Soil quality improving method via arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and scented flowers
An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and soil technology, applied in the agricultural field, can solve problems such as reduced soil fertility, low organic carbon content, and impact on crop yields, and achieve the effects of improving soil quality, simple methods, and promoting sustainable development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Propagation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF): use Glomus mosseae (Gm) for propagation, use 10cm×15cm plastic flowerpots for potted propagation, and soak and disinfect the flowerpots with 0.1% potassium permanganate solution , and rinse with running water. White clover was selected as the host plant, and the clover seeds were treated with 10% H 2 o 2 Soak for 5 minutes for surface disinfection, rinse with distilled water, soak the seeds for 24 hours for later use / place them on wet filter paper for 24 hours to germinate. Field soil was used as the culture substrate, and the "two-layer inoculation method" was used to inoculate, that is, a certain height of sterilized substrate was first placed in the test pot, and then a layer of inoculum (the inoculum containing spores and hyphae) was evenly sprinkled. soil and the root mixture of its host plant), about 10 g, followed by a layer of substrate, followed by an inoculant, a layer of substrate, on which the seeds a...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The composting treatment of embodiment 2-rose pomace, differs from embodiment step in that,
[0039] Rose dregs: The mass ratio of water is 1:2, the mass ratio of rose dregs to putrid agent is 10:2, and the moisture content is kept at 50%.
[0040] "Effect Test"
[0041] 1. Propagation effect: Table 1 shows the spore density and infection rate after the proliferation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, indicating that the rot
[0042] Ripe rose slag infection rate is low.
[0043]
[0044] 2. Criteria for judging the maturity of biomass
[0045] 2.1 Qualitatively judge whether the biomass is decomposed, and the characteristics of decomposing are as follows:
[0046] (1) The temperature will naturally decrease in the later stage,
[0047] (2), no longer attract mosquitoes,
[0048] (3), there will be no more unpleasant smell,
[0049] (4) Due to the growth of fungi, there are white or off-white hyphae attached to the surface of the compost,
[0050] (5) The compos...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 - Returning decomposed rose residue to the field and inoculating with AMF.
[0063] (1) Collect field soil and pass it through a 2.5 mm sieve, then put it in a large oven and keep the temperature at 160 °C for 6 hours to obtain sterile soil; (2) Add mineralized and decomposed rose residue to the In sterile soil; (3) Inoculate the expanded AMF in sterile soil at a ratio of 0.05-0.1% according to the existing "two-layer inoculation method".
[0064] "Effect Test"
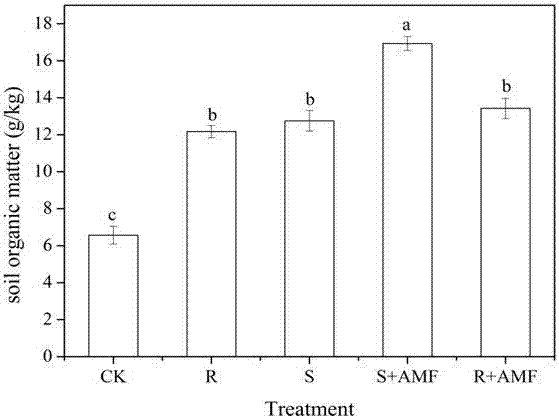
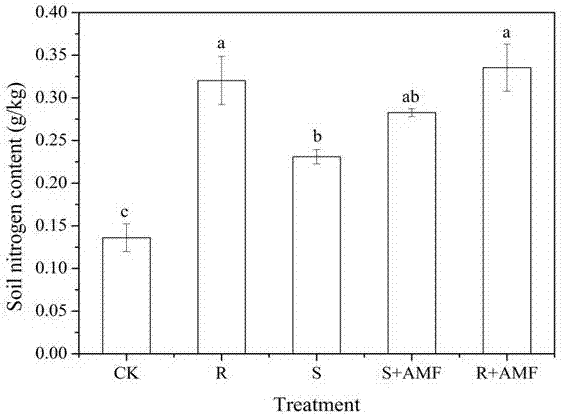
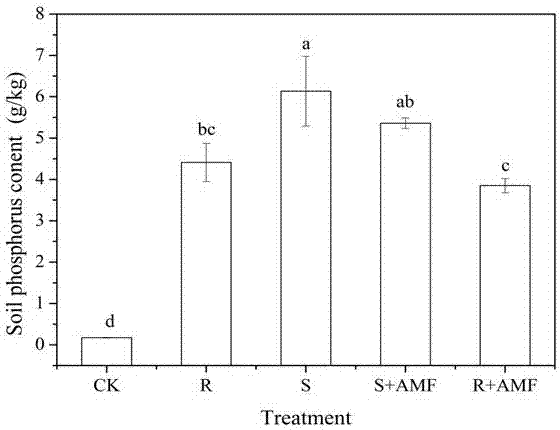
[0065] In this experiment, indoor pot experiments were used to study the effects of different treatments of rose residues combined with AMF on soil quality and whether inoculation of AMF was beneficial to increase the mineralization rate of decomposed rose residues.
[0066] 1. Explanation of test conditions: The test was carried out in a greenhouse. The test uses a plastic bucket with a height of 25cm, an upper diameter of 23cm, and a lower diameter of 18cm. The soil in the plow layer of the field...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com