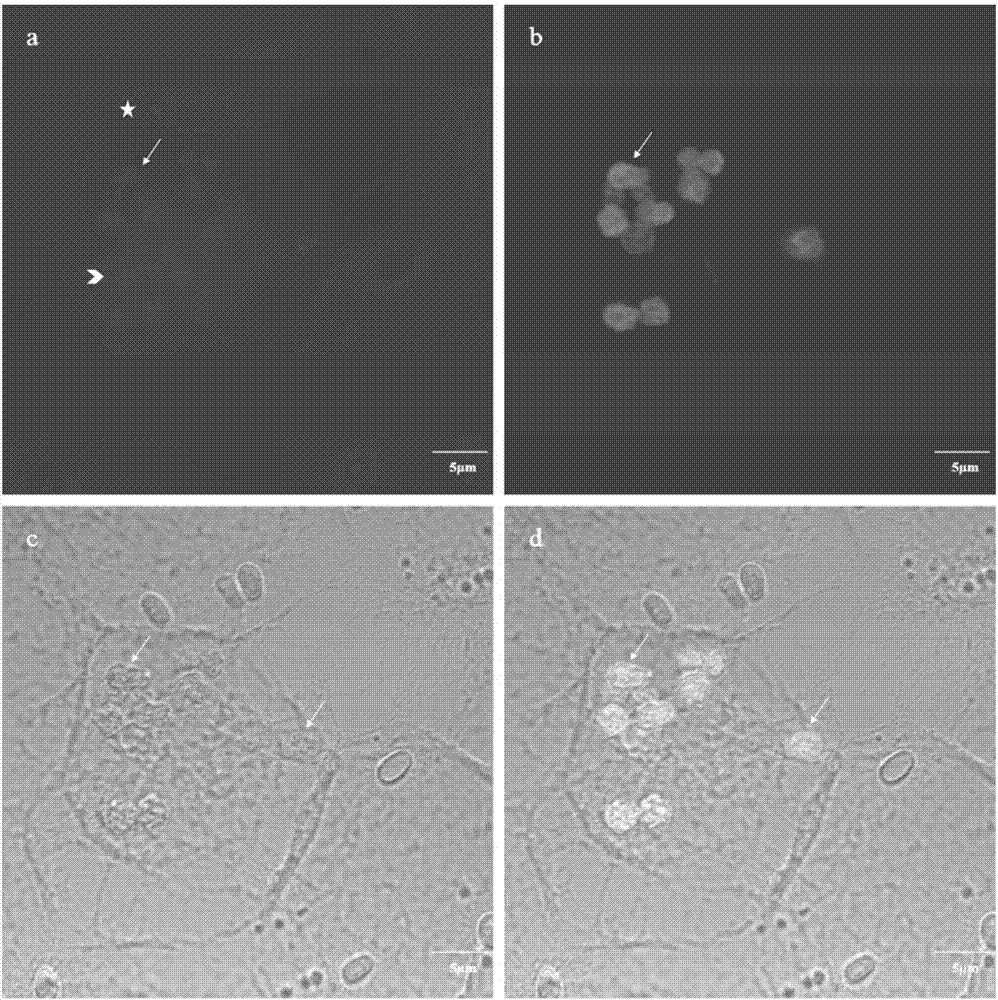
[0048] The method and result of embodiment 3NbLSU-V1-Cy3 in situ hybridization experiments
[0049] 1) Preparation of silkworm BmE cells infected with N.b
[0050] Normal silkworm embryo cells (BmE) were counted according to 1X10 6 Sub-power climbing sheet (diameter 20mm), meanwhile, under aseptic conditions, get the silkworm chrysalis blood that infects Nosema bombycis (Nosema bombycis, N.b), the N.b spore wherein is counted, after counting with N.b:cell=10: The ratio of 1 was used to infect BmE cells, and the medium was changed after 6 hours of infection.
[0051] 2) FISH probe labeling of silkworm BmE intracellular hybridization N.b
[0052] 45 hours after N.b infected BmE cells, BmE cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and the NbLSU-V1-Cy3 probe was diluted with hybridization solution (900mM NaCl, 20mM Tris[pH 7.5], 0.01%SDS), The final concentration was 5ng / μL, and the hybridization was carried out at 46°C for 12 hours. After the hybridization, the non-specifica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com